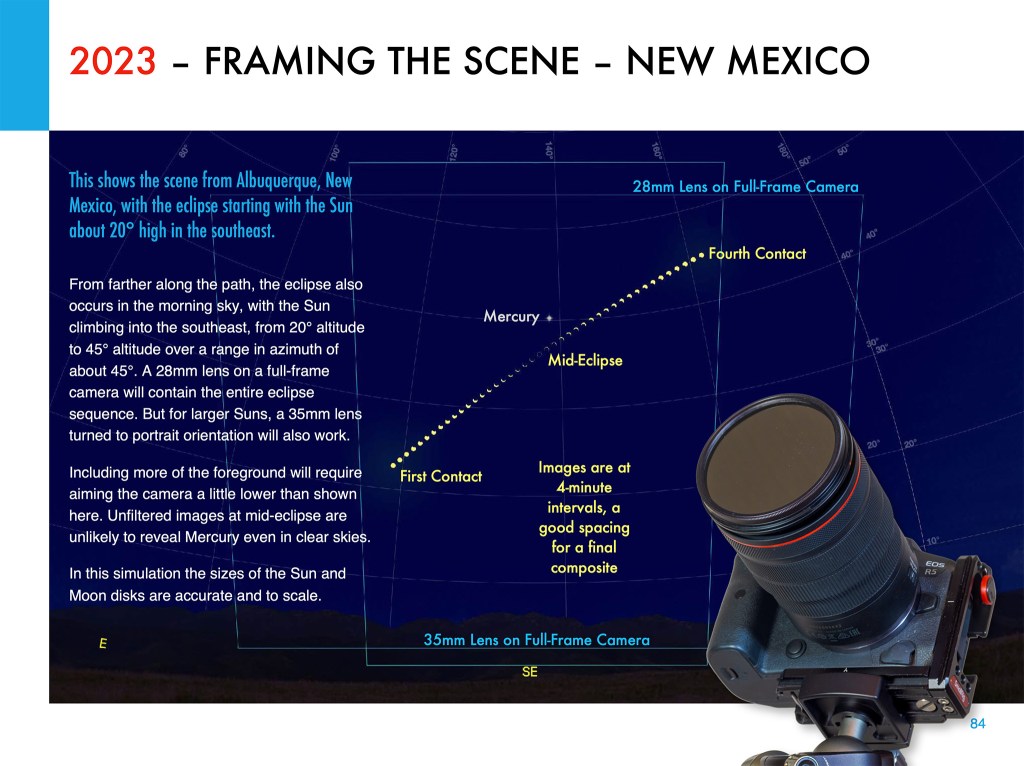
Like all eclipses, seeing the October 14 annular eclipse of the Sun was not a certainty. As good luck and planning would have it, the sky and location could not have been better!
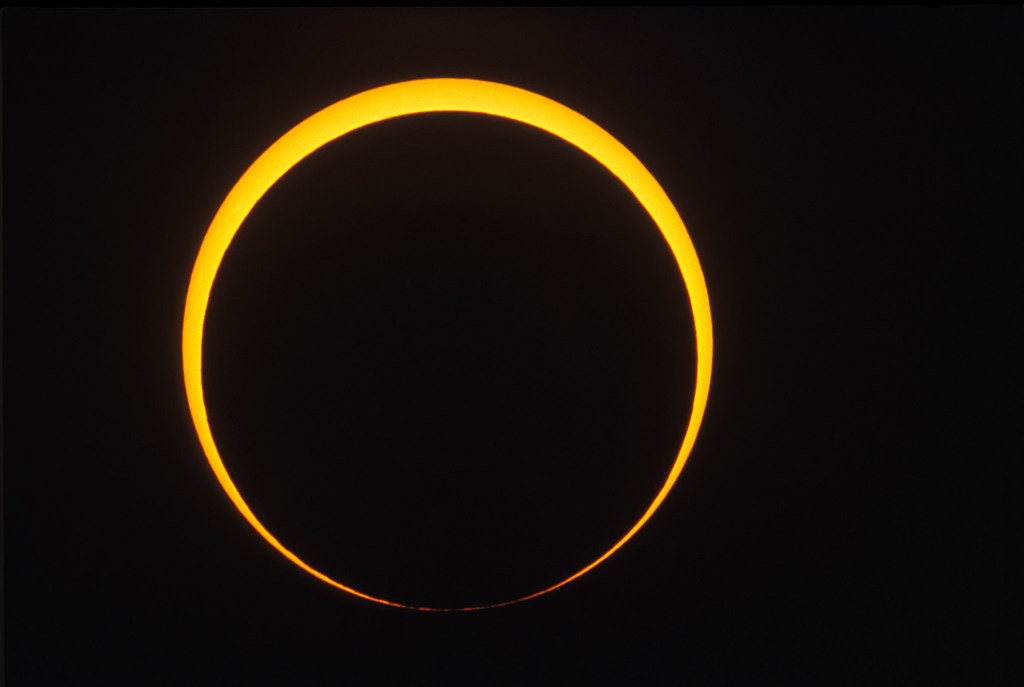
Annular eclipses of the Sun don’t present the spectacle of a total eclipse. Because the Moon is near its farthest point from Earth, its disk is not large enough to completely cover the Sun. At mid-eclipse, as I show below, a ring of sunlight (dubbed a “ring of fire”) remains, still too bright to view without a solar filter.

While lacking the jaw-dropping beauty of a total, annular eclipses are rare and unique enough that every ardent skywatcher should make a point of seeing one.
Prior to October 14, I had seen only one, on May 10, 1994, from southeast Arizona, an event I captured on film of course back then.


A sunset annular on June 10, 2002 that I traveled to Puerto Vallarta, Mexico to see was mostly clouded out. The annular of May 20, 2012 traced a similar path across the U.S. Southwest as the 2023 eclipse. But work commitments at the science centre in Calgary kept me home for that one. A sunrise annular on June 10, 2021 in Northwestern Ontario was essentially out of reach due to COVID travel restrictions.
With no other annular eclipses within easy reach in North America until 2039 and 2046, this was my next, and perhaps last, opportunity to see one, unless I chose to travel the world.



