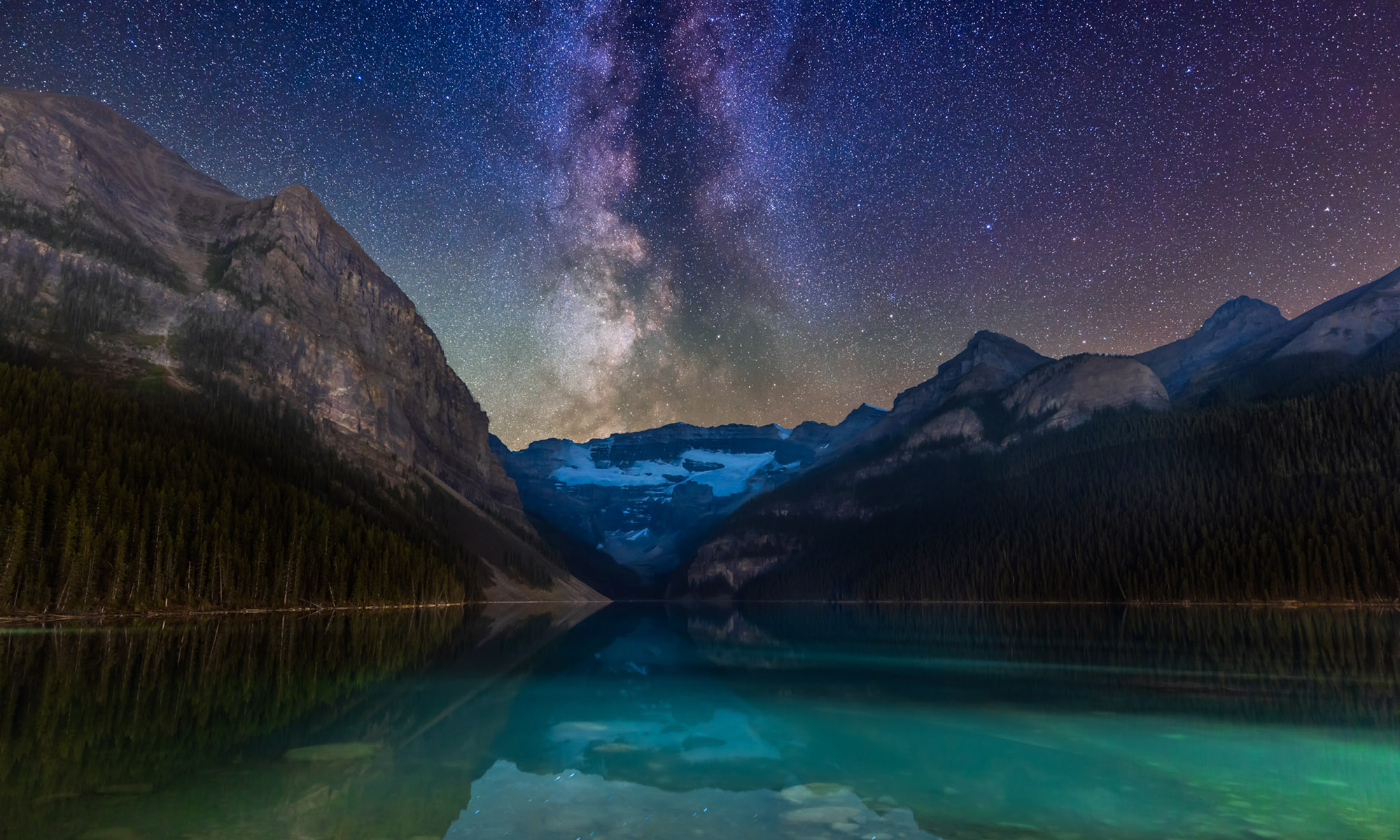
I present a selection of new images taken at local World Heritage Sites, along with some advanced nightscape shooting tips.
I’m fortunate in living near scenic landscapes here in southern Alberta. Many are part of UNESCO World Heritage Sites that preserve regions of unique scenic and cultural significance. In early June I visited several to shoot nightscapes of starry skies over the scenic landscapes.
I also took the opportunity to experiment with some new shooting techniques. So I’ve included some tips and techniques, most of the advanced variety.
First up was Dinosaur Provincial Park.
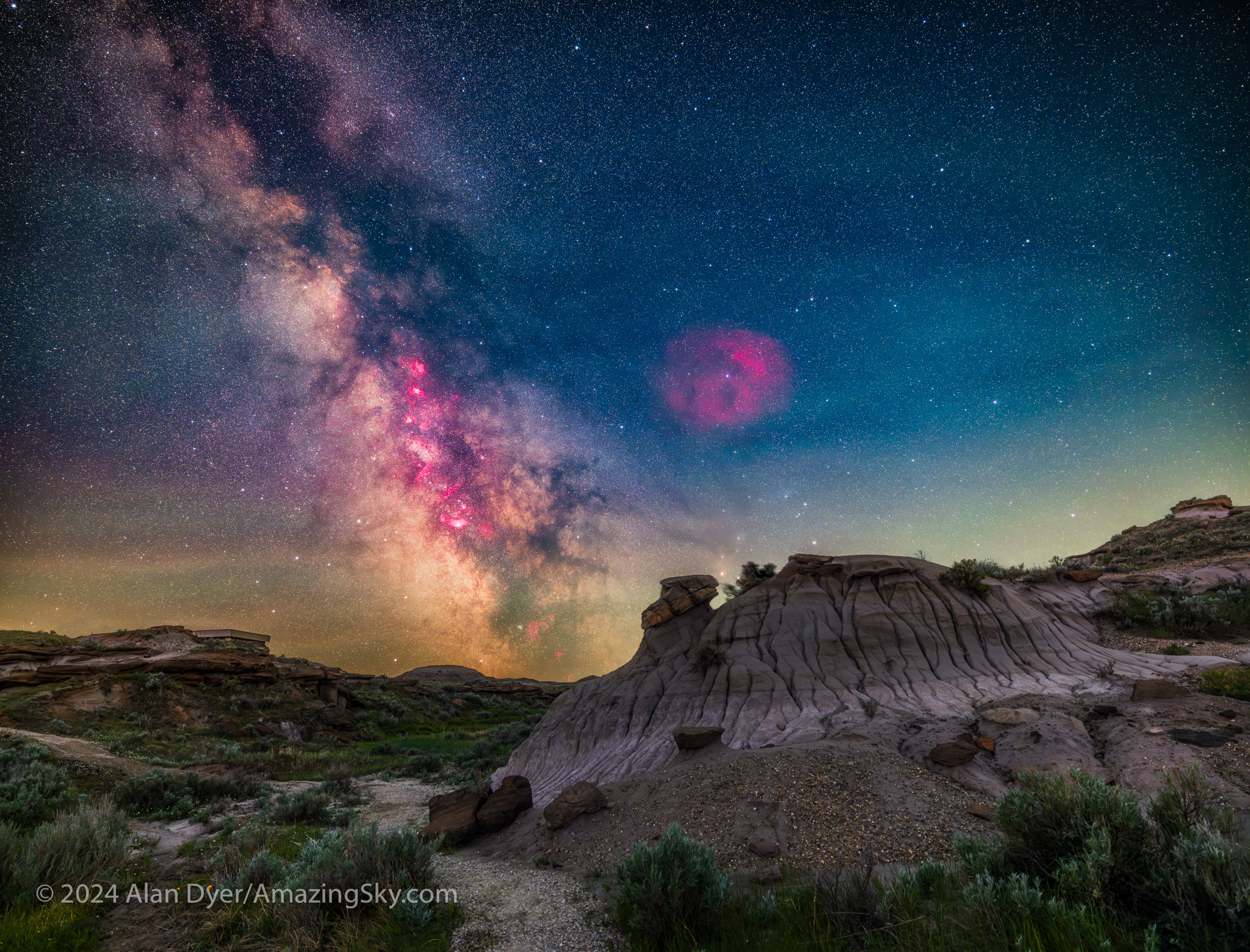

