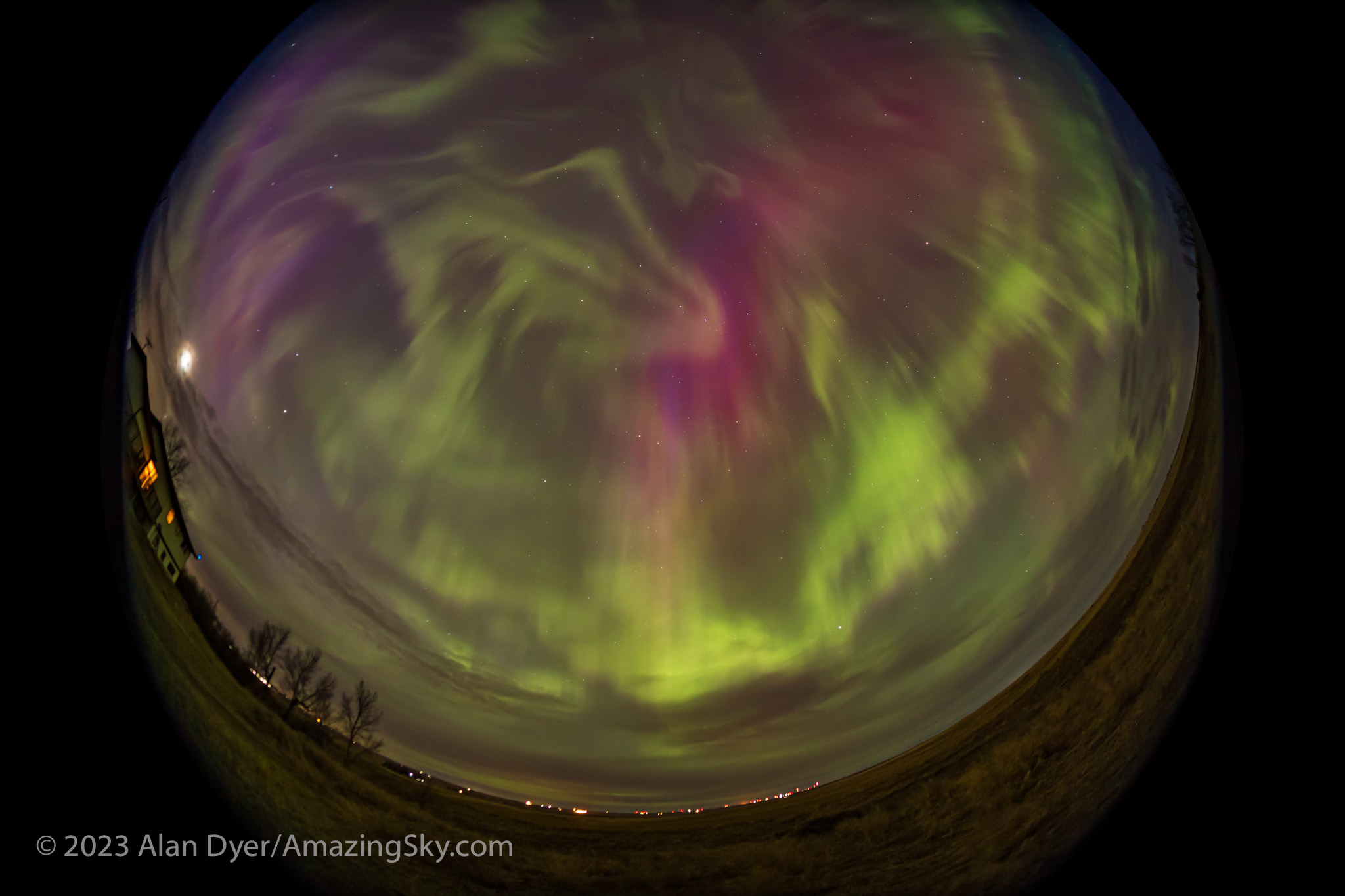
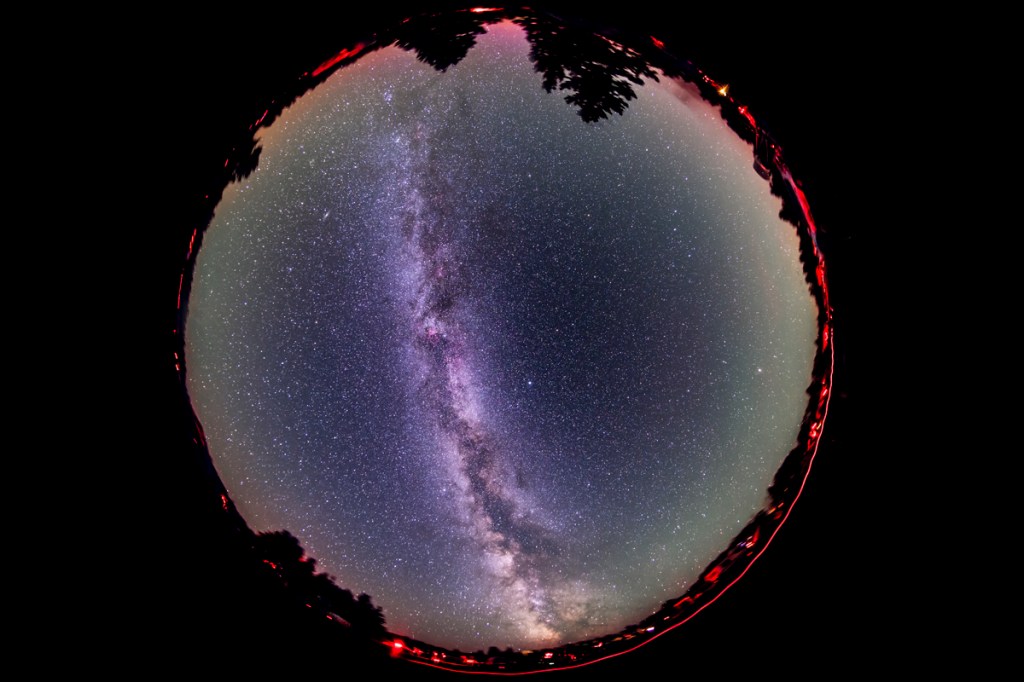
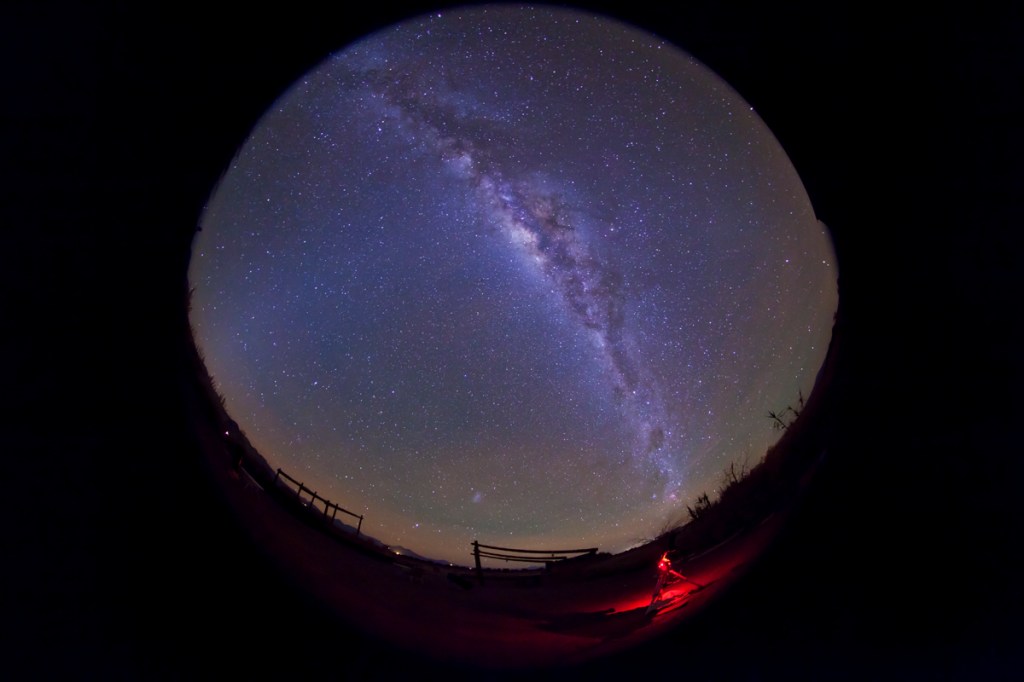
I test a trio of wide-angle, auto-focus lenses for astrophotography, all for Nikon Z mount: the Nikkor 20mm f/1.8 S, the Viltrox 16mm f/1.8, and the Laowa 10mm f/2.8 Zero D.
As a bonus, I also test a fourth lens: the TTArtisan manual-focus 7.5mm f/2 fish-eye.
NOTE: Images are large and may take a while to load.
While the selection of lenses for Nikon Z mirrorless cameras is not as diverse as it is for Sony E-mount, Nikon shooters have more brands of lenses to pick from than do users of Canon R mirrorless cameras. For nightscapes and Milky Way photography we want fast, wide-angle lenses, usually in the 14mm to 24mm range.
Canon, Nikon, and Sony all have excellent zoom lenses that cover the range. I use Canon’s RF 15-35mm L lens a lot, and reviewed it here on my blog from 2022.
But all these wide-angle zooms are f/2.8. While that’s a good speed for most astro work, having an even faster lens can be valuable. An aperture of f/2 or faster allows for:
— Shorter exposures for untrailed stars when shooting just on a tripod with no tracker.
— Capturing fainter and more numerous meteors during a shower.
— Rapid-cadence time-lapses of auroras, freezing the motions of curtains.
— Real-time movies of auroras and satellite passages at lower, less noisy ISO settings.
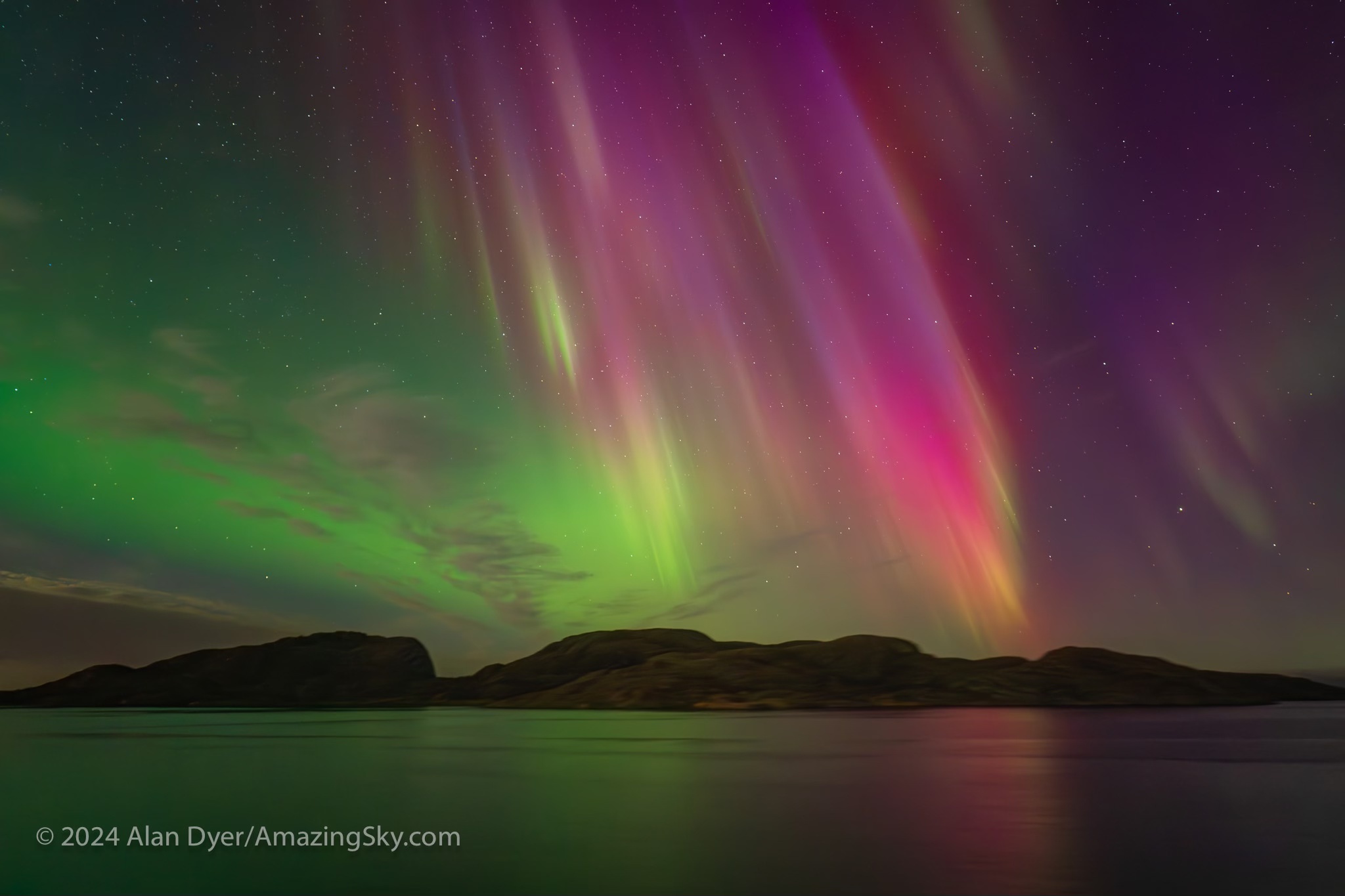