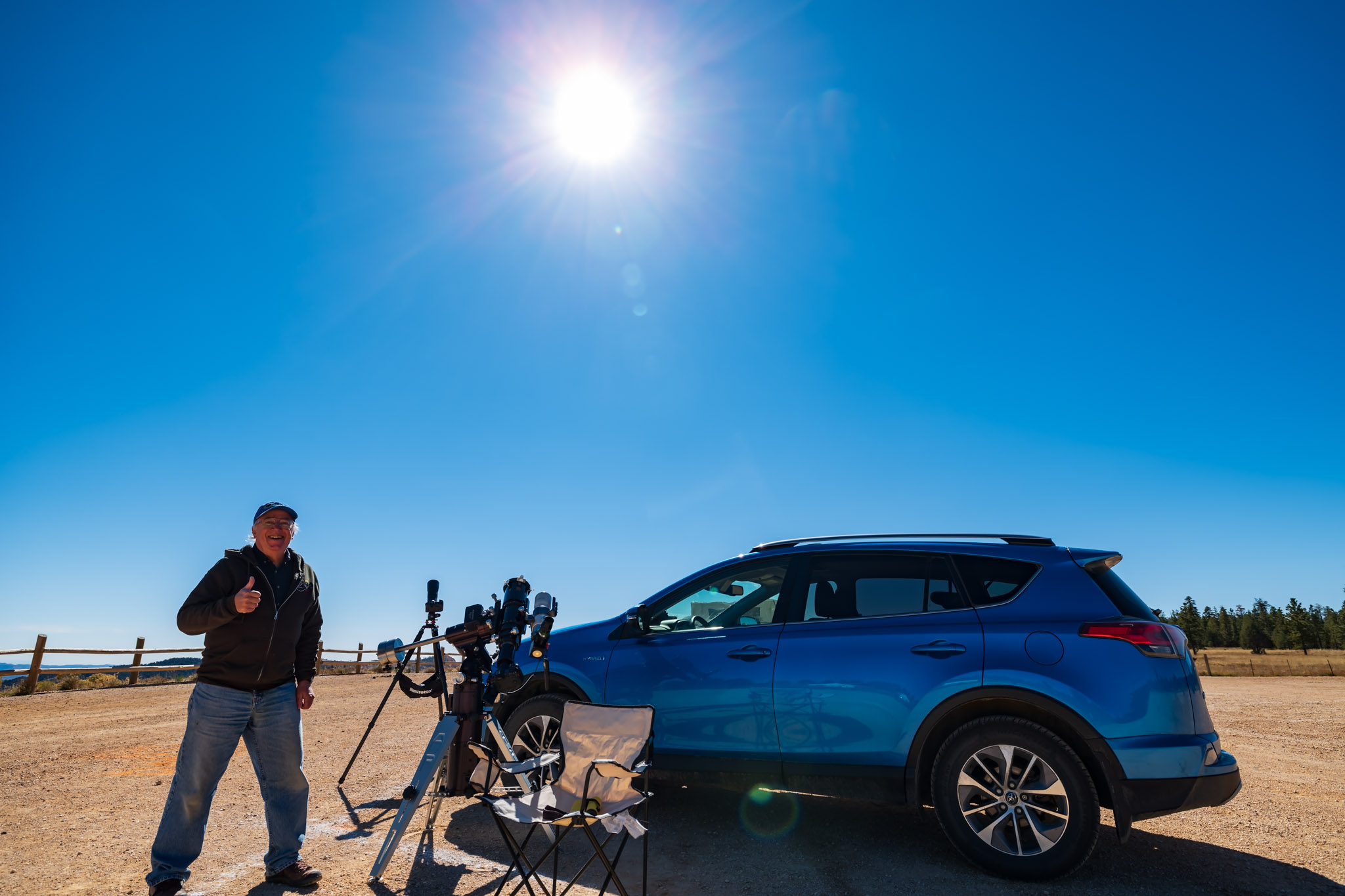
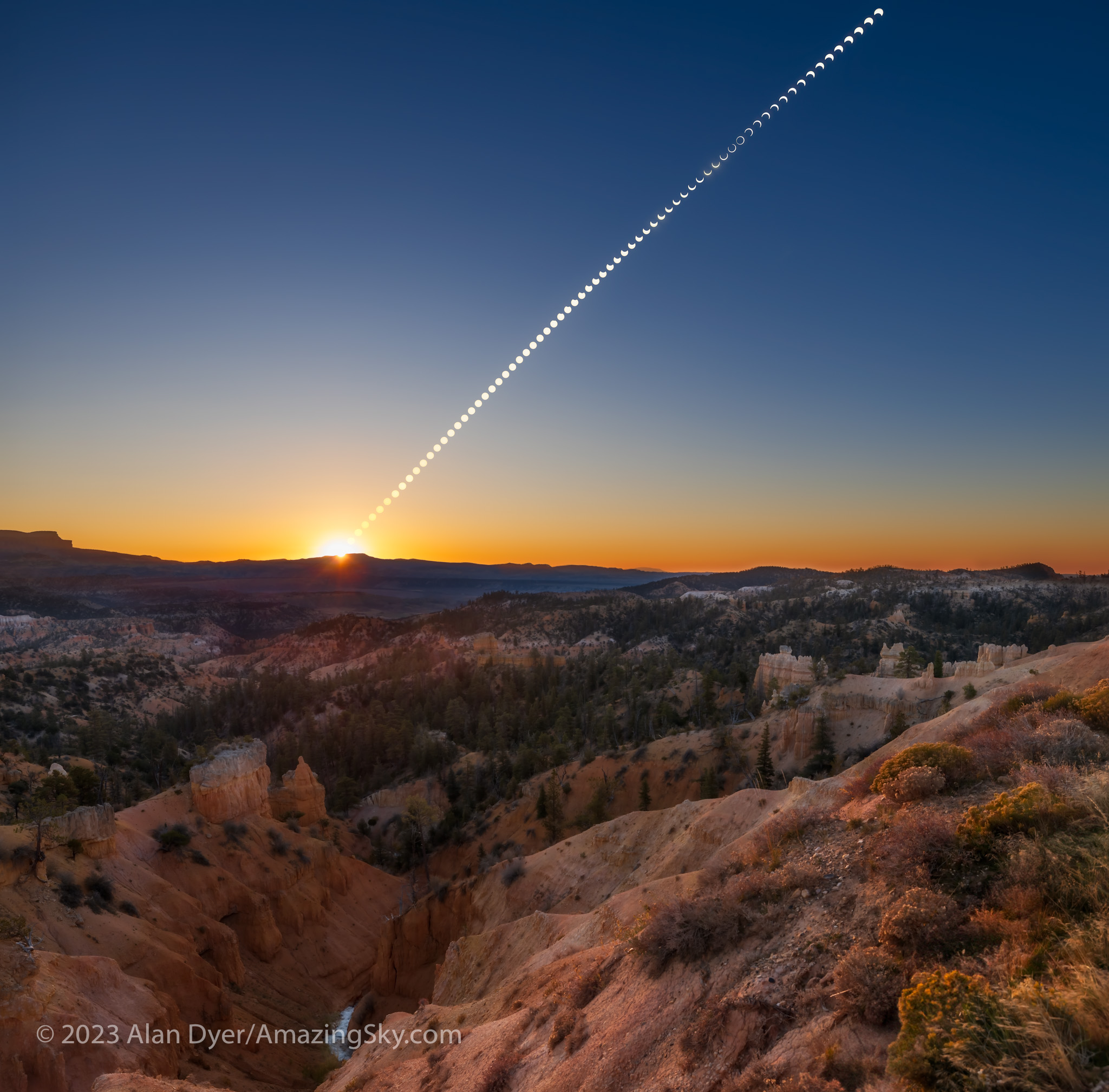
I had planned for several months to watch the annular eclipse from southern Utah, ideally from Bryce Canyon National Park, shown above. (Clicking on the images brings them up full screen.) I booked accommodations in January 2023, finding even then that popular hotels in the area were already sold out.