After nearly a month of rain and clouds, the night of May 31/June 1 proved wonderfully clear at last. I headed to a favourite location in the Red Deer River valley, amid the eroded badlands formations of Dinosaur Provincial Park, site of late-Cretaceous fossil finds.
The bright core of the Milky Way in Sagittarius would be in the south. With the night only three weeks before summer solstice, from the Park’s latitude of 50.5° N the sky would not get astronomically dark. But it would be dark enough to show the Milky Way well, as above in this framing looking south on the Trail of the Fossil Hunters.
However, May and June are “Milky Way Arch” months, at least for the northern hemisphere. The full sweep of the northern Milky Way, from Perseus in the northeast to Sagittarius in the southeast, then stretches across the sky — high enough to be impressive, but low enough (unlike later in summer) to be framable in a horizontal panorama.
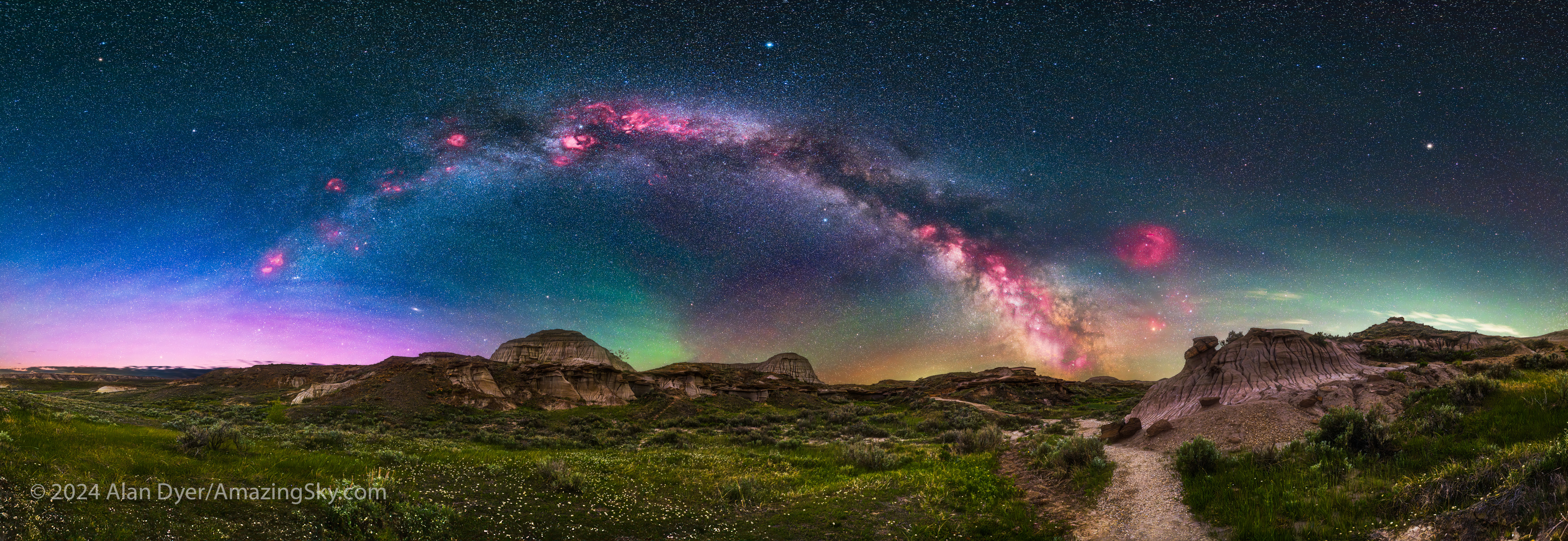

To capture the arc of the Milky Way I shot a panorama — in fact three:
- one exposed for the ground
- one exposed for the sky, but with the camera now tracking the sky to keep stars pinpoint
- and a final sky panorama but with a specialized filter installed in front of the camera sensor to let through only the deep red light emitted by nebulas along the Milky Way
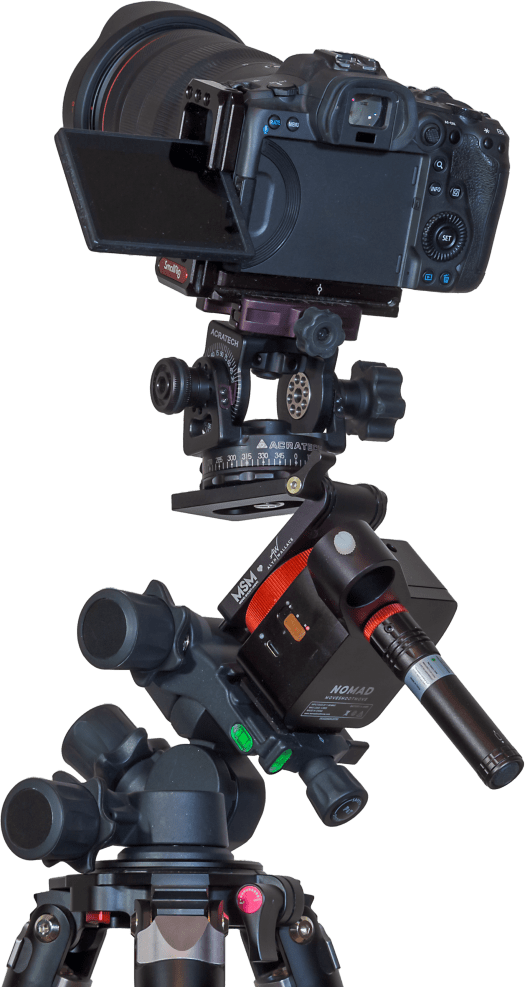

The image above shows my rig for taking tracked panoramas. The rectangular box is the little Nomad sky tracker from Move-Shoot-Move (MSM), here equipped with its accessory laser pointer to aid the “polar alignment” that is needed for this or any tracker to follow the turning sky properly.
A review of the MSM Nomad will be forthcoming (subscribe to my blog!). However, I’ve found it works very well, much better than MSM’s original Rotator tracker, which was entirely unreliable!
On top of the little Nomad is an Acratech pano head, so I can turn the camera by a specific angle between each pano frame, both horizontally from segment to segment, and vertically if needed when raising the camera from the ground pano to the sky pano.
The pano head is on a “V-Plate” sold by MSM and designed by the late, great nightscape photographer (and engineer by trade), Alyn Wallace. The V-Plate allows the camera to turn parallel to the horizon when on a tipped-over tracker. The entire rig is on a Benro 3-Axis tripod head (also sold by MSM, but widely available) that makes it easy to precisely aim the tracker for polar alignment and then hold it rock steady.
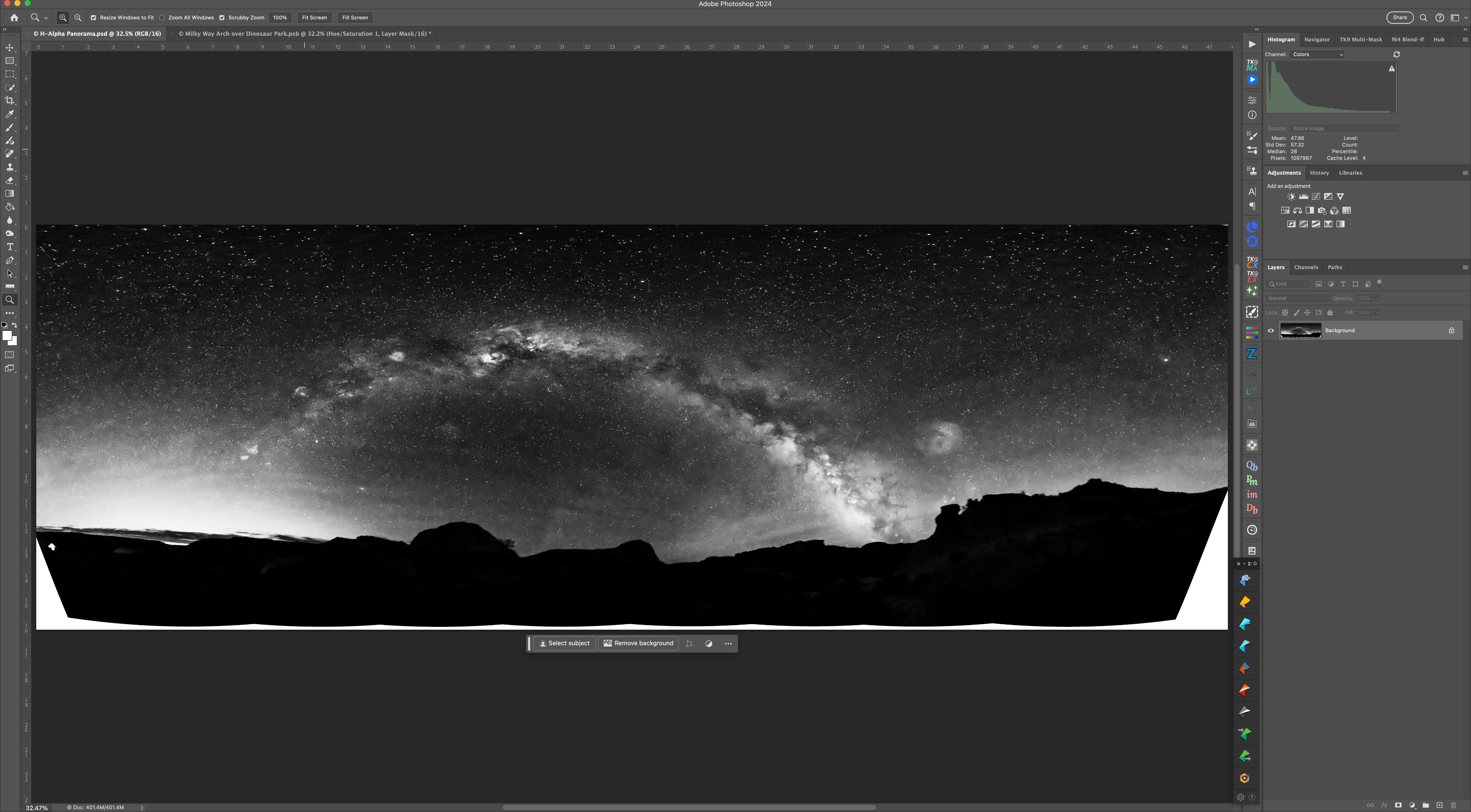
I’d taken many panos before using sets of untracked ground and tracked sky panoramas. New this night was the use a “narrowband” Hydrogen-Alpha filter to take a final pano that brings out the red nebulas. I used a filter from Astronomik that clips into the camera in front of the sensor. Such a filter has to be used on a camera that has been modified to be more sensitive to deep red light, as the Canon Ra shown below is (or was, as Canon no longer makes it).
While a modded camera brings out the nebulas, using an H-Alpha filter as well really shows them off. But using one is not easy!