Also, stopping those faster lenses down to f/2.8 can sometimes yield better image quality than shooting with a native f/2.8 lens wide open.
Canon and Sony each have fast f/2 zooms that cover the range from 28mm to 70mm. While those focal lengths can be useful, both lenses are expensive and heavy. And they are still not wide enough for many astro subjects. For fast lenses with even shorter focal lengths we need to turn to “prime” lenses, ones with fixed focal lengths.
As of this writing Canon has few fast, wide primes for their RF lens mount (their new 24mm f/1.4 VCM is a costly choice designed primarily for video use). A few third-party lens makers offer fast (f/2 or faster) primes for Canon full-frame cameras, always as manual focus lenses. For example, Laowa has a 15mm f/2, and TTArtisan has a 21mm f/1.5.
Yes, Sigma now offers auto-focus 16mm and 23mm f/1.4 primes, and Samyang has a new 12mm f/2, but they are only for Canon RF-S cropped-frame cameras. Canon has yet to allow other companies to produce auto-focus lenses for their full-frame cameras.
Nikon has been restrictive as well. Sigma’s much-lauded Art series that includes the 14mm rectilinear (i.e. the horizon remains straight) and 15mm fish-eye (with a curved horizon), both f/1.4 and aimed at astrophotographers, are not offered for Nikon or Canon, only for Sony E-mount and Panasonic/Leica L-mount cameras.
However, while Sigma lenses are missing, there is a wider choice of third-party lenses for Nikon Z-mount compared to Canon RF, plus Nikon itself makes a very fine 20mm prime in their premium S-series.
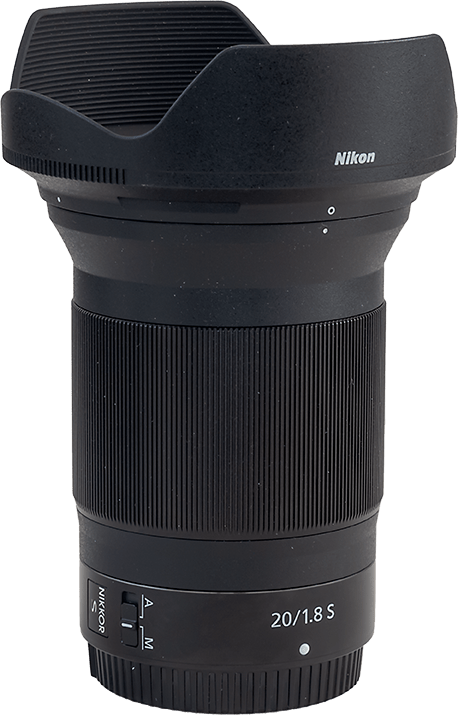



That’s what I test here — three wide-angle rectilinear primes for Nikon Z: A 20mm Nikkor, and two third-party primes: one from Viltrox, their 16mm; and one from Laowa, their new 10mm.
As a bonus, I add in a test of a fast fish-eye lens, from TTArtisan, their 7.5mm f/2.
NOTE: All test images can be downloaded as full-resolution JPGs for closer inspection. Click or tap on the images.
Prices are from B&H Photo, but will vary with sales and special promotions.
The Nikkor 20mm S-Line Lens ($1,050)