The attraction was the landscape below the morning Sun, for a planned composite image of the eclipse over the hoodoos of Bryce. However, I had learned weeks earlier that traffic was going to be restricted to just park shuttle buses on eclipse day. Should Plan A not work out then Plan B was Kodachrome Basin, a state park nearby, which a park employee assured me would be open to cars well before sunrise on eclipse day.
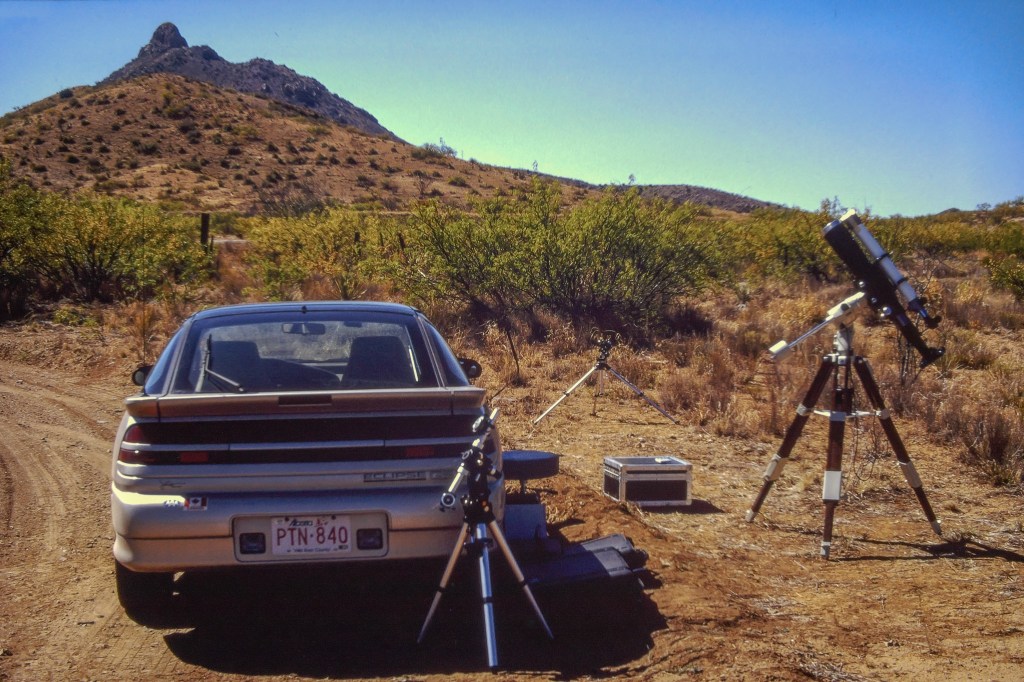
So I made my plans to drive south, taking with me a carload of telescope and camera gear, an array I would never be able to take to an overseas eclipse. The centrepiece was my venerable Astro-Physics Traveler 105mm (4-inch) refractor, a telescope created for the 1991 total eclipse in Mexico. Since I bought mine in 1992 I’ve used it for five central solar eclipses, including now two annulars. It’s in the 1994 and 2023 site images above.
As per the instructions in my eclipse ebook, I practiced with the gear in the summer of 2023, documented here on my previous blog.
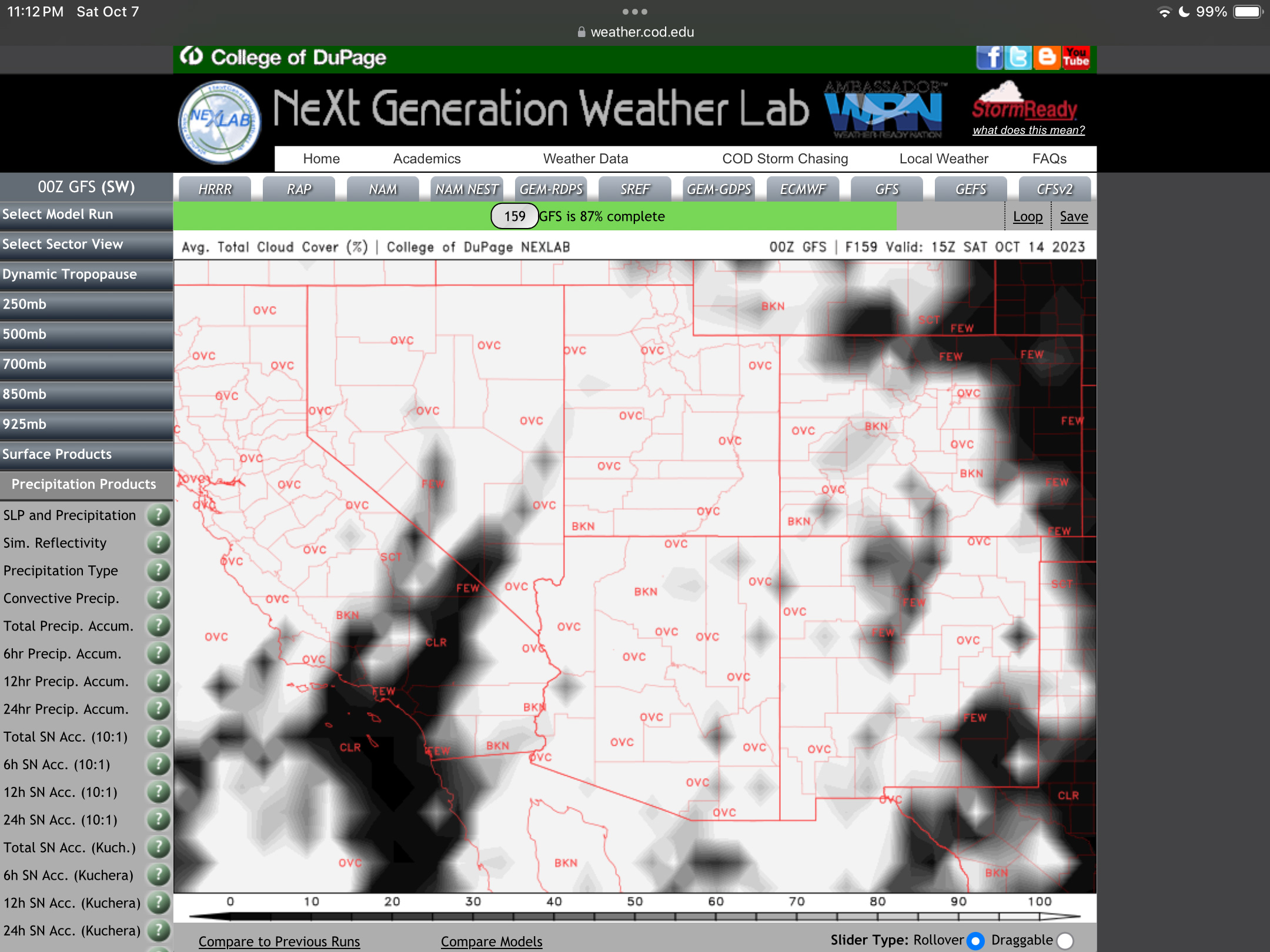
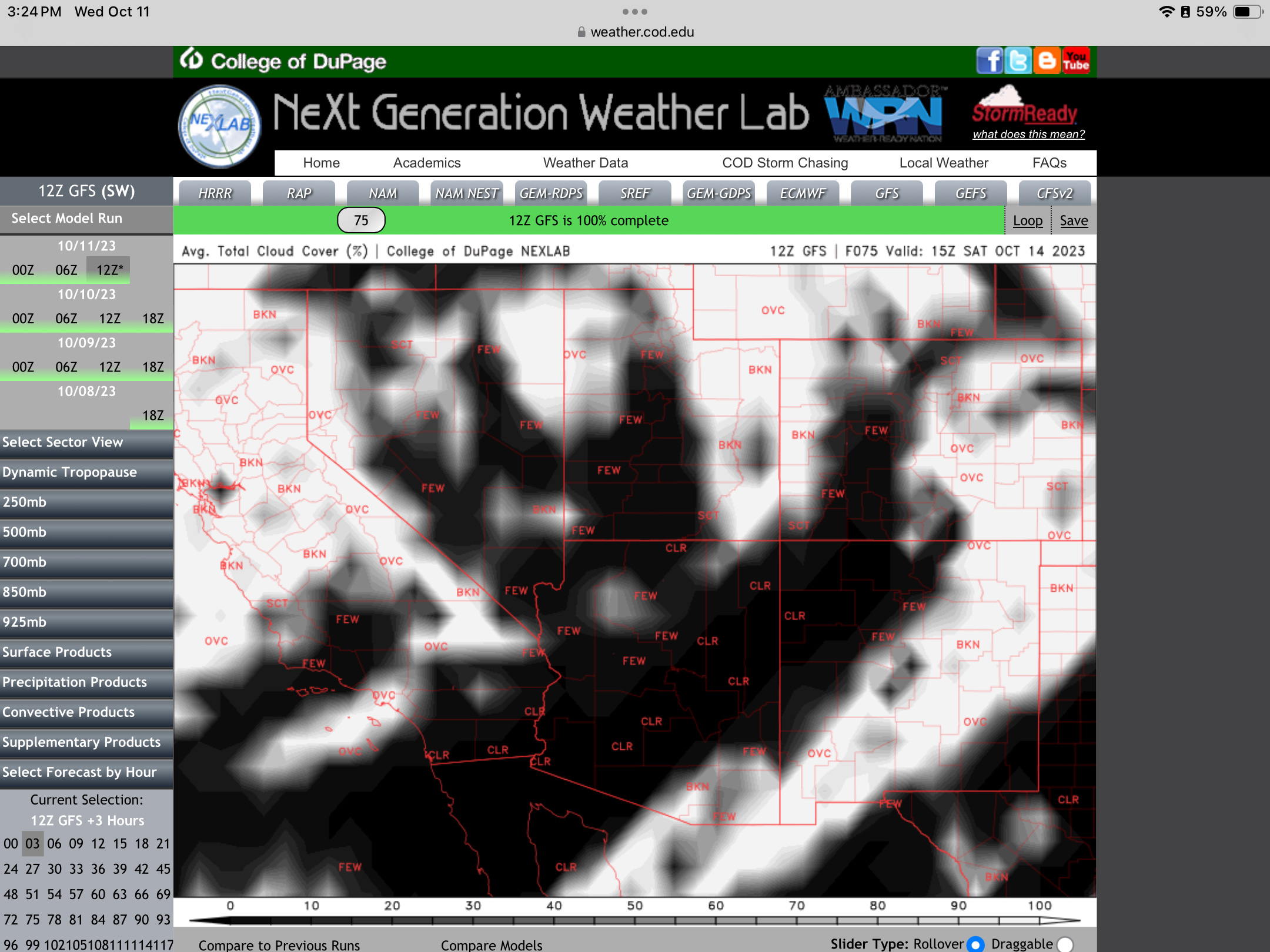
A week before the eclipse (as above at left), the weather prospects for the entire southwest looked poor. It was to be clouds everywhere. I even considered Plan S – Stay Home! And watch the 60% partial eclipse from Alberta where skies were to be clear.
But undaunted, six days before the eclipse, I headed south on Interstate 15, checking the weather each day, and seeking out Plan C sites in New Mexico or Texas south of the projected mass of clouds. I checked where accommodation could be had at the last minute.