The clip-in placement (unlike a filter in front of a lens) requires that the lens be refocused — infinity focus now falls at the 3 to 6 metre point (the focus shift varies with the lens and focal length — the wider the lens the greater the shift). With the image so dark and deep red, seeing even a bright star to manually focus on is a challenge.
Shifting the lens focus also changes the overall image size (called “focus breathing”) and often introduces more off-axis lens aberrations, again depending on the lens.
So, blending the H-Alpha pano (which I rendered out in monochrome, above) into the final stack is tough, requiring lots of manual alignment, image warping, BlendIf adjustments, and masking. This is where I added in the red colouration to taste. Careful here, as the “Saturation Police” patrolling social media will issue tickets if they judge you have exceeded their “speed limit.”
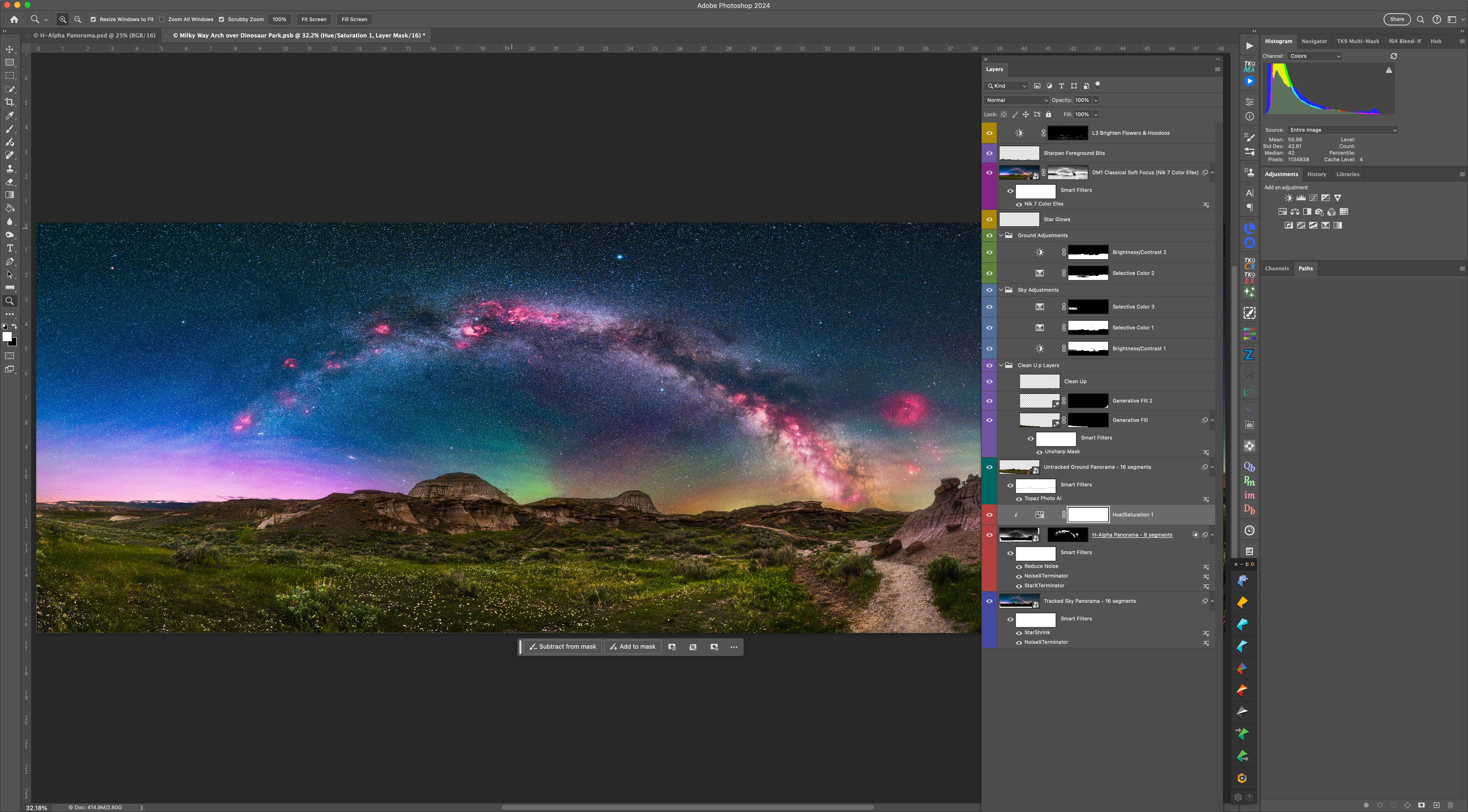
The final pano required a complex blend of image and adjustment layers, all applied non-destructively, so the many elements of the scene can be individually tweaked at any time.
The work was worth it, as the final pano records the deep red nebulas contrasting with the deep blue of a sky still lit partly by twilight, a magenta aurora to the north, and bands of green and yellow airglow, all above the earth tones of the Badlands. It is one of my favourite nightscape panoramas.
As a further note on software: For stitching panos I try to use Adobe Camera Raw first. It can work very well. But complex panos, especially taken with very wide lenses, often require the specialized program PTGui, which offers more choice of pano projection methods, cleaner stitching, and control of panorama framing and levelling.
Next up was Writing-on-Stone Provincial Park.
A week later, with the waxing Moon beginning to appear in the western sky and the promise of clear nights, I headed south to the 49th parallel borderlands of the Milk River and Writing-on-Stone Provincial Park, known as Áísínai’pi to the Blackfoot First Nation who revere the site as sacred.
My plan was a framing of the galactic centre over the Milk River valley and distant Sweetgrass Hills in Montana, perhaps using the H-Alpha filter again. But clouds got in the way!
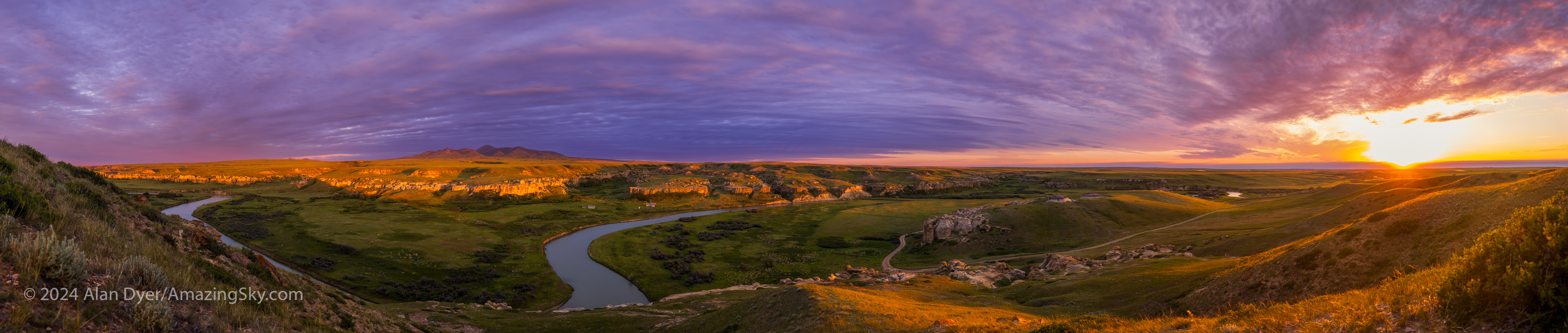