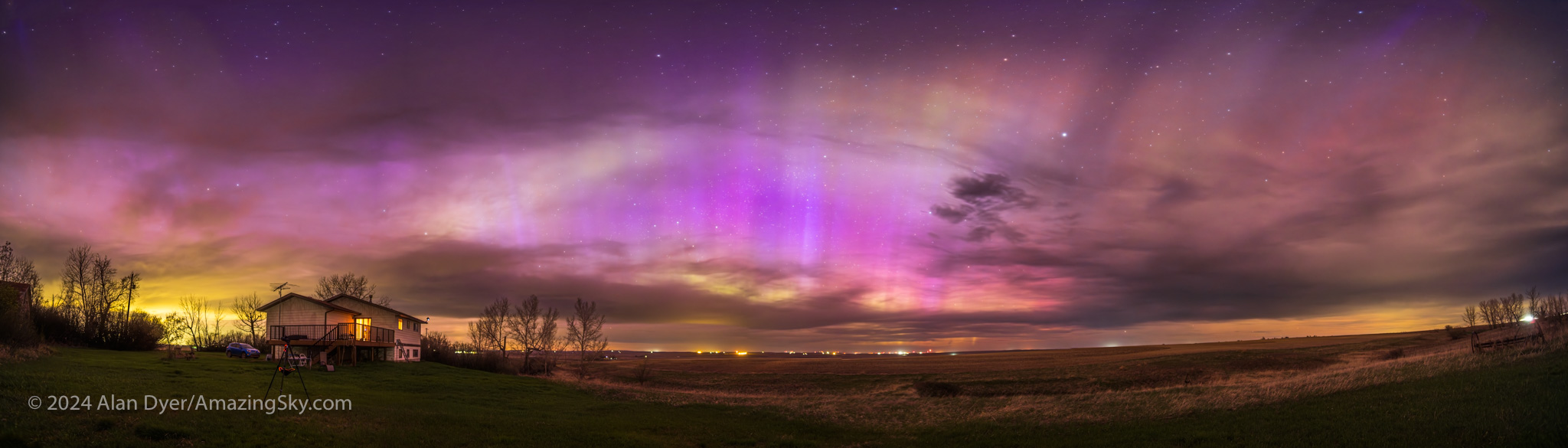
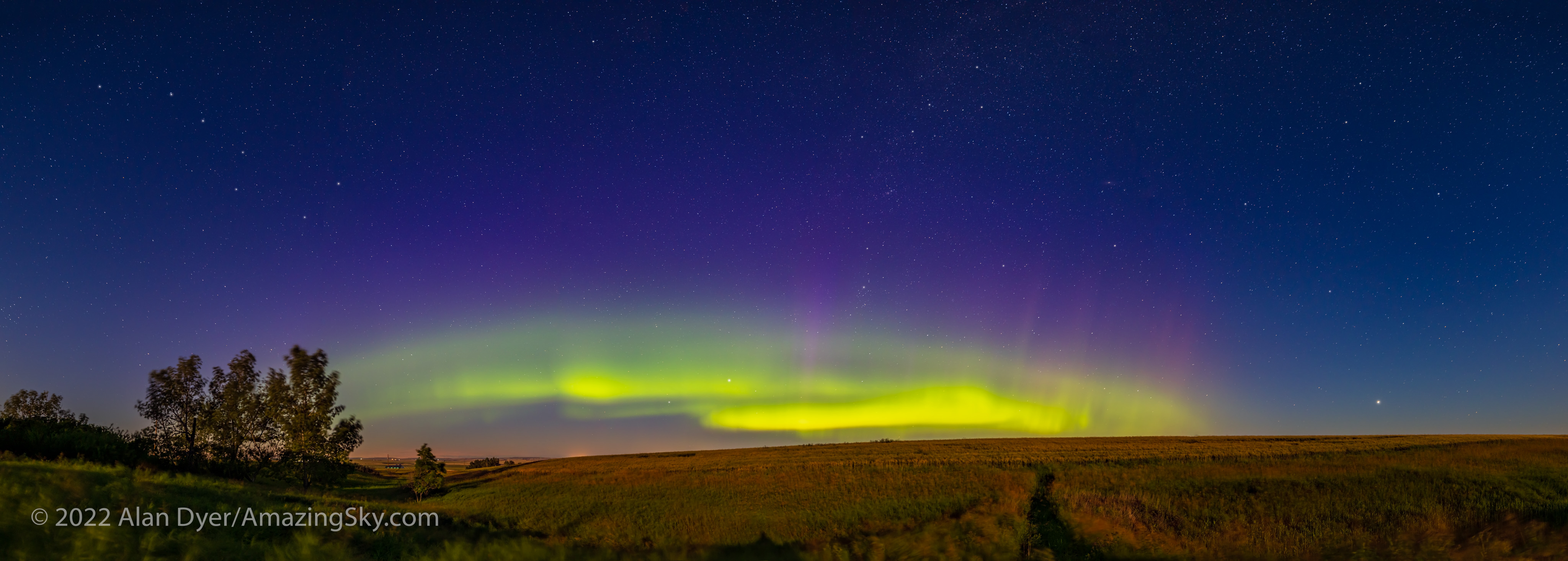
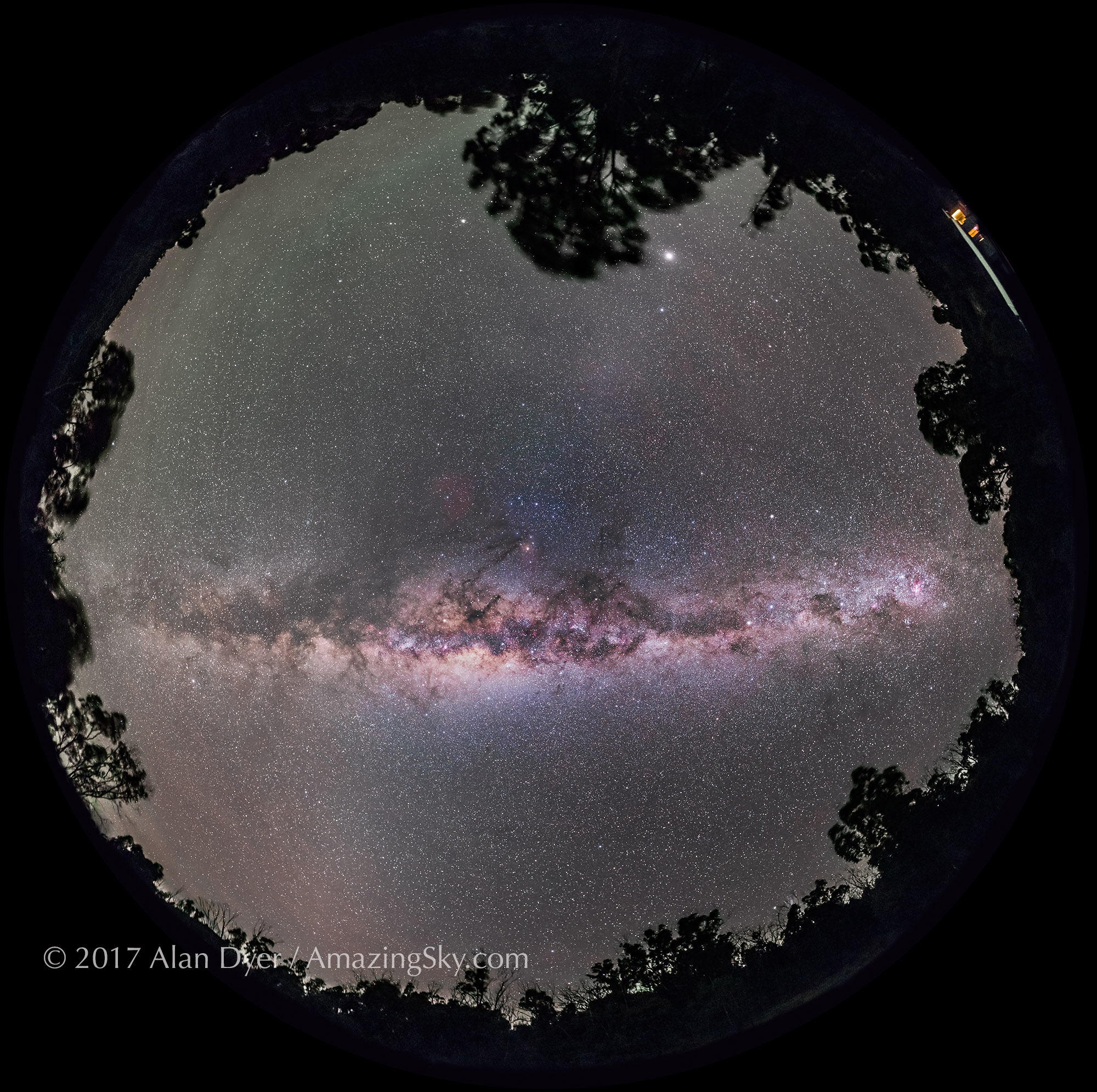
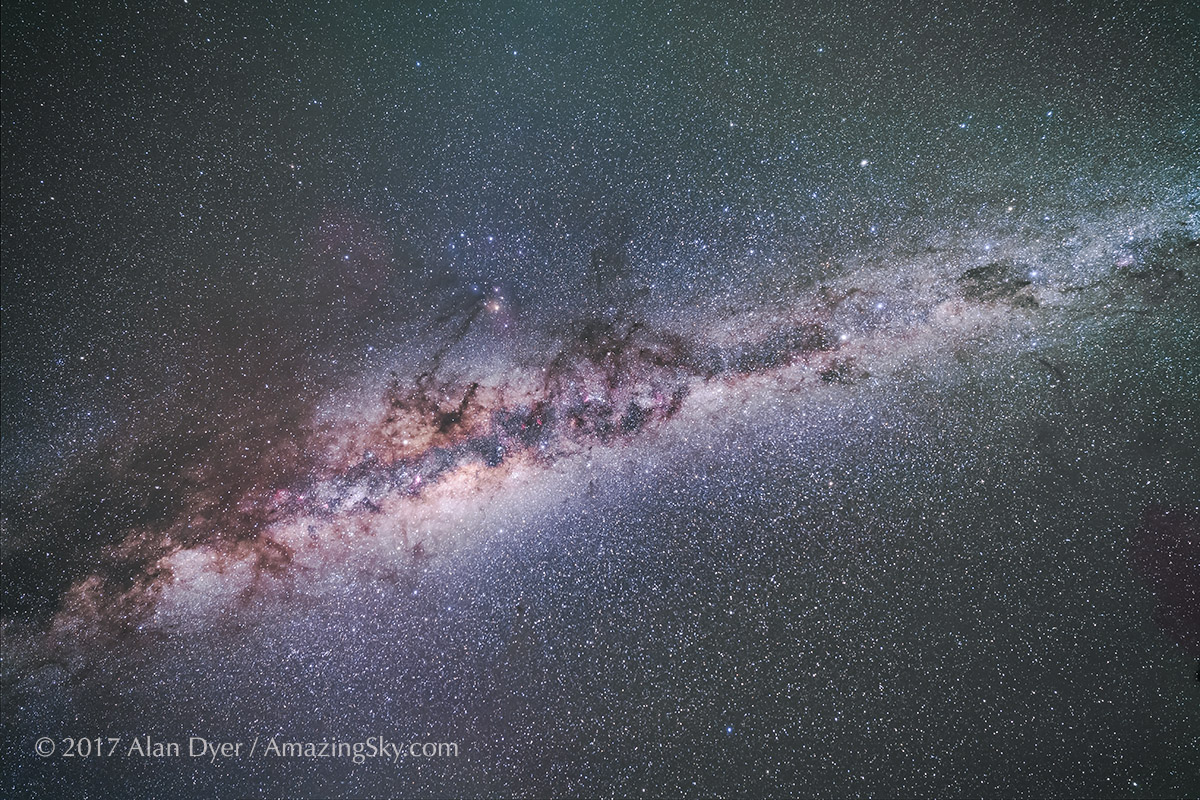
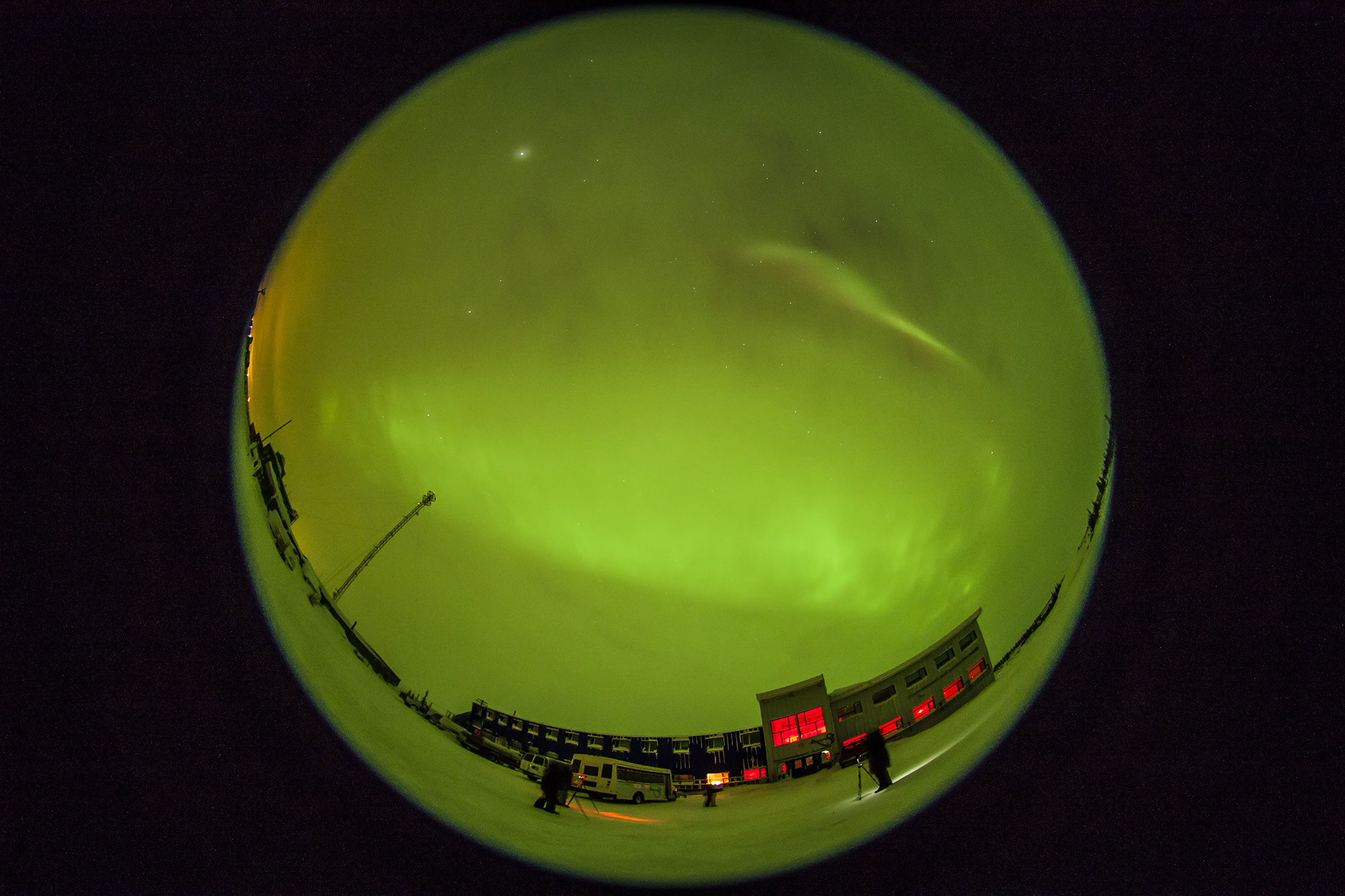
I shot the northern summer Milky Way (below) with the three rectilinear wide-angle lenses (meaning these are not fish-eyes) with the camera on a star tracker, to prevent star trailing. The tracker was the Move-Shoot-Move Nomad, reviewed here on my blog.
I shot with Nikon’s new Z6III, a 24-megapixel full-frame camera I reviewed in the December 2024 issue of Sky & Telescope magazine. It offers a number of excellent features for nightscape photography. Most notably, auto-focus lenses zip to the infinity focus point automatically when the camera is turned on, something I wish Canon cameras would do.