At my stop in Richfield, Utah, four days before the eclipse, I had a crossroads turning point: either continue south to Bryce down US-89 (above), or head east on I-70, then south into New Mexico or Texas, with enough time to get there if needed.
But by now the weather prospects were turning around. By three days out, and with the forecasts now much more reliable, it looked like southern Utah would be in the clear. I continued with my original plan to Bryce. But where exactly?
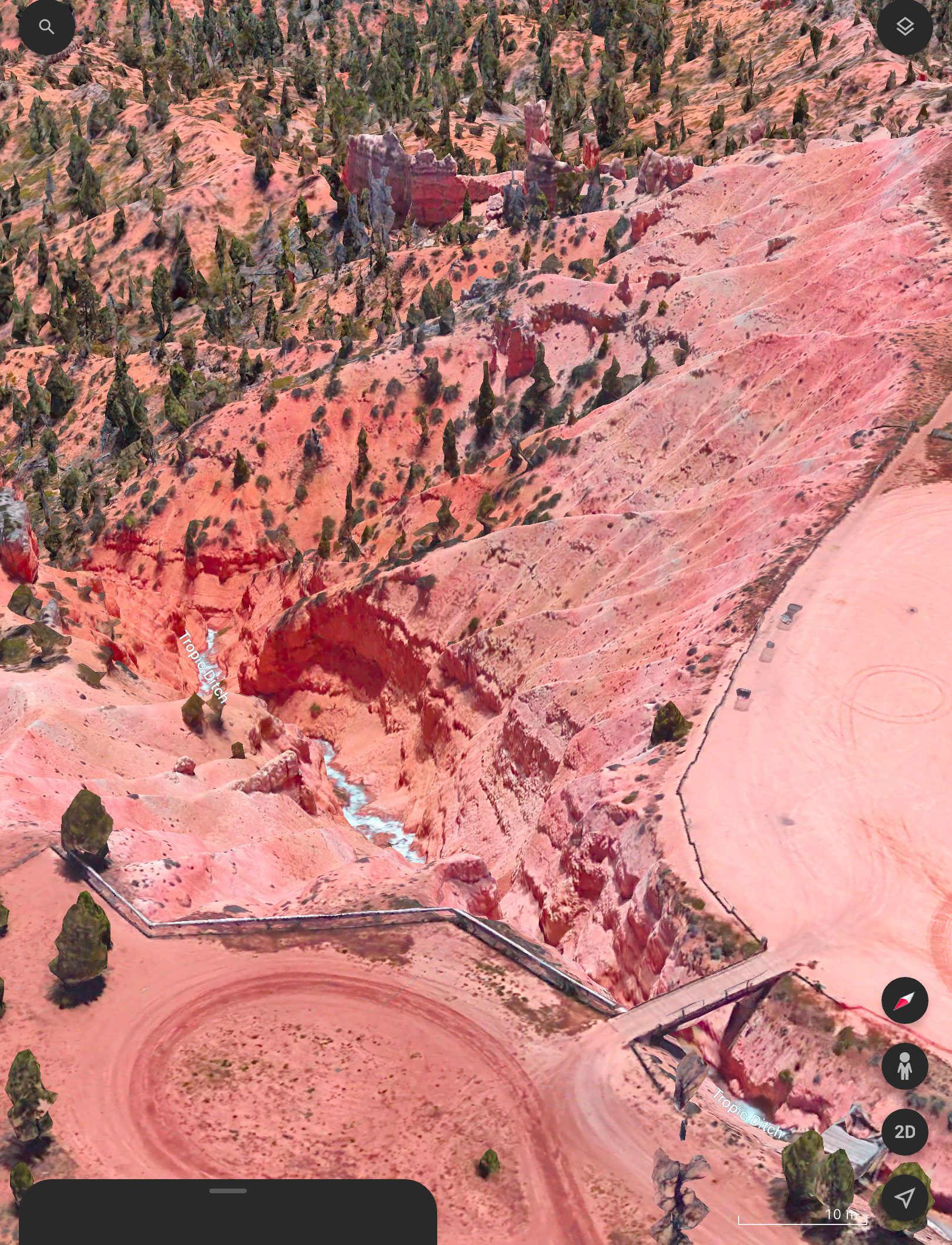
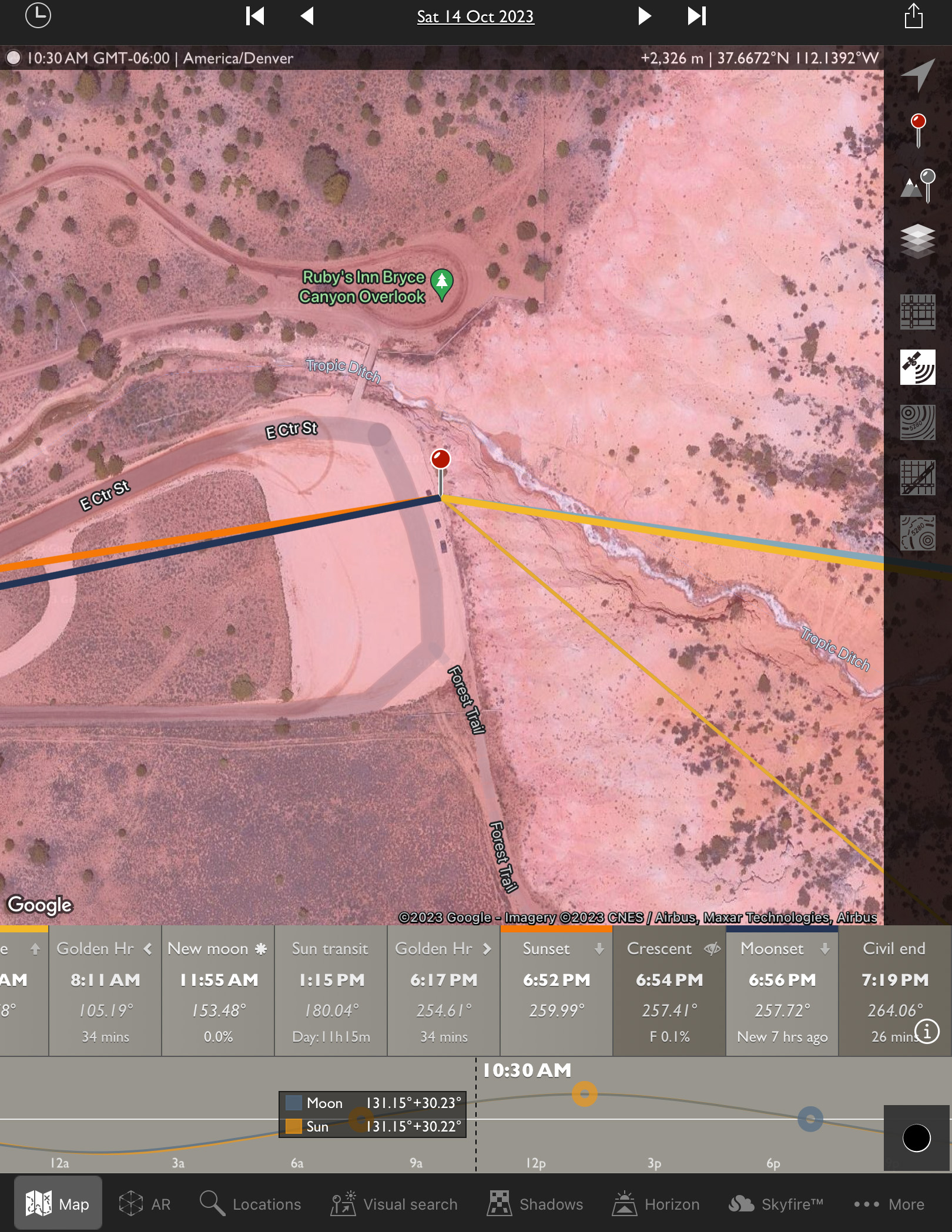