When you are faced with a cloudy sky, you make use of it for a colourful sunset. I like shooting panoramas at such sites as they capture the grand sweep of the “big sky” and prairie landscape. Above is the scene at sunset.
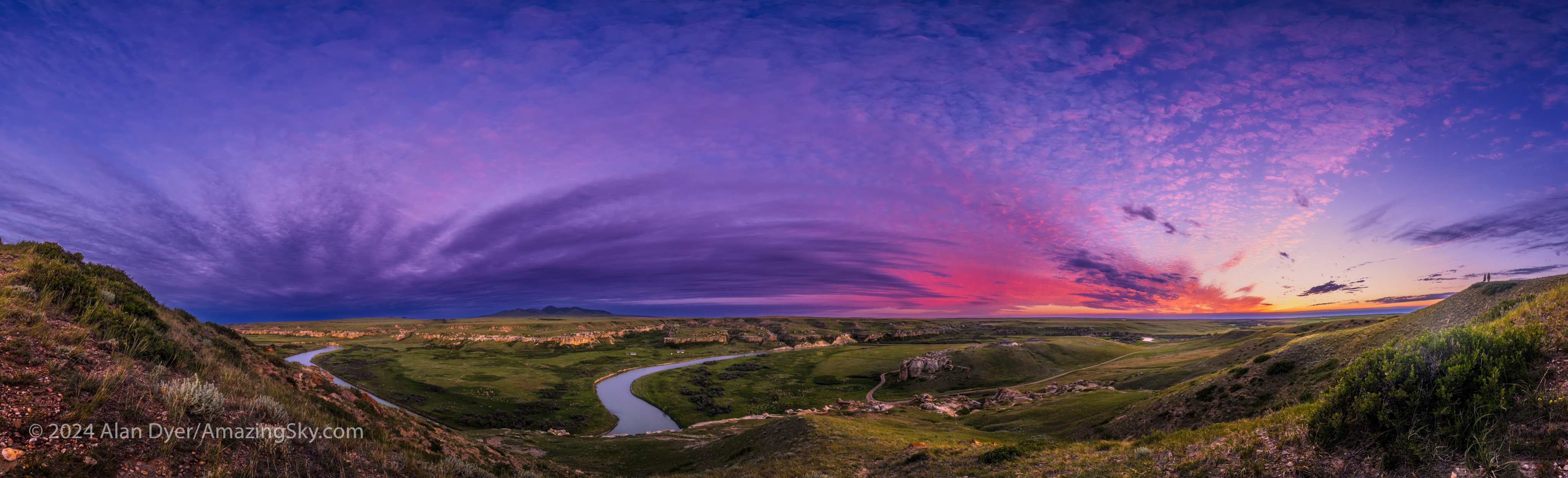

Above is the same scene a few minutes later as the Sun, though now set, still lights the high clouds with its red light, mixing with the blue sky to make purples. On the hill at right, a couple admires the sunset, adding a human scale to the vast skyscape.
This pano was with the Canon RF15-35mm lens at 15mm and the camera in portrait orientation to capture as much of the sky and ground as possible in a single-row pano.
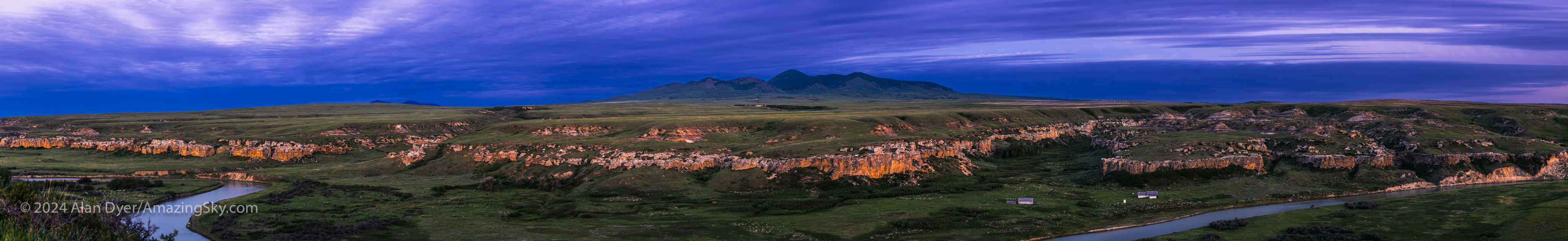

I finished the evening with another panorama, but using a Canon RF70-200mm telephoto lens at 70mm to zoom in on the Sweetgrass Hills in the deepening twilight.
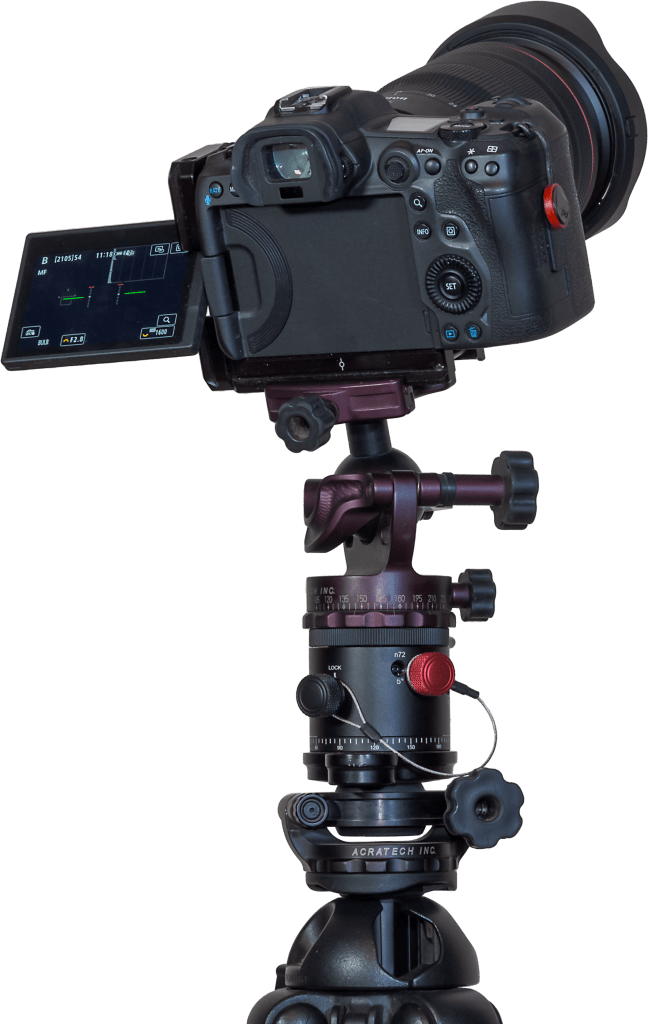