The Nikkor 20mm is the widest prime lens in Nikon’s premium S-Line series. It offers what I consider to be an ideal focal length for most nightscape and wide-field Milky Way images.
While a 14mm lens is often thought of as the default nightscape lens, a 20mm presents less distortion (objects leaning in or stretched out at the corners) and a more natural perspective. Plus the lens can be made faster (in this case f/1.8), smaller, and not cost as much as an ultra-fast 14mm like the Sigma f/1.4 Art lens.
Nikkor 20mm Corner Aberrations

Sharp stars right to the corners is the ideal for all forms of astro images. We don’t want stars to turn into winged seagulls or coloured streaks. They should remain as pinpoint as possible.
The Nikkor 20mm shows very little aberrations across the frame. Stars are elongated by tangential astigmatism and discoloured by lateral chromatic aberration only slightly and only at the extreme corners.
Stopping down the lens decreased the aberrations, but some residual astigmatism remained, even at f/4. However, the corner aberrations are low enough, and so restricted to the very corners, that this is a lens you can certainly use wide open at f/1.8, or perhaps at f/2, without any penalty of image sharpness.
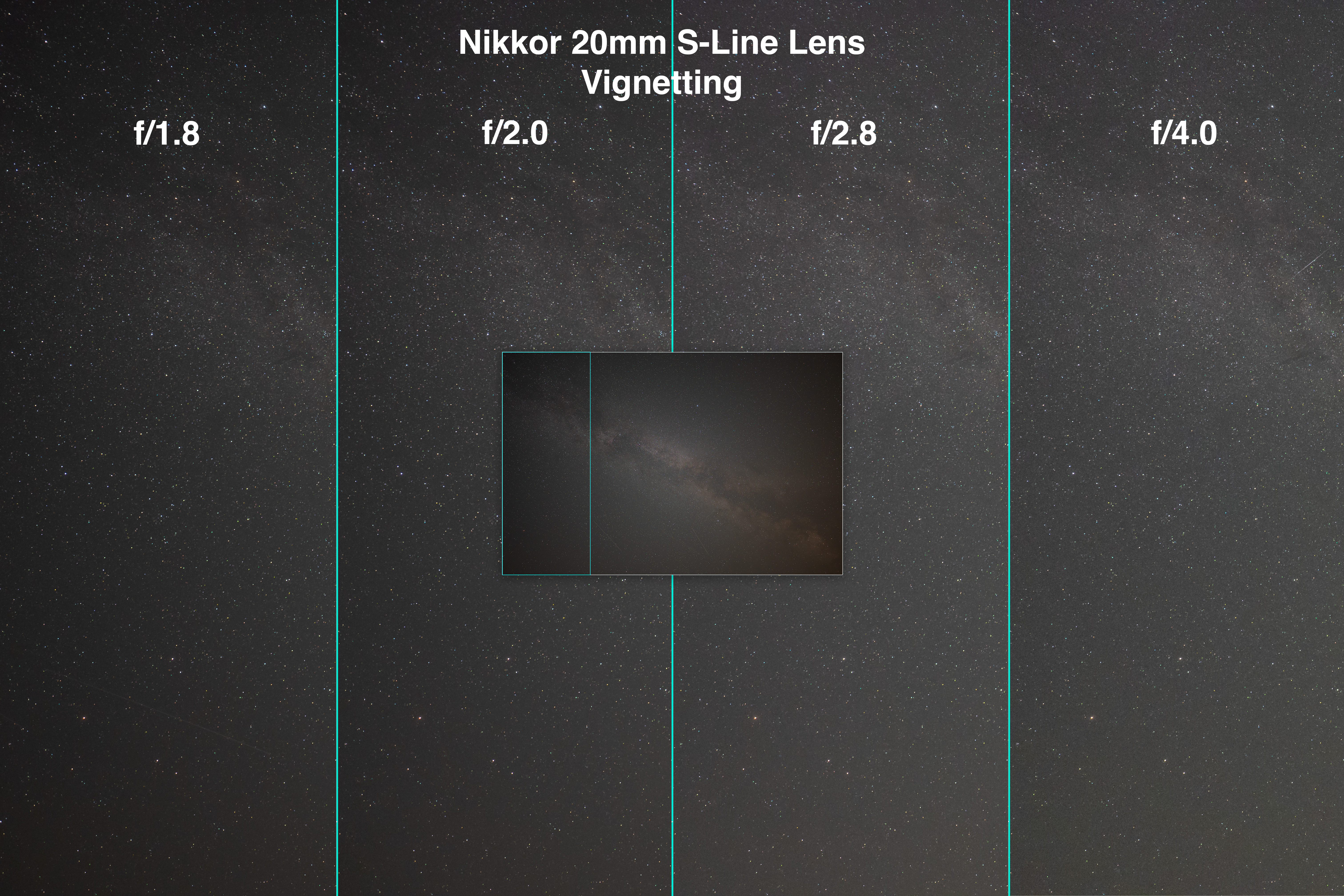
Nikkor 20mm Vignetting
Ideally, we also want images to be as fully-illuminated across the frame as possible. Light fall-off, or vignetting, creates dark corners with less signal reaching the sensor. Less signal gives rise to more noise, noticeable when brightening the corners in processing. That can reveal unsightly noise, banding, and discolouration in nightscapes, especially in the ground, often the darkest part of a scene, not the starry sky.
The 20mm shows a fair degree of edge and corner darkening when wide open at f/1.8. Stopping the lens down to f/2 improves the field illumination notably. And by f/2.8 the field is fairly uniformly lit. There is little need to go as slow as f/4.
In all, the Nikkor 20mm S is a superb lens ideal for nightscapes and Milky Way images.
The Viltrox AF 16mm STM ASPH ED IF ($580)
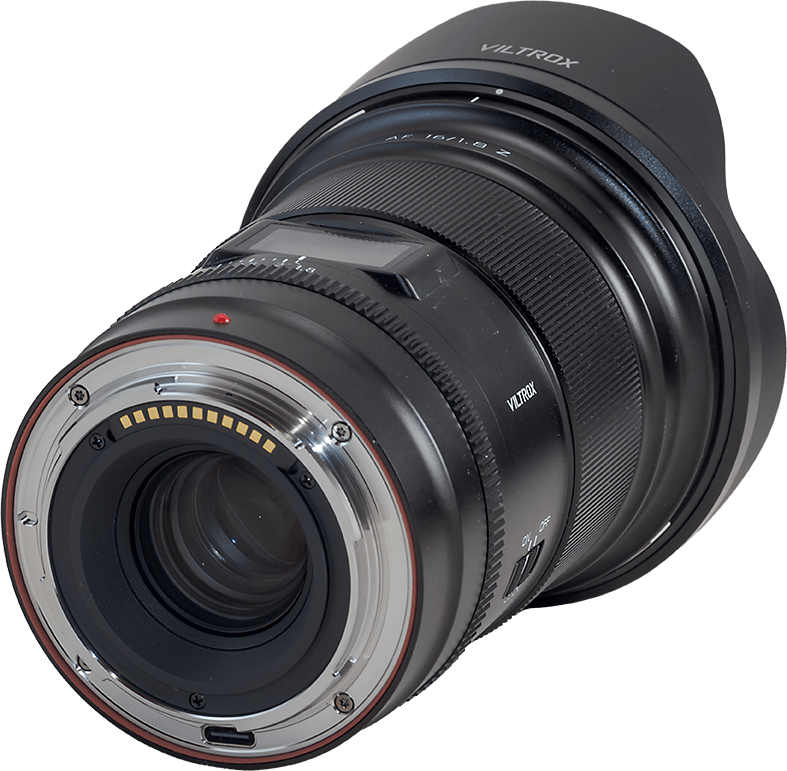


The new company Viltrox has been making a name for themselves recently with the introduction of a number of top-quality pro-grade lenses to compete with the best from any brand, and at much more affordable prices.

Their 16mm is an auto-focus lens that, on the Nikon, can actually auto-focus on stars, as can the Nikkor 20mm. However, it, too, will zip to infinity focus when powered up. Plus two function buttons can be programmed to rack between two preset focus distances, one of which can be infinity.
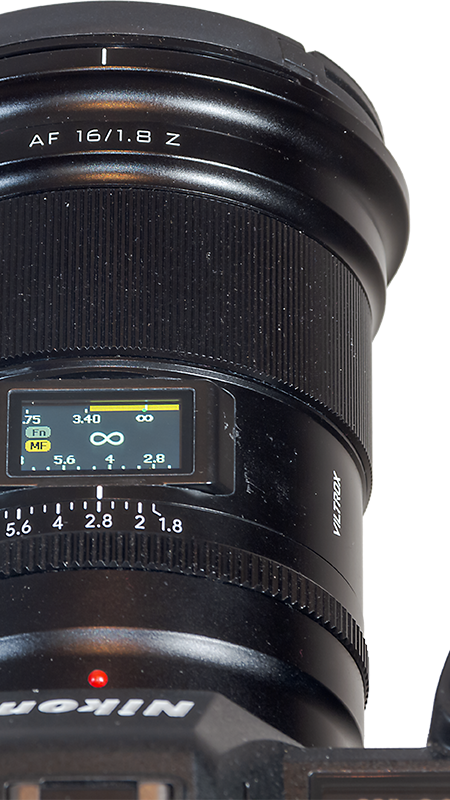


A manual aperture ring (above left) has 1/3rd-stop detents, or it can be set to A for controlling the aperture in the camera.
A colour OLED display (above right) shows the focus distance and aperture, a nice way to confirm your settings at night. The display is too bright on the darkest nights; I cover it with red gel.
An option to turn it red using the Viltrox app would be welcome. Or to turn it off! ….
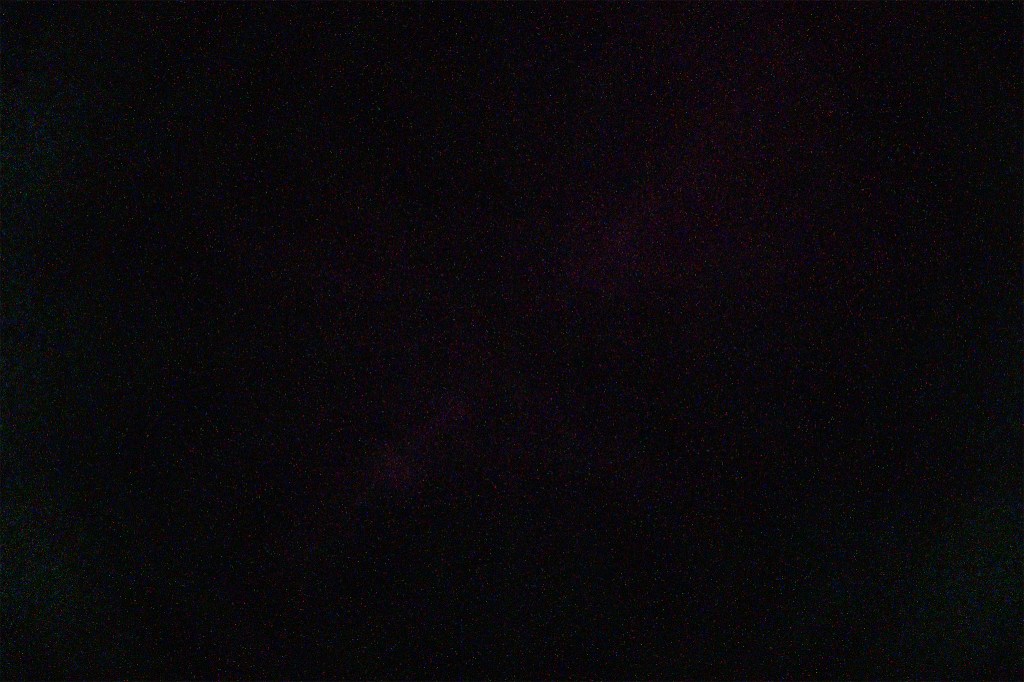
NOTE ADDED FEB 24, 2025 — I tested all lenses on a stock camera. But when used on an astro-modified camera with greater red and infra-red sensitivity, the Viltrox 16mm can add a noticeable red glow or flare to images, as a colleague has found and reported to me. I did confirm this with very long exposures and high ISOs with my stock Z6III. It barely shows up in dark frames boosted a lot for brightness (see below – it’s the faint magenta band across the centre of the frame).
But in modded cameras it is much more obvious. This comes from the lens’s top OLED display. The trick is to slightly dismount the lens, which turns the display off, but still maintains data contact to the camera. Viltrox is aware of the issue and has said they will fix it in a firmware update.