I had looked at possible sites on Google Earth and with the Sun-angle planning apps I use (such as The Photographer’s Ephemeris, or TPE) and found one just outside the Park that I hoped would be accessible to drive into.
Upon arriving in the area three days early, the first priority was to inspect the site in person. It looked perfect! Almost too good to be true!
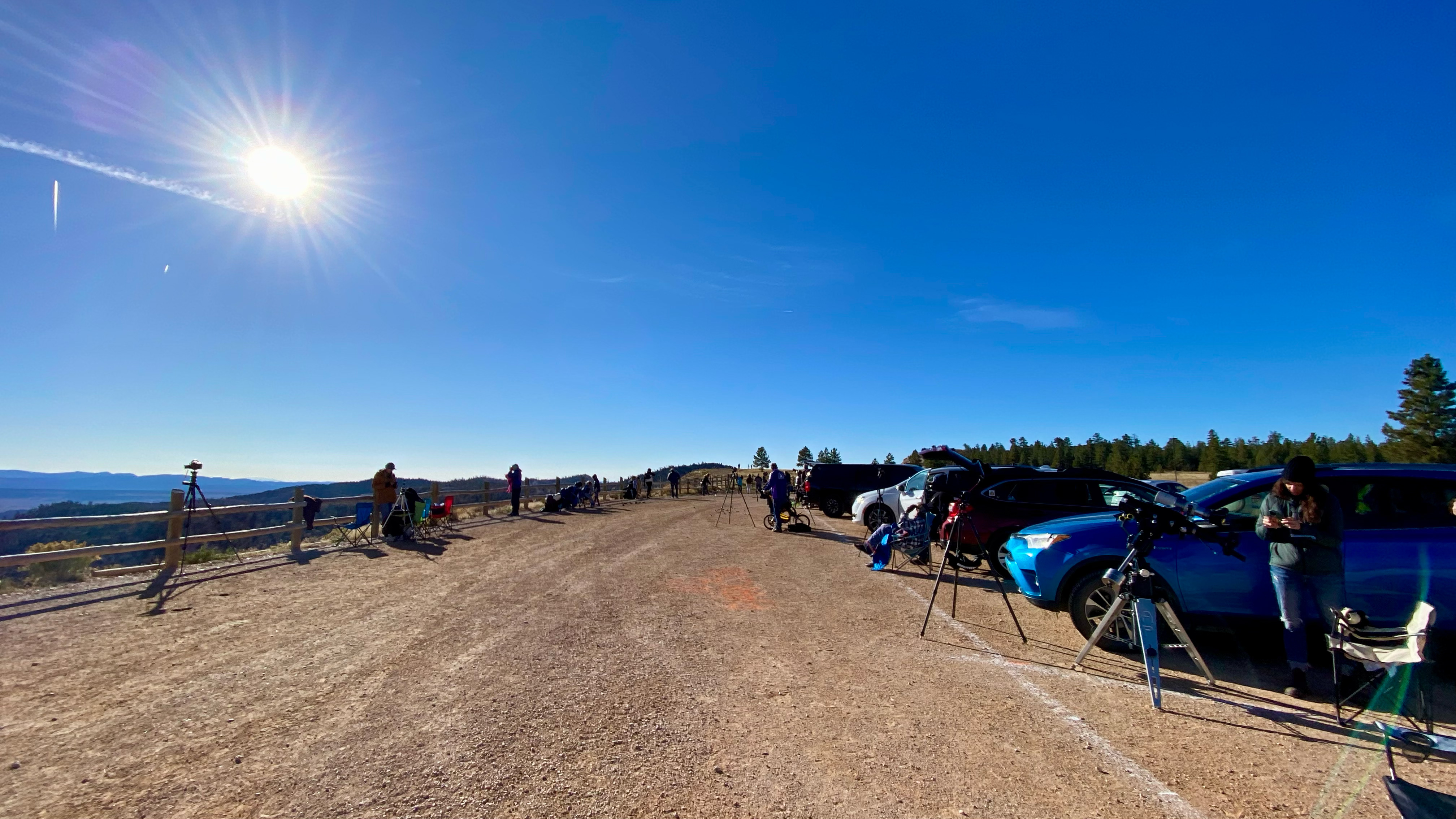