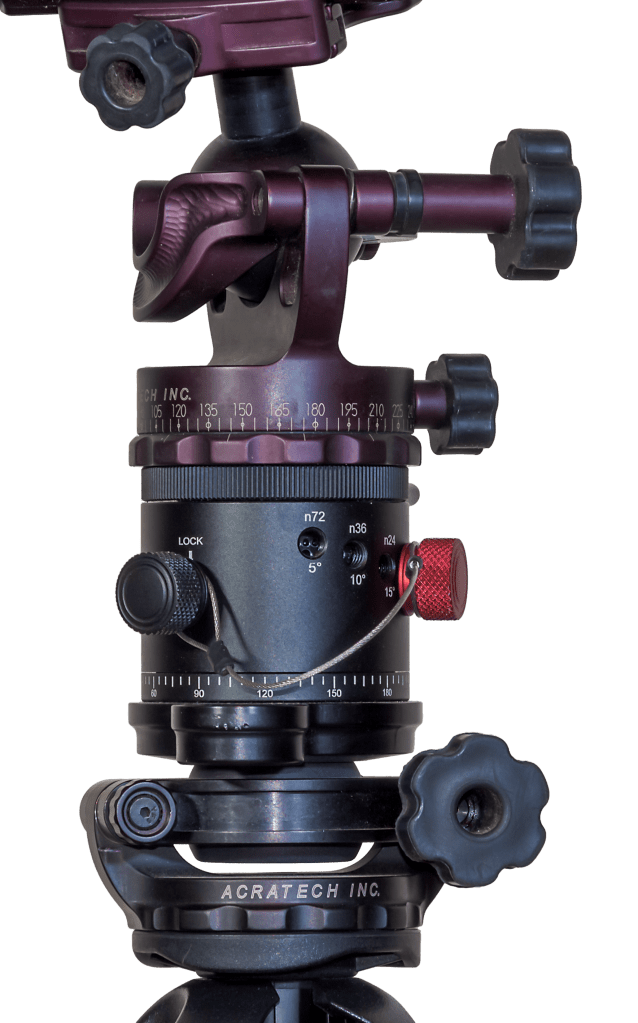
For these panoramas, exposures were short, so I didn’t need to track the sky. I used another combination of gear shown above. An Acratech ball head sits atop another style of panorama head that has adjustable click stops to make it easy to move the camera from segment to segment at set angles. When the lighting is changing by the second, it helps to be quick about shooting all the pano segments. Such pano heads are readily available on Amazon.
That pano head sits atop an Acratech levelling head (there are many similar units for sale), an essential addition that makes it easy to level the pano head so the camera turns parallel to the horizon. Any tilt will result in a panorama that waves up and down, likely requiring fussy warping or cropping to correct. Avoid that; get it right in-camera!
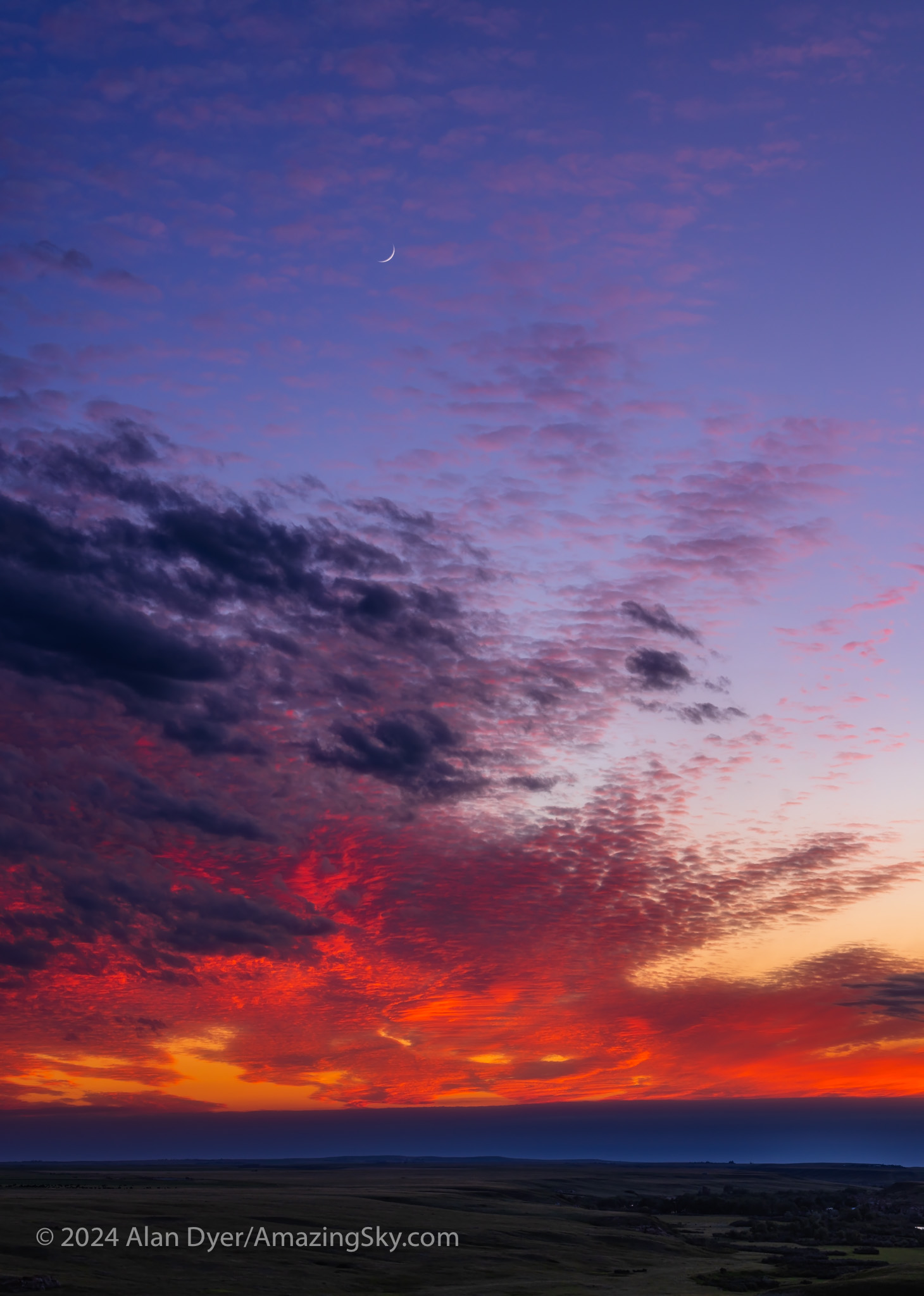

As the sky lit up, I also shot the crescent Moon above the sunset clouds and prairie scene. While the clouds made for a fine sunset, they did not clear off, thwarting my Milky Way plans this night. I headed back to Milk River, to travel farther west the next day.
From Writing-on-Stone I drove along scenic Highways 501 and 5 to Waterton Lakes National Park.
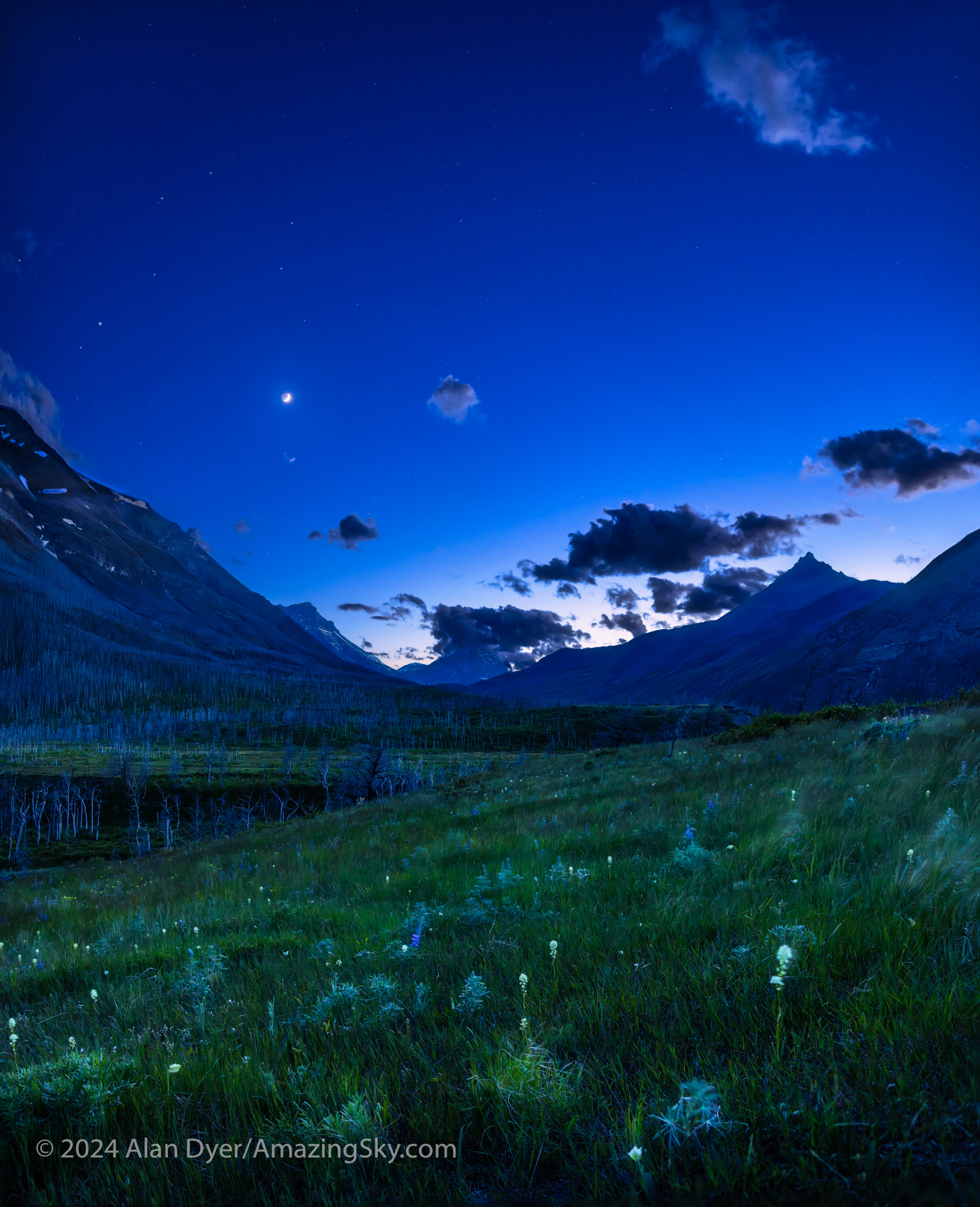