Uniquely, this and other Viltrox lenses have Bluetooth built in, for direct connection to a mobile device for firmware updates and lens settings, shown above. However, I found the app buggy; it would connect to the lens, but then refuse to allow settings to be changed, claiming the lens was not connected. Or the app would freeze, disconcerting during a firmware update. Luckily, that did not brick the lens.
Viltrox 16mm Corner Aberrations

At the extreme corners, the Viltrox shows some softness (perhaps from field curvature), but only minimal astigmatism and lateral chromatic aberration when wide open at f/1.8, and slightly sharper corners at f/2. At f/2.8 corner performance is nearly perfect, and certainly is at f/4.
This is a level of aberration correction even the most premium of lenses have a hard time matching.
Viltrox 16mm Vignetting

As is often the case with wider lenses, the Viltrox does show a great deal of vignetting at f/1.8, more so than the Nikkor 20mm. While this can be corrected in processing it will raise noise levels.
Stopping down to just f/2 helps, but the field becomes more uniform only at f/2.8, the sweet spot for this lens for the best all-round performance. But it offers the speed of f/1.8 when needed, such as for auroras.
If you prefer a wider field than a 20mm provides, the Viltrox 16mm (also available for Sony) is a great choice that won’t break the bank. Until Canon changes their third-party lens policy, Canon owners are out of luck getting this excellent lens.
The Venus Optics/Laowa 10mm Zero-D FF ($800)
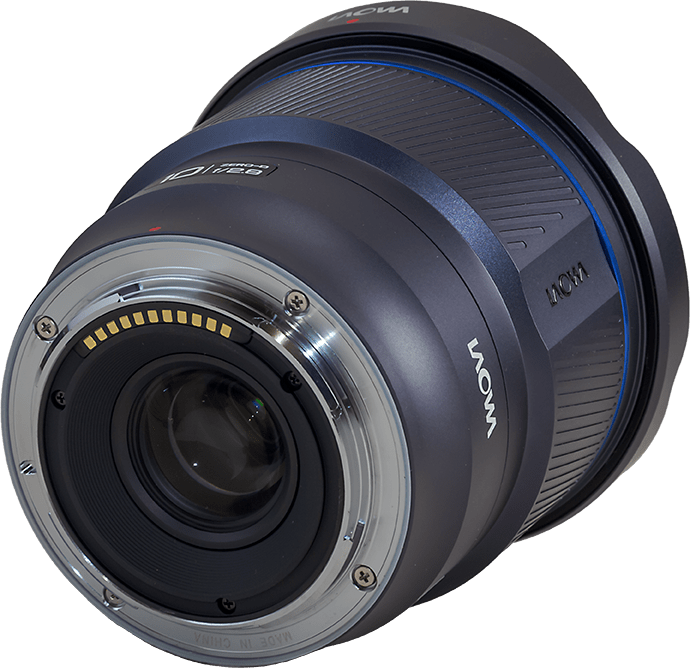


The lens maker Venus Optics (aka Laowa) is known for its innovative and often unusual lens designs.
Introduced in 2024, their new 10mm offers the widest field available in a rectilinear (not fish-eye) lens for full-frame cameras. The “Zero-D” label is for the lens’s lack of pincushion or barrel distortion. Horizons remain straight no matter where they fall on the frame. However, objects at the corners become elongated a lot.

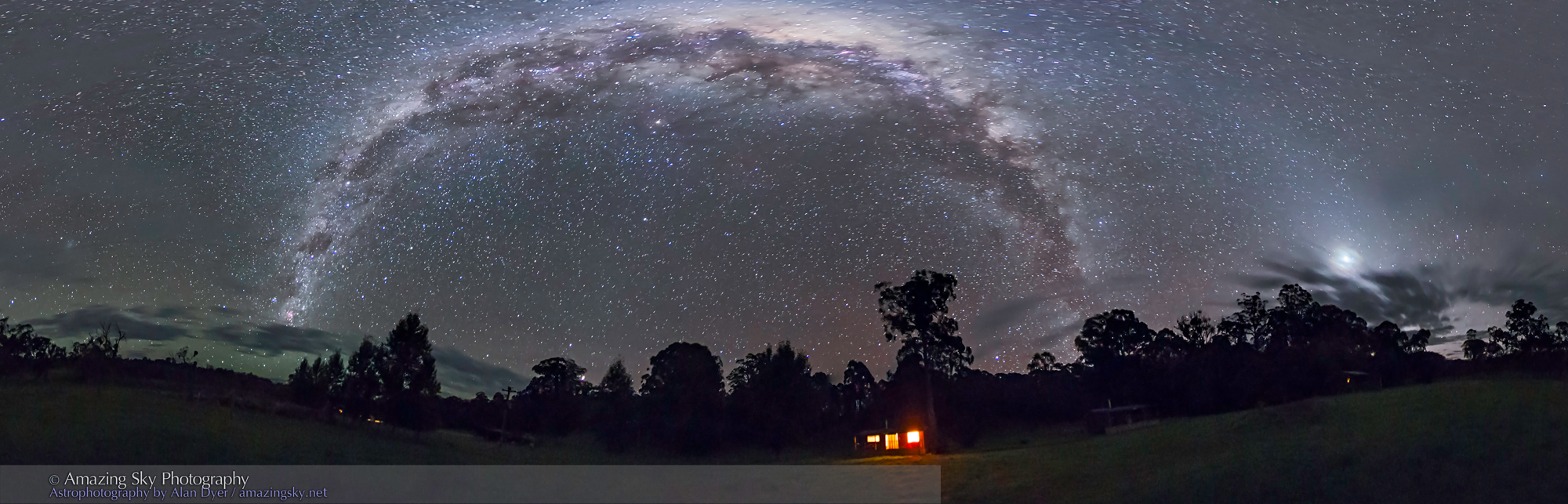
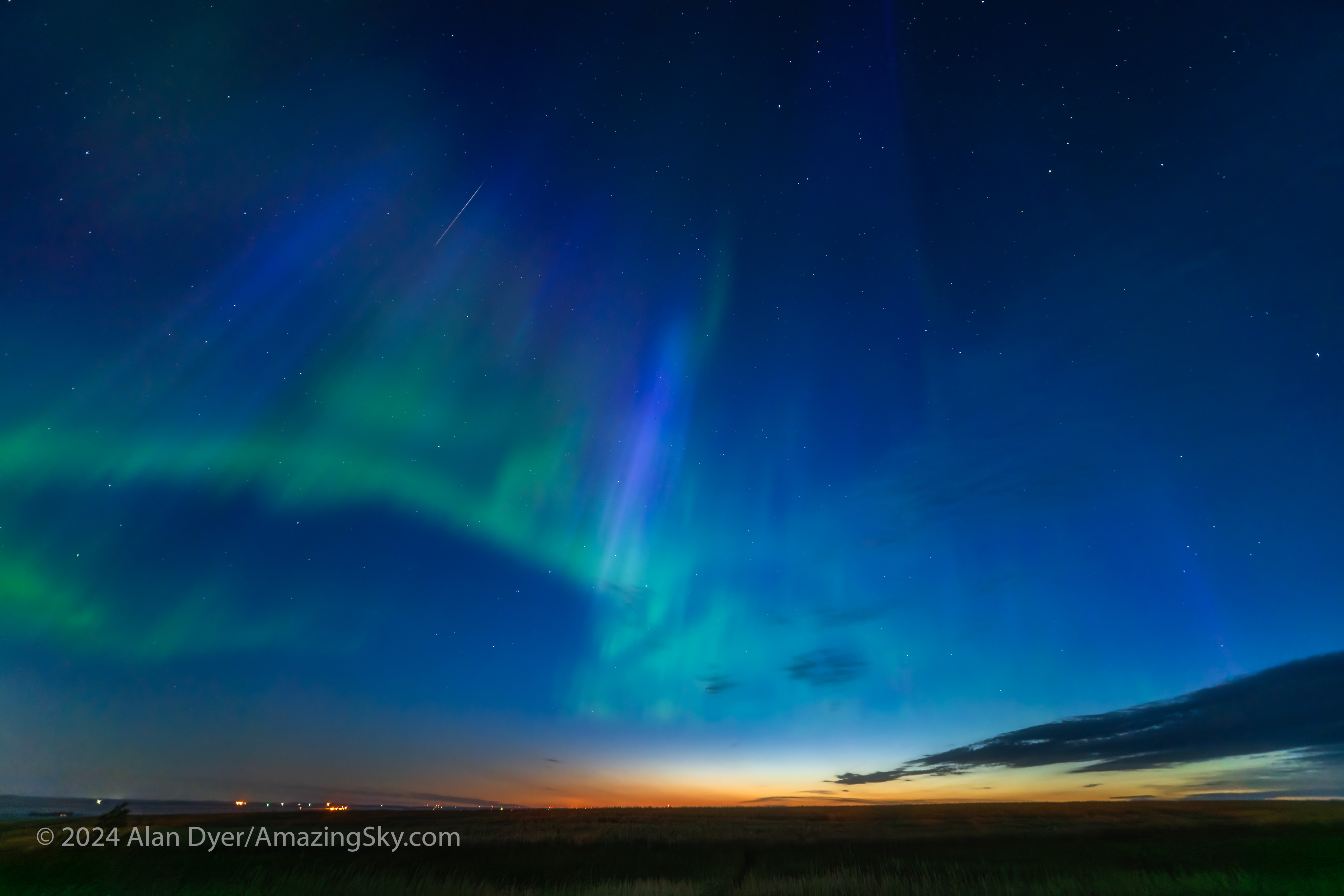
Even so, there’s a lot to be said for having a field that extends for 130° across the long dimension of a full-frame sensor. That’s more than enough to go from well below the horizon to past the zenith when the camera is in portrait orientation. Even in landscape orientation (as above) the lens covers nearly a 90° field across the short dimension, enough to go almost from horizon to zenith.
The f/2.8 speed is slower than the other lenses on test here, but is still faster than most ultra-wide lenses. Remarkably, it accepts common 77mm filters, the same as the Nikkor 20mm and Viltrox 16mm.
The 10mm is available as an auto-focus lens for Sony E and Nikon Z, and in manual focus versions for Canon RF and Panasonic L, oddly all at the same price.
Laowa 10mm Corner Aberrations