The site, known as the Ruby’s Inn Overlook, provided a great view toward the eclipse with a stunning landscape below, including a river! (Well, it was actually an irrigation channel called the Tropic Ditch.) And I could park right next to my wide-angle landscape camera, to keep an eye on it over the five hours of shooting, while setting up the scope gear next to my car.
I stayed at the Bryce View Lodge on eclipse eve, a hotel just a few hundred metres from the site. So no long pre-dawn drive on eclipse morn. However, the gated site was not going to be open until 7 a.m. on eclipse day. And admission was $20 per car, a cash donation to the Bryce Canyon City school sports teams. Fine!
As it turned out, by the time I got on site and setup the priority wide-angle camera for the base-image sunrise shots at 7:30 a.m., the sky was too bright to polar align the telescope mount on Polaris, for accurate tracking of the Sun across the sky.
It turned out that was the least of my concerns.

As I unpacked the carload of scope gear at 8 a.m. I realized I had forgotten a crucial cable to connect the mount to the drive electronics. So the mount was not going to be able to track anyway!
So much for my plans for a time-lapse through the scope. I had to manually centre the Sun every minute or so. I took lots of photos, but gave up on any effort to take them at a regular cadence. But I had enough images for the singles and composites shown here.

Of course, once I got home the first thing I did was look downstairs in my scope room. Sure enough there was the cable, mixed up with the similar electronics from another mount I have from the same company, as I had been testing both prior to the eclipse. So much for my checklists! They’re only good if they list every critical bit, and if you use them.
So that was one big user error.
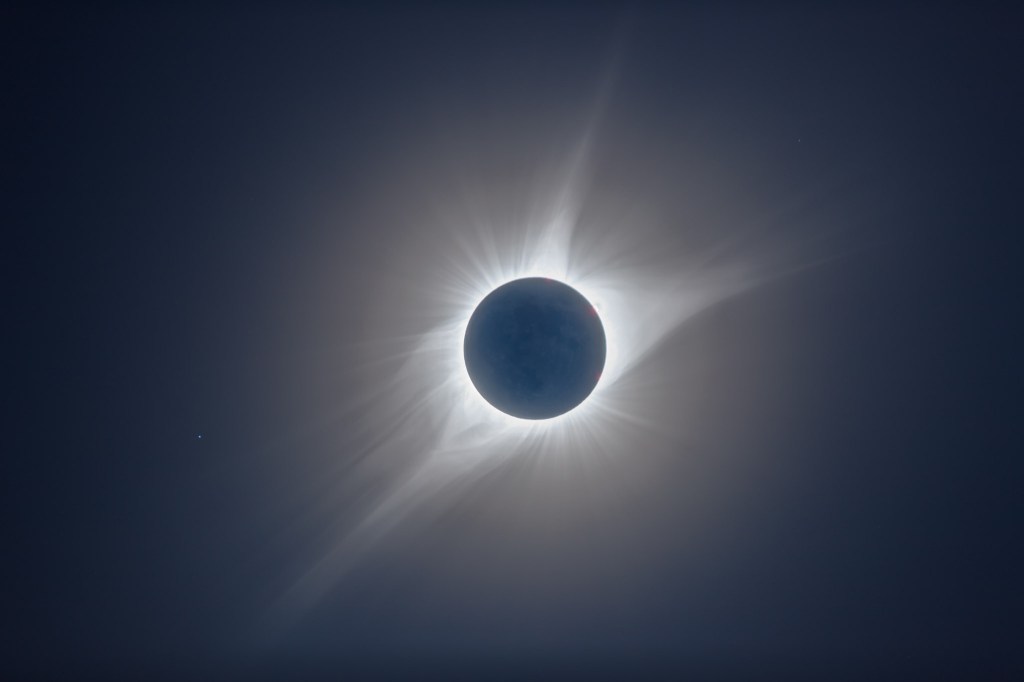
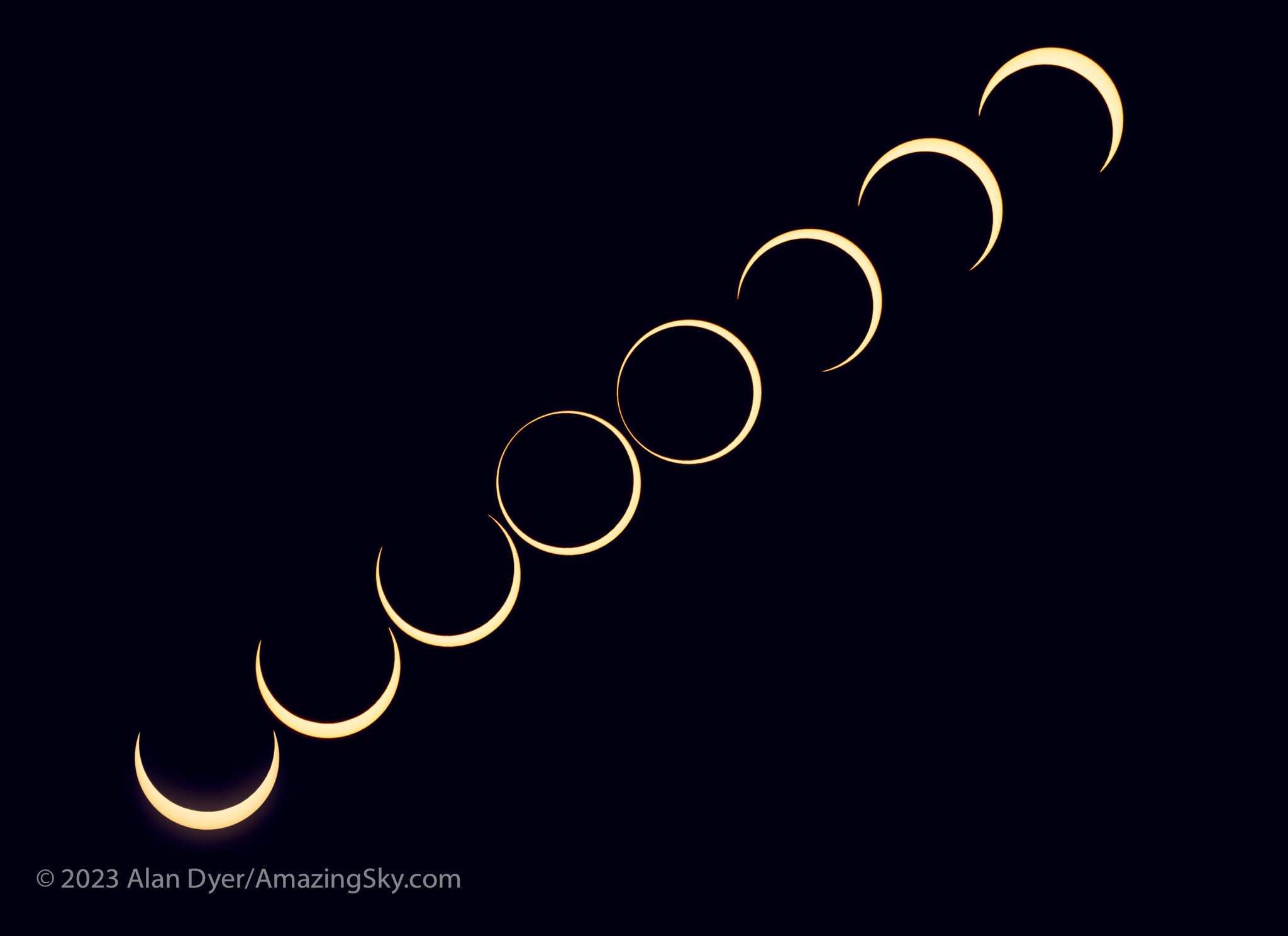
The other was a camera error, in fact Error70! I had set my main telescope camera to take rapid bursts of images (at up to 20 frames per second) at the crucial second and third contacts when annularity began and ended. With the Moon’s rough limb tangent to the inside edge of the Sun, you see beads of light rapidly form and disappear at the contacts.