After an initial cloudy night, I made use of the (mostly) clear night on June 10 to shoot twilight scenes with the now four-day-old crescent Moon in the evening sky. Here I wanted to play with another technique I had not used much before: focus stacking.
To keep exposures short (here to minimize the blurring effects of the constant wind at Waterton) you have to shoot at wide apertures (f/2 in this case). But that produces a very shallow depth of field, where only a small area of the image is in focus.
So I shot a series of six images, shifting the focus from near (for the foreground flowers) to far (for the mountains and sky). Photoshop has an Auto Blend function that will merge the images into one with everything in focus. I also shot separate images exposed for the bright sky, shooting a vertical panorama — dubbed a “vertorama” — moving the camera up from frame to frame.
I shot an additional short exposure just for the Moon, to prevent its disk from overexposing too much, as it did in the twilight sky images.
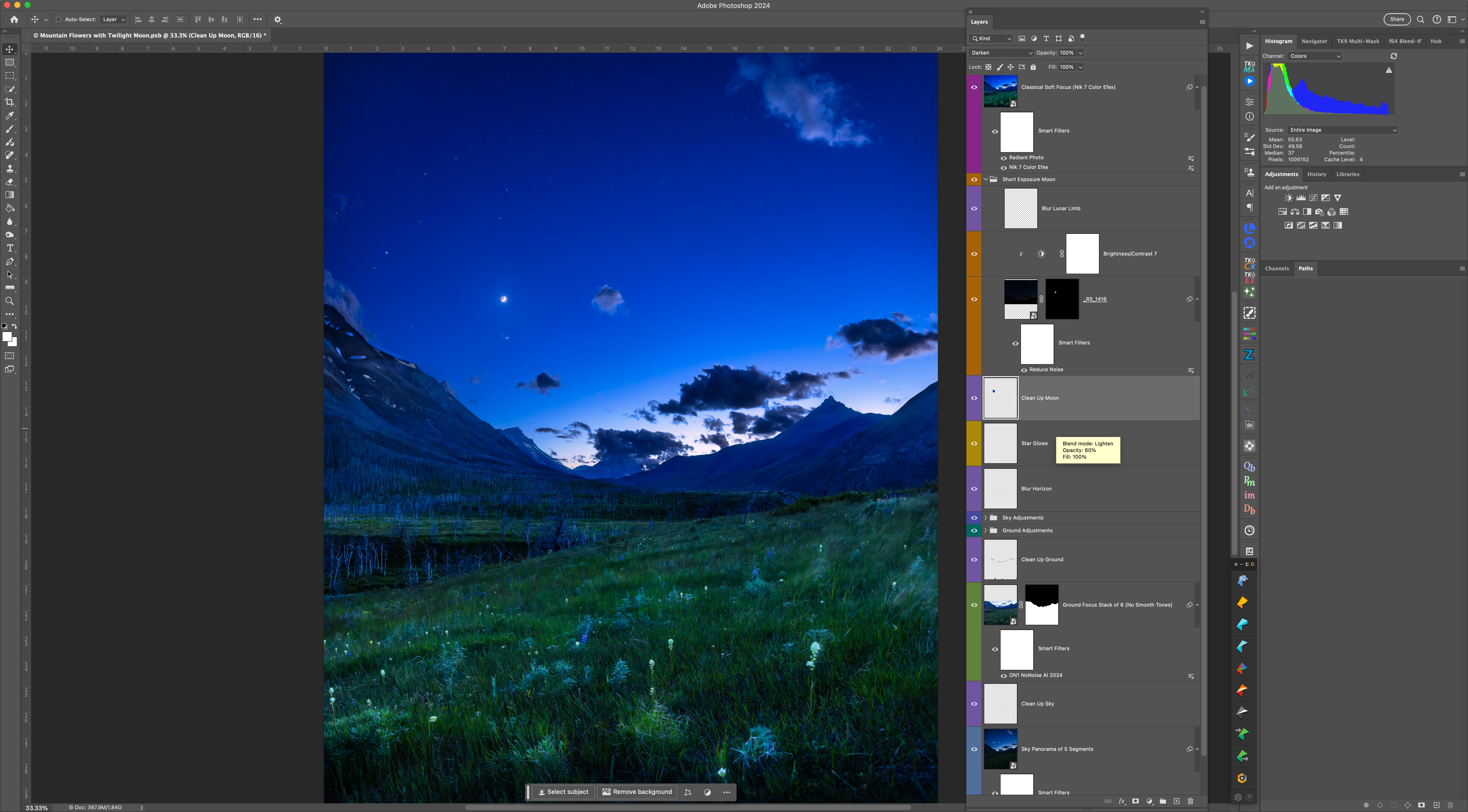
So what looks like a simple snapshot of a twilight scene is actually a complex blend of focus-stacked ground images, panoramic sky images, and a single short image of the Moon replacing its otherwise overly bright disk. But the result better resembles what the eye saw, as single exposures often cannot record the range of brightness the eye can take in.
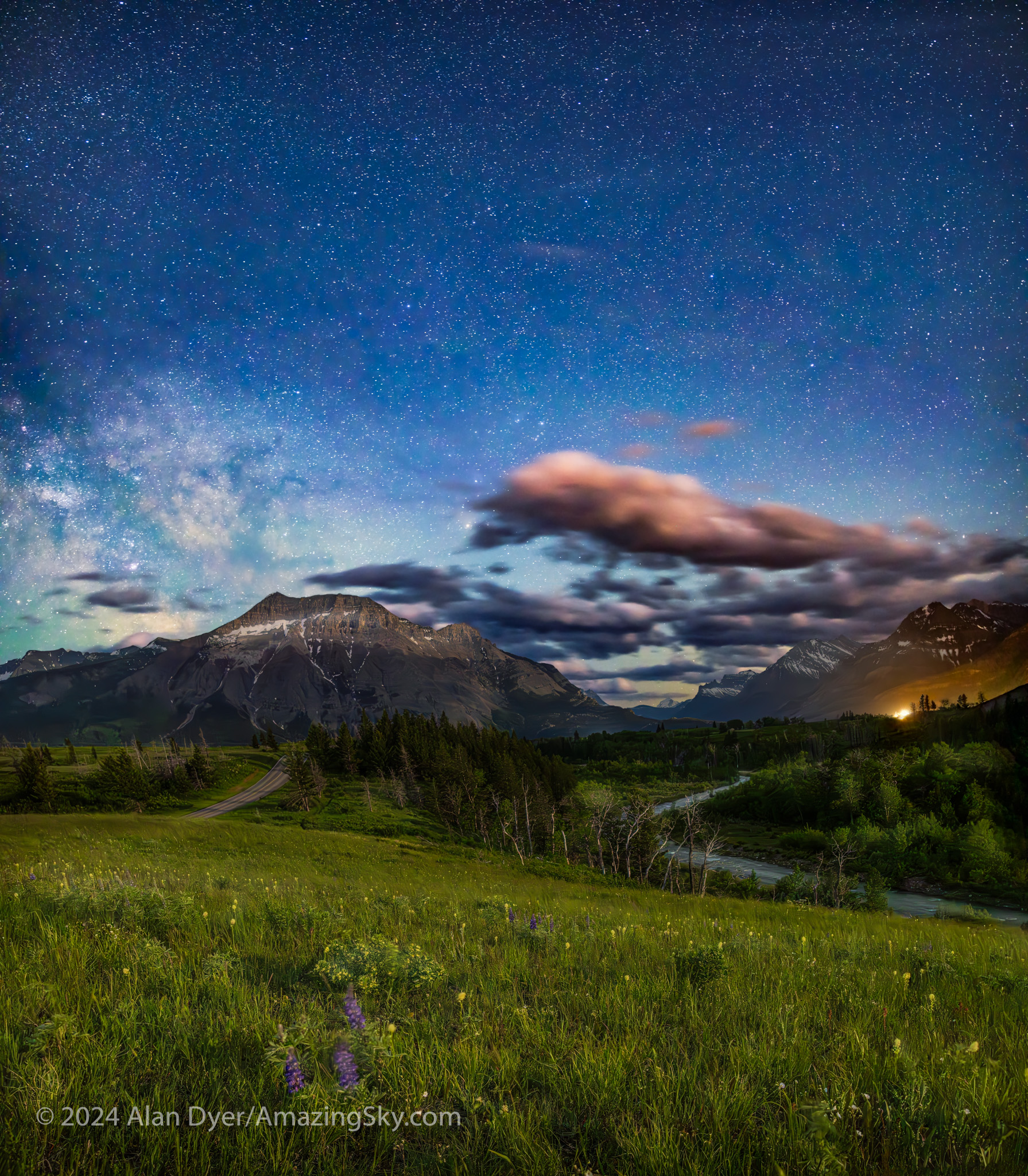