Corner aberrations are much worse than in the 20mm and 16mm lenses, showing a fair degree of tangential and sagittal astigmatism, elongating stars radially and adding wings to them, respectively. The aberrations are larger and reach deeper into the frame than in the Nikkor and Viltrox lenses.
There’s also some lateral chromatic aberration adding blue and purple fringes to the stars at the corners. Stopping down to f/4 improves, but doesn’t eliminate, the aberrations.
Laowa 10mm Vignetting

Edge and corner darkening were also worse than in the other lenses and required about a +50 setting to correct in Adobe Camera Raw, far less than the maximum of +100. So it’s still quite acceptable and correctable.
However, while stopping the lens down to f/4 improves vignetting, it does not eliminate it, still requiring a +40 correction. Vignetting will be a factor to deal with in all astrophotos with this ultra-wide lens.
Laowa 10mm Lens Flares

With such a wide lens, the Moon or other bright light sources are bound to be within the frame. The Laowa exhibits a prominent internal lens flare when bright objects are in the corners, but just in the corners. Objects near the edge but centered are fine.

Stopping down the lens adds diffraction spikes (or “sunstars”) to bright lights, but doesn’t eliminate the circular internal reflection. None of this is a serious issue for most images, but it is something to be mindful of when framing nightscapes.

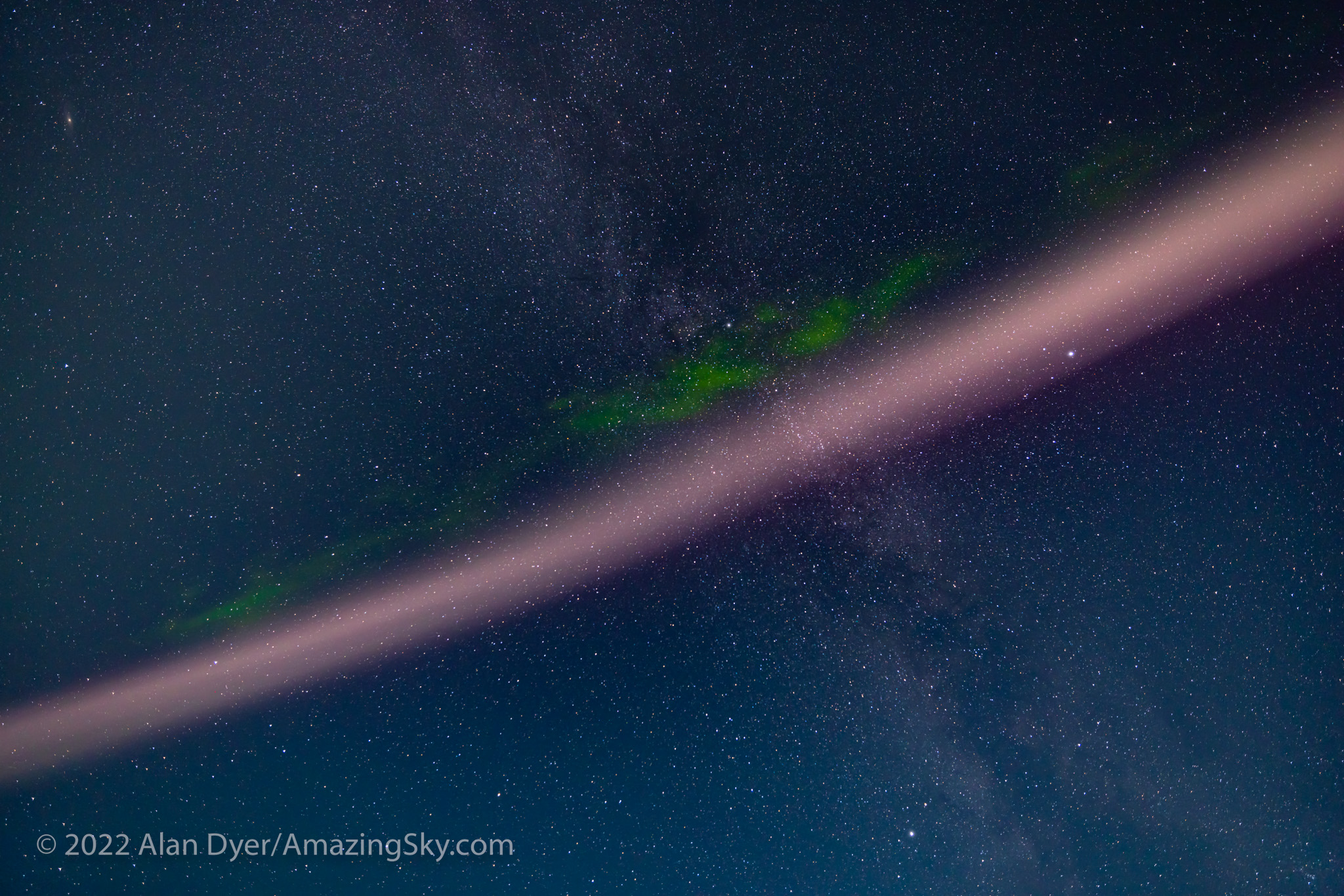
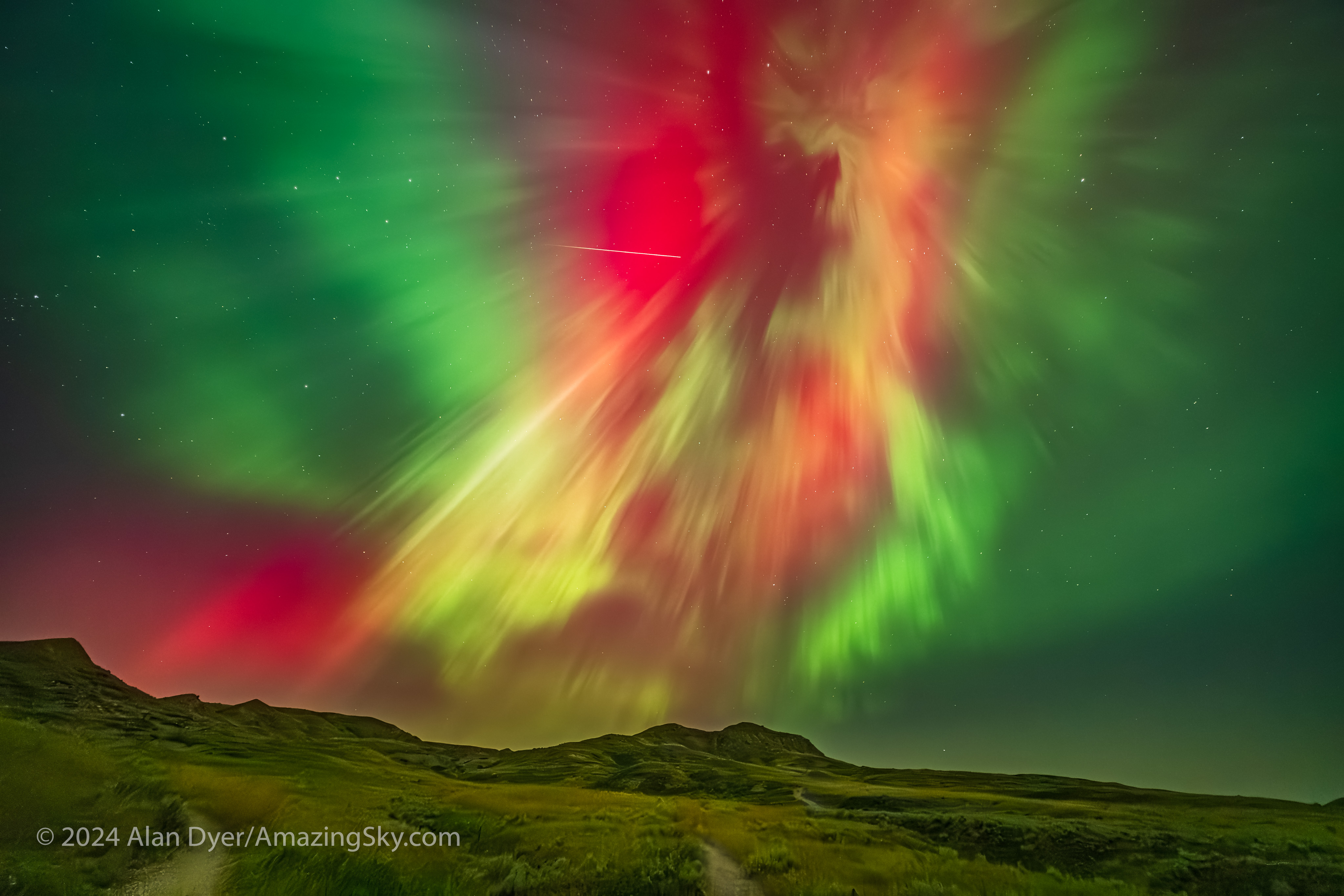
In Milky Way and starfield images, constellations in the corners can distort into unnatural shapes that look odd, as I show above. While the lens can take in a great swath of sky, its distortion and corner aberrations make it less than desirable for tracked Milky shots.