The camera worked great at second contact, shooting 344 frames over 20 seconds. A composite of 15 of those frames is above, layered to exaggerate the rough lunar limb and its mountain peaks. A time-lapse from those frames is below.
And it appeared to be working at third contact three minutes later. Until I looked down and saw the dreaded error message. In checking the camera later, none of the third contact images had recorded to either memory card.
It is a known but intermittent bug in Canon firmware that can happen when the camera is not connected to a Canon lens (it was on a telescope it cannot communicate with). I saw the error once in testing. And I had a hard time reproducing it to take the screen shot above once I got home. But if something can go wrong …!

Despite the errors both human and machine, I count eclipse day as successful, considering a week earlier prospects had looked so poor. As it was, apart from some thin but inconsequential cloud that drifted through before mid-eclipse, the sky was perfect.
As was the site. I enabled me to get the main shot I was after, the wide-angle composite, above. It’s a winner! And it accurately depicts the size of the Sun and its motion across the sky, albeit set into a twilight sky taken at sunrise.
As it had been 29 years since my last annular, I wasn’t sure what to expect. But the darkening of the sky and eerie level of sunlight, despite a blazing Sun in the day sky, were impressive. The morning just looked strange! It was a taste of the total to come.
Venus at its widest angle west of the Sun was easy to spot in the deep blue sky. I regret not thinking to shoot even a phone camera image of that sight.
I had pleasant chats with other folks at the site, and enjoyed showing them telescopic views though the smaller visual scope I had piggybacked on the main scope, one that was just for looking through. Plus folks shot phone pix of my camera screen.
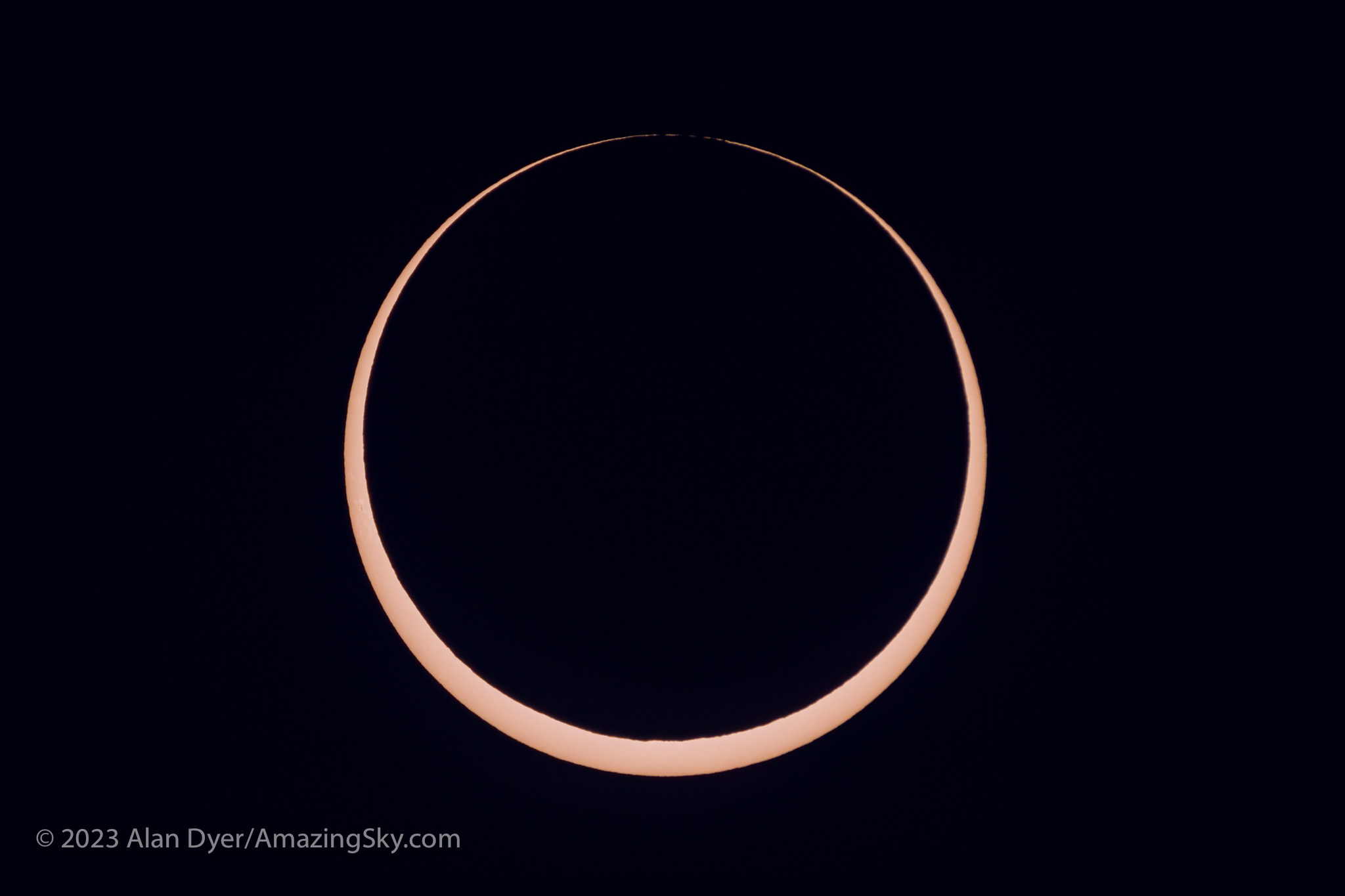

But at the critical contacts, I was glued to that visual scope for the amazing sight of the horns of the crescent Sun rapidly wrapping around the Moon at second contact, then unwrapping at third contact.