About an hour later, from the same location, I shot the other way, toward the Milky Way rising over Vimy Peak, but the sky still lit blue by moonlight. This, too, is a blend of focus-stacked ground and panorama sky images. But the camera was on a fixed tripod for exposures no longer than 15 seconds. So I didn’t use the tracker.
And here the longer exposures do pick up more (colours, fainter stars, and brighter ground detail) than was visible to the eye. Revealing more than the eye can see is the essence and attraction of astrophotography.
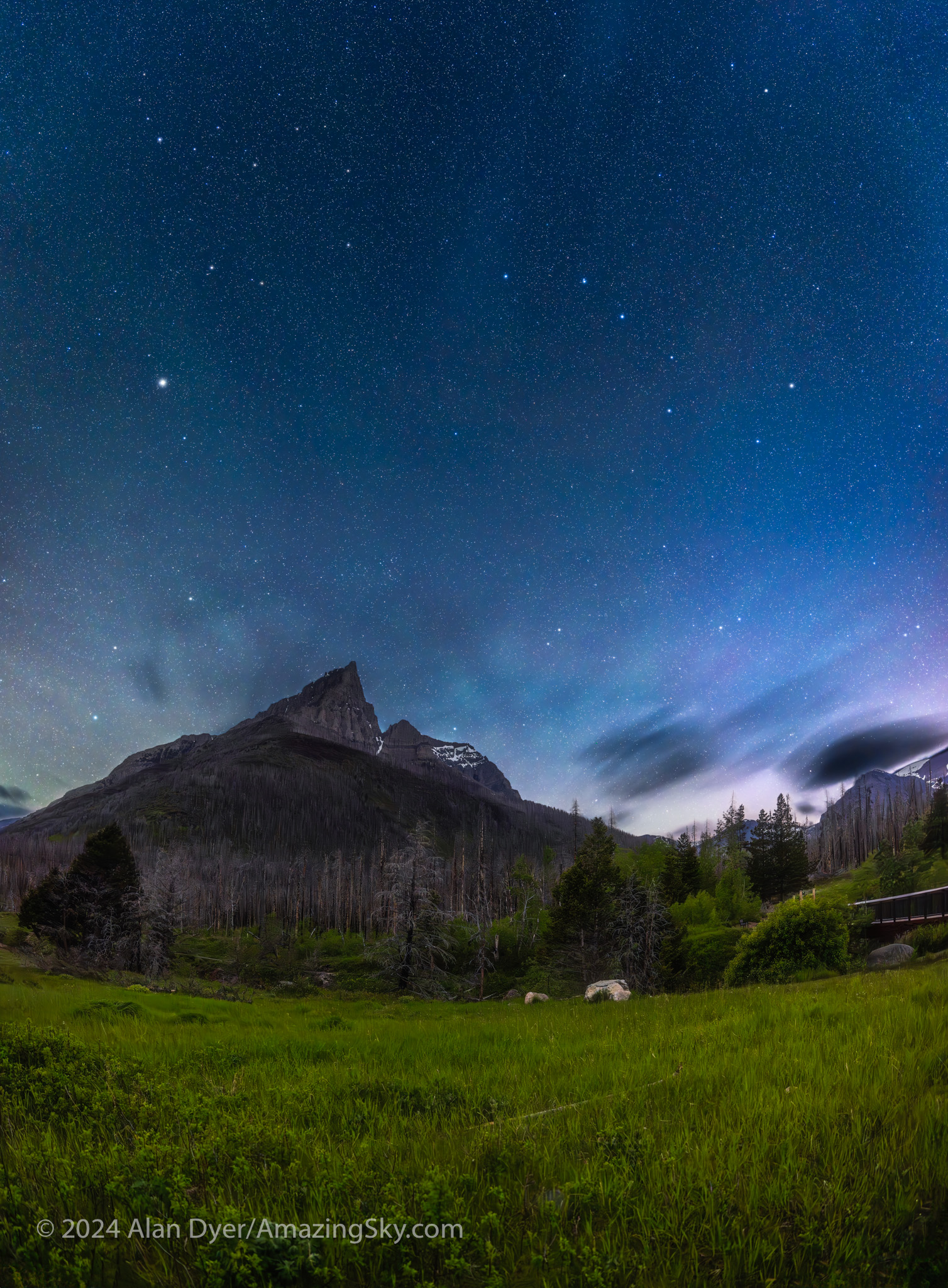

Heading down the Red Rock Canyon Parkway, I set up the tracker rig for the darker sky, now that the Moon was nearly setting. I shot a vertical panorama, with two untracked ground segments and four tracked sky segments, to capture Arcturus and the Big Dipper over the iconic Anderson Peak.
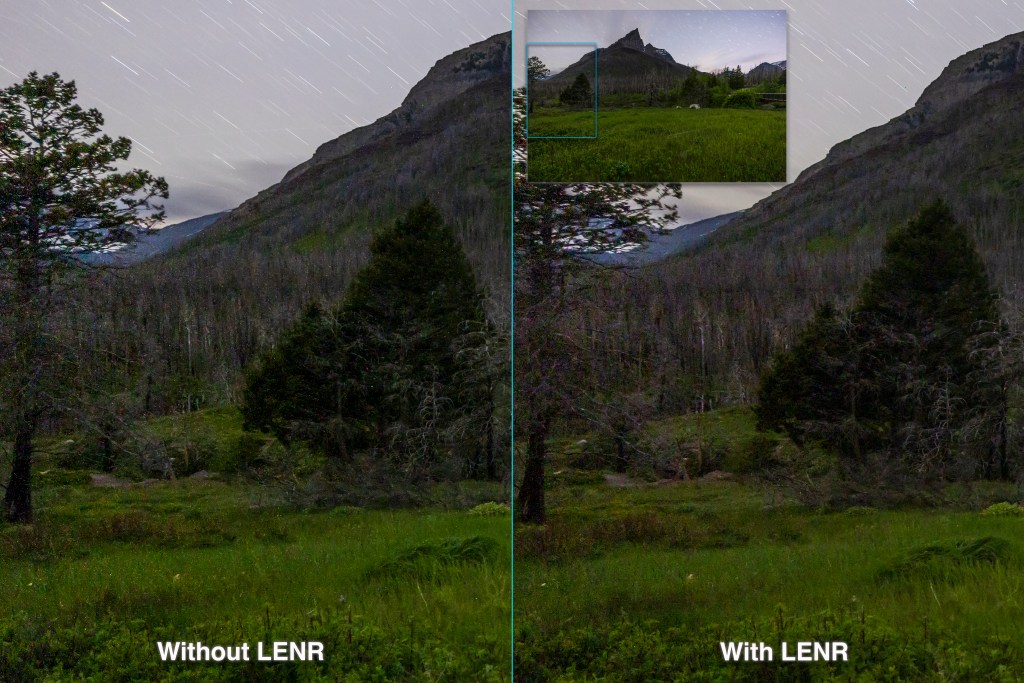