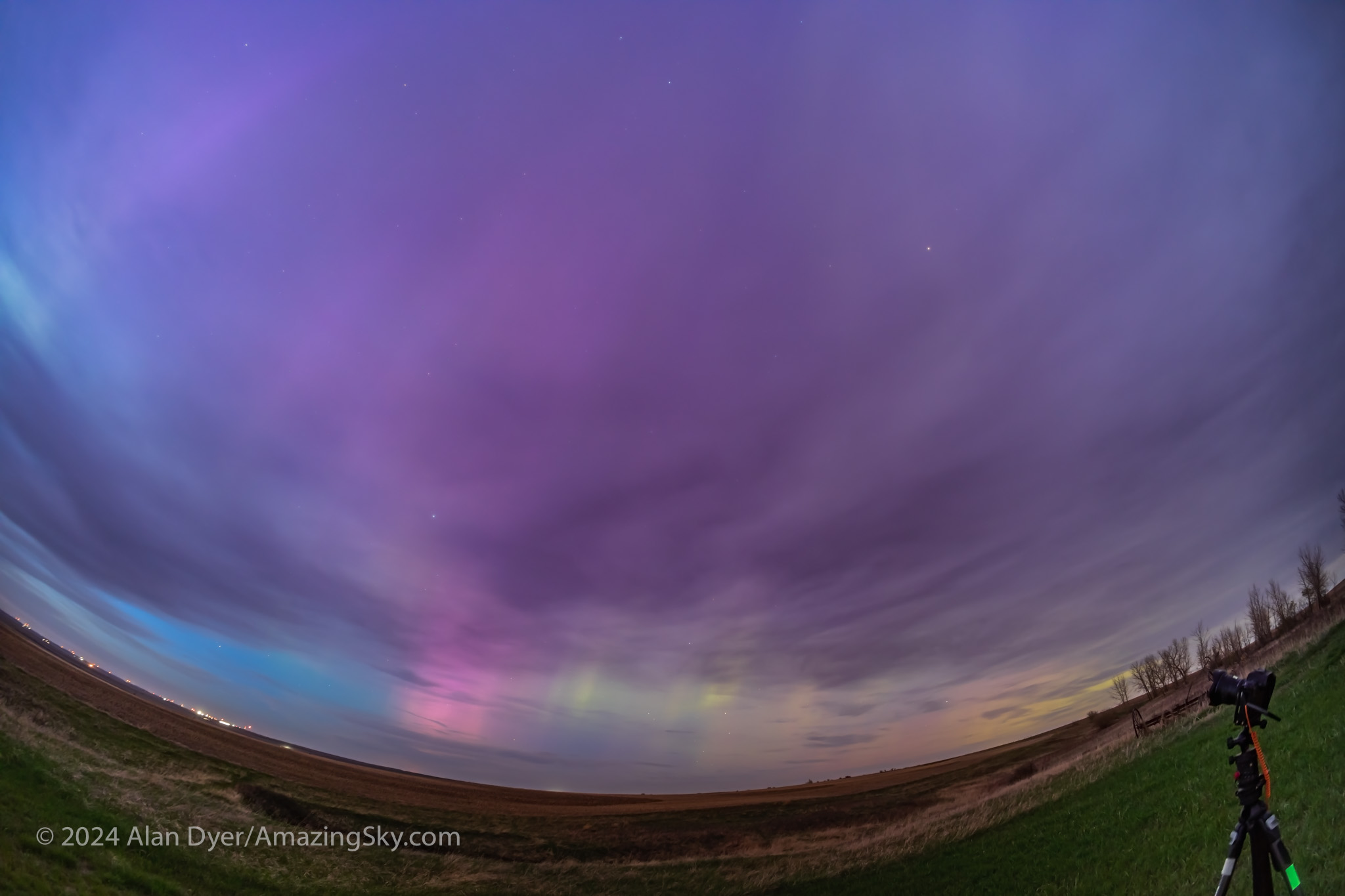
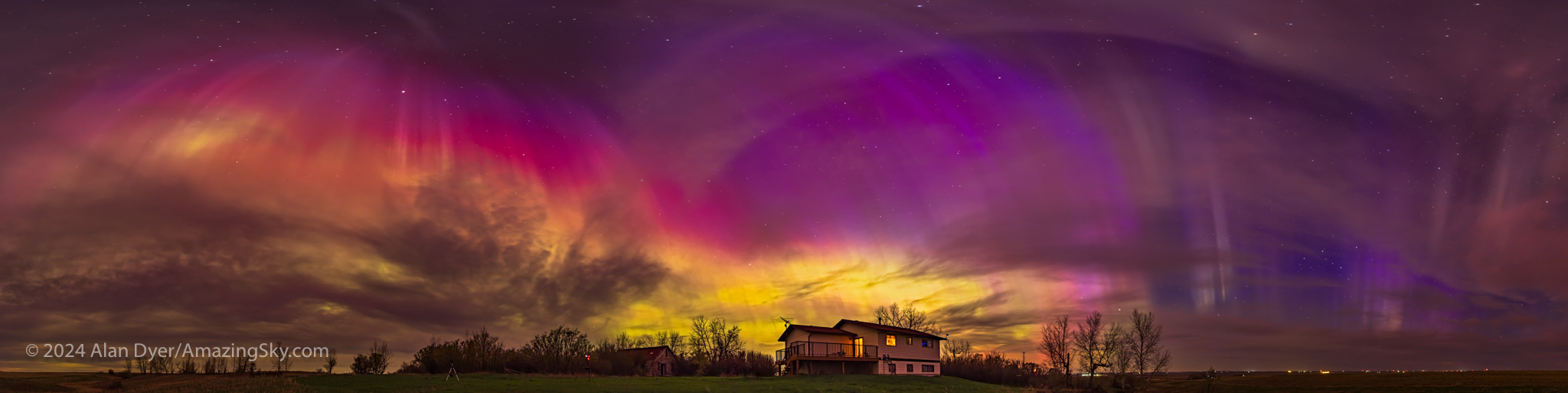