The breakup of the rim of sunlight into beads of light along the cratered and mountainous edge of the Moon was also impressive. I was not at the optimum site for seeing those beads, as the landscape dictated my choice of location. But those that I saw at each of the internal contacts were a fine bonus to a memorable morning.

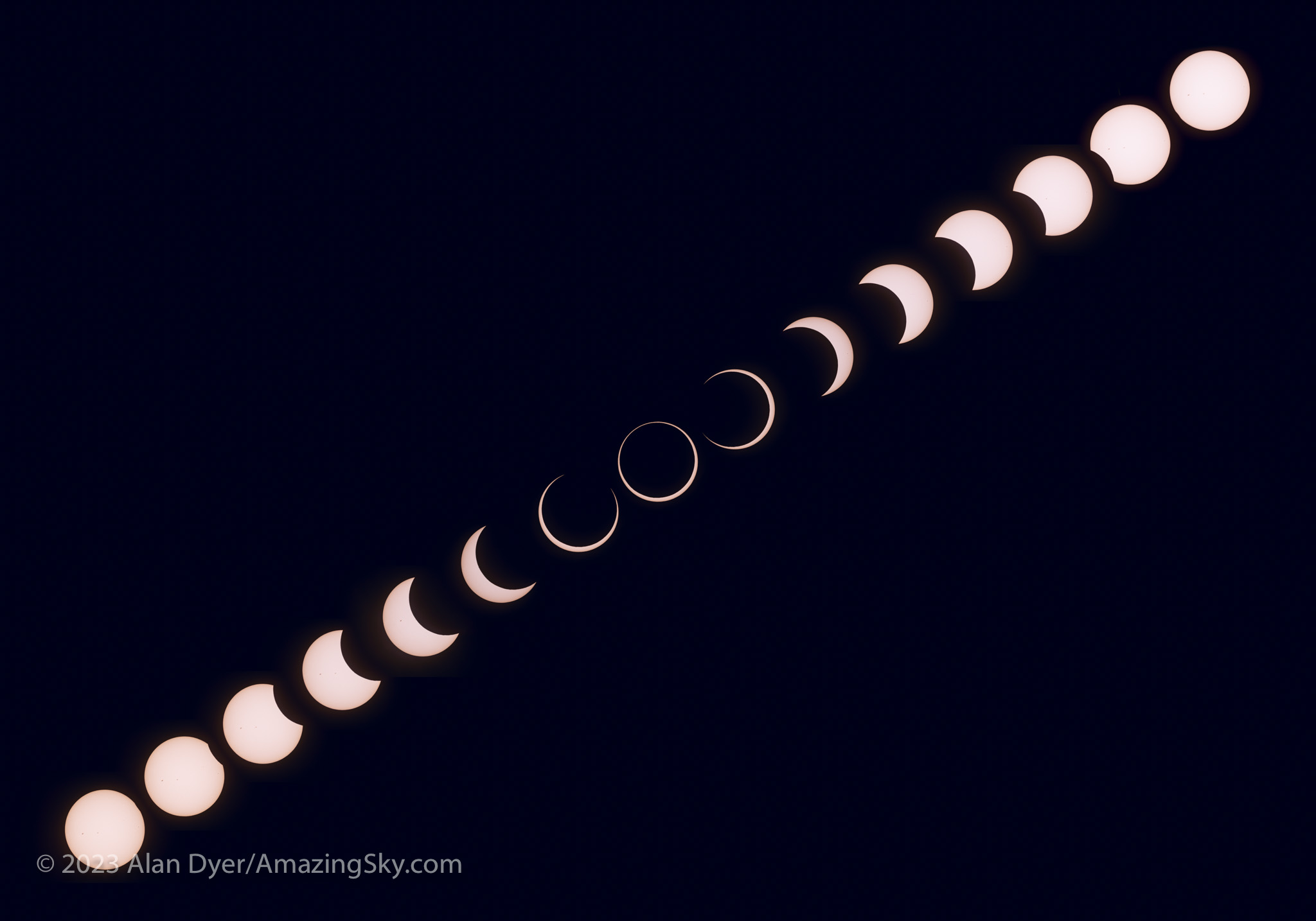
A third camera shooting a sequence with an untracked 400mm telephoto lens worked well. I used a subset of its images to create a still-image composite (above) and the full set for a time-lapse (below), with the position and motion of the Sun authentic, produced by the natural east-to-west motion of the sky. But against that you see the Moon’s orbital motion moving its dark disk down across the disk of the Sun.
As soon as annularity ended, everyone else started to pack up and leave. For them the show was over. Understandably. On many total eclipse tours I’ve been on we’ve been on the road back to the hotel after totality and the requisite happy group shot.
But at this eclipse my shooting plan dictated that I stick it out. By the end of the eclipse I was the last one standing, alone to enjoy last contact and then lunch, killing time for any road congestion to diminish, as I had to head to another motel for the post-eclipse night, in nearby Panguitch.

I had a celebratory dinner and Moab-brewed beer that night at Cowboy’s, the best restaurant in Panguitch, sporting my Annular 2023 eclipse hat!
But the next day I started the drive north again, for the three-day trek back up I-15 to the border, then home.
Priority one upon getting home was to finish processing images, and to include them in a revised version of my ebook How to Photograph the Solar Eclipses. It is linked to above and here on the title. Images of some sample pages from the revised edition are in the slide show below.
Post-annular, the book’s title remains the same, but I revised the pages in Chapter 4 on planning for the 2023 eclipse with pages on “lessons learned!” And there were several!
I expanded Chapter 11 on processing to include tutorials on assembling annular eclipse composites, now that I actually have some!
Such as the composite of first- to last-contact telescopic close-ups below.

The new version of my ebook is 20 pages larger than the pre-annular edition.
An email has gone out from eJunkie to all buyers of the earlier-edition PDF to alert them to the new version, and with a download link. Apple Books readers should get a notice when they open the book on their Mac or iPad in the Books app that a new version is available.
I suspect that will be the last revision of my ebook before the big event – the total eclipse of the Sun on April 8, 2024.
Here’s wishing us all clear skies for that one! That eclipse will indeed require a drive to Texas. This time I’ll remember that damned cable!
— Alan Dyer, October 31, 2023