For all the images at Waterton and Writing-on-Stone I used the 45-megapixel Canon R5 camera, great for high resolution, but prone to noise, especially colourful thermal hot pixels. (See my review here.)
For all the long exposures I turned on Long Exposure Noise Reduction, a feature most cameras have. LENR forces the camera to take a “dark frame,” a second exposure of equal length, but with the shutter closed. The camera subtracts the dark frame (which records only the hot pixels) from the previous light frame. The final image takes twice as long to appear, but is much cleaner, as I show above. So a two-minute exposure requires four minutes to complete.
While there are clever ways to eliminate hot pixels later in processing (using Photoshop’s Dust and Scratches filter), doing so can blur details. I’ve long found that doing it “in-camera” always produces better results.
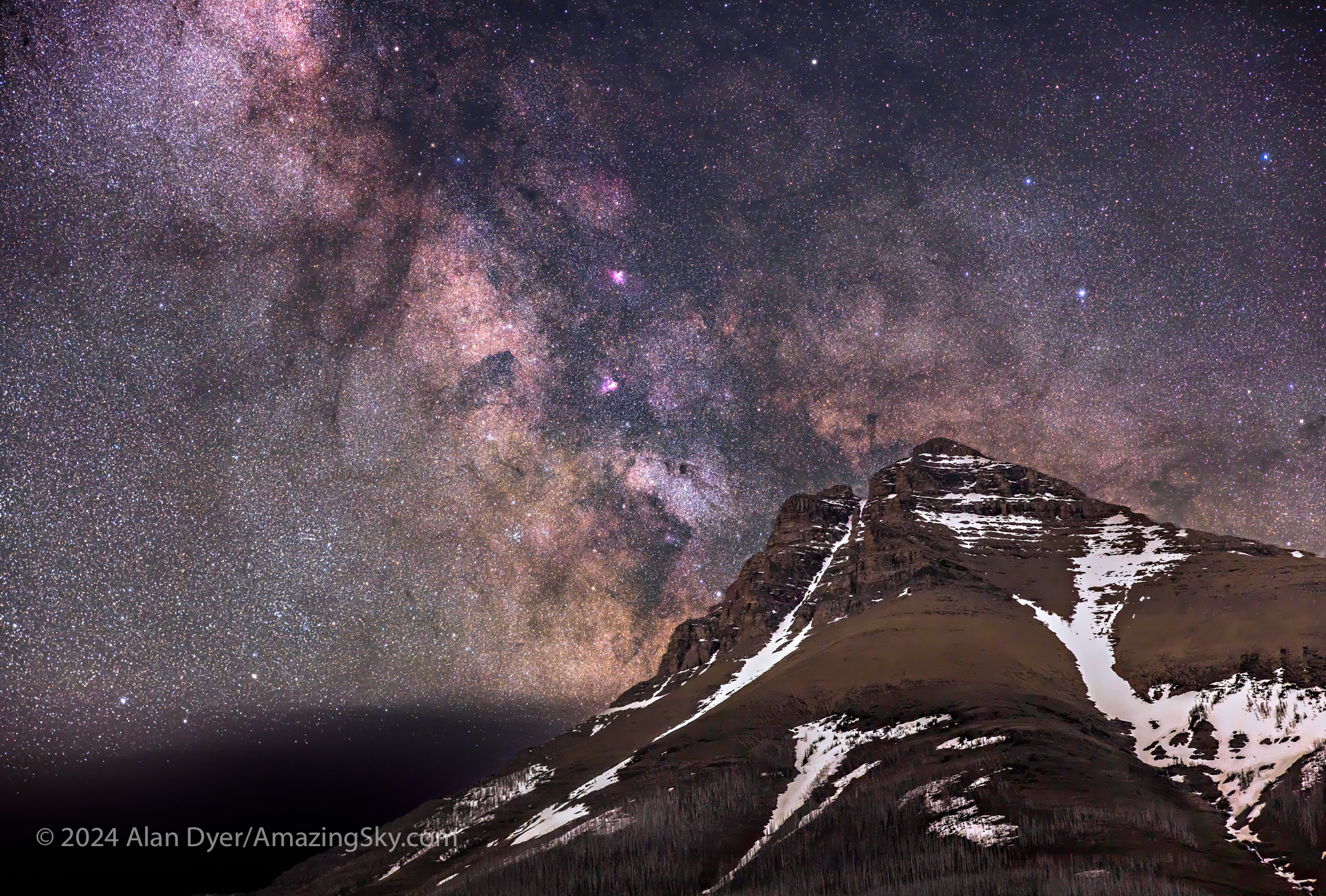

With the Moon now down, I turned the camera the other direction toward Mt. Blakiston, to capture the star clouds of the summer Milky Way rising behind the mountain, in an example of a “deepscape,” a nightscape with a telephoto lens. This is another technique I’ve not used very often, as the opportunities require good location planning and timing, transparent skies, and a tracker. Apps like ThePhotographersEphemeris coupled with TPE3D, and PlanItPro can help.
Deepscapes frame landscape fragments below some notable deep-sky objects and starfields, in this case a region with several “Messier objects” — nebulas and star clusters well-known to amateur astronomers.
This was a blend of one untracked and one tracked exposure, again on the Nomad. Taking more frames for stacking and noise reduction, while a common practice, was not practical here — at this focal length of 70mm the sky was moving enough that the mismatch between sky and ground would make blending tough to do.
And the reality is that today’s AI-trained noise reduction software (see my test report here) is so good, image stacking is not as essential as it once was.
For many of the Waterton images I used the Canon RF28-70mm lens, usually wide open at f/2. For the image below I used the RF15-35mm lens at its maximum aperture of f/2.8. (See my test report on these lenses here.)
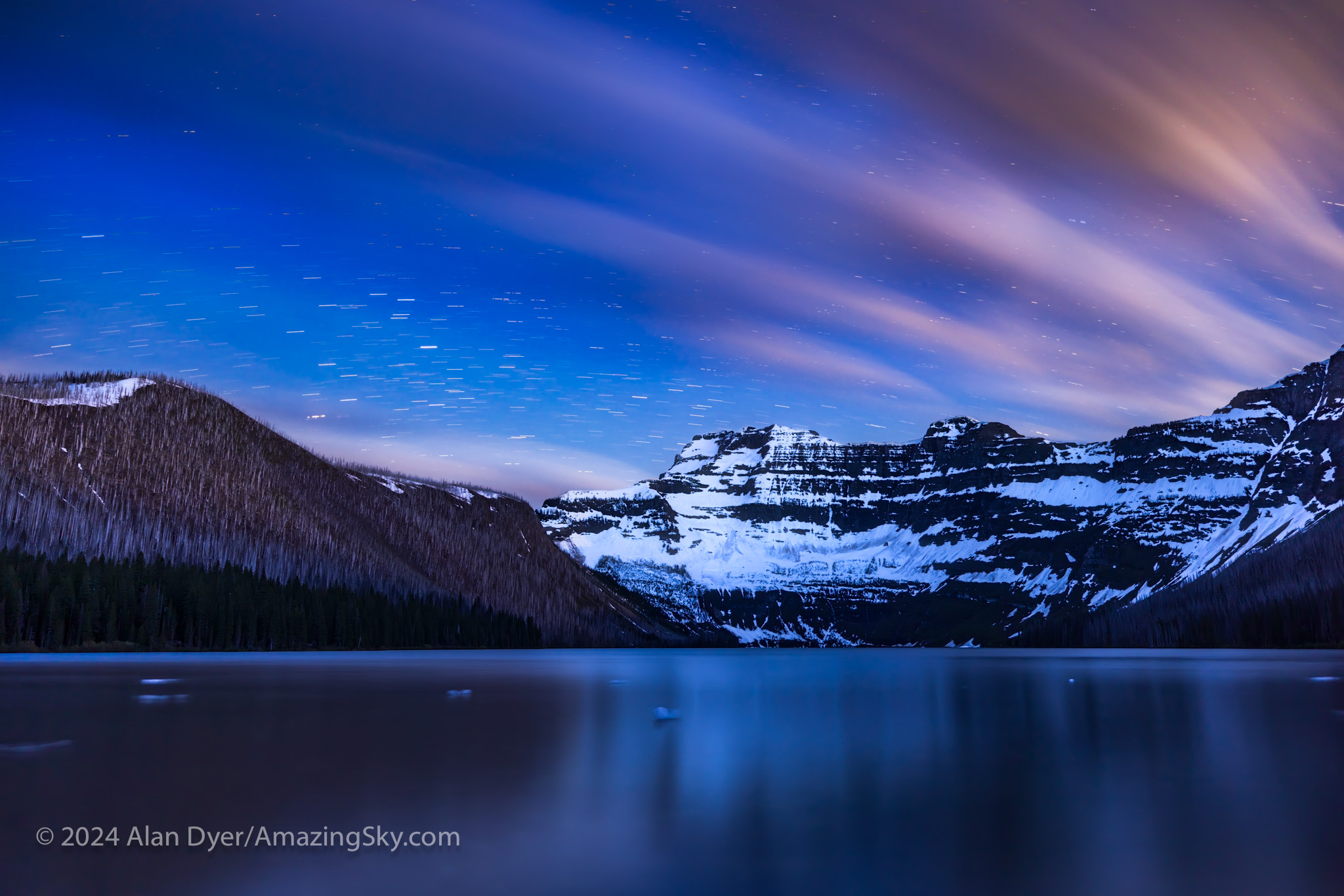

On my final night in Waterton I drove the Akamina Parkway to Cameron Lake, located in extreme southwest Alberta on the borders with British Columbia and Montana. The glaciated peak to the south is Mt. Custer in Glacier National Park, Montana.
Again, I had hoped to get a deepscape of the photogenic starfields in Scorpius above Mt. Custer. But as is often the case at this site, clouds wafting over the Continental Divide defeated those plans. So Plan B was a set of long exposures of the clouds and stars trailing with the last light of the low Moon lighting parts of the scene. Chunks of ice still drift in the lake.
This is a blend of separate multi-minute exposures for the ground and sky, all at the slow ISO of just 100, and all untracked to purposely create the star trails, not avoid them.
So over a total of four nights at these wonderful World Heritage Sites, I was able to try out some new shooting techniques:
- H-Alpha blending
- Focus stacking
- Deepscapes
- As well as panoramas, both horizontal and vertical
Every nightscape outing is a learning process. And you have to be prepared to change plans as the clouds dictate. I didn’t get all the shots I had hoped to, but I still came away with images I was very pleased with.
I hope you enjoyed them. Clear skies!
— Alan Dyer / AmazingSky.com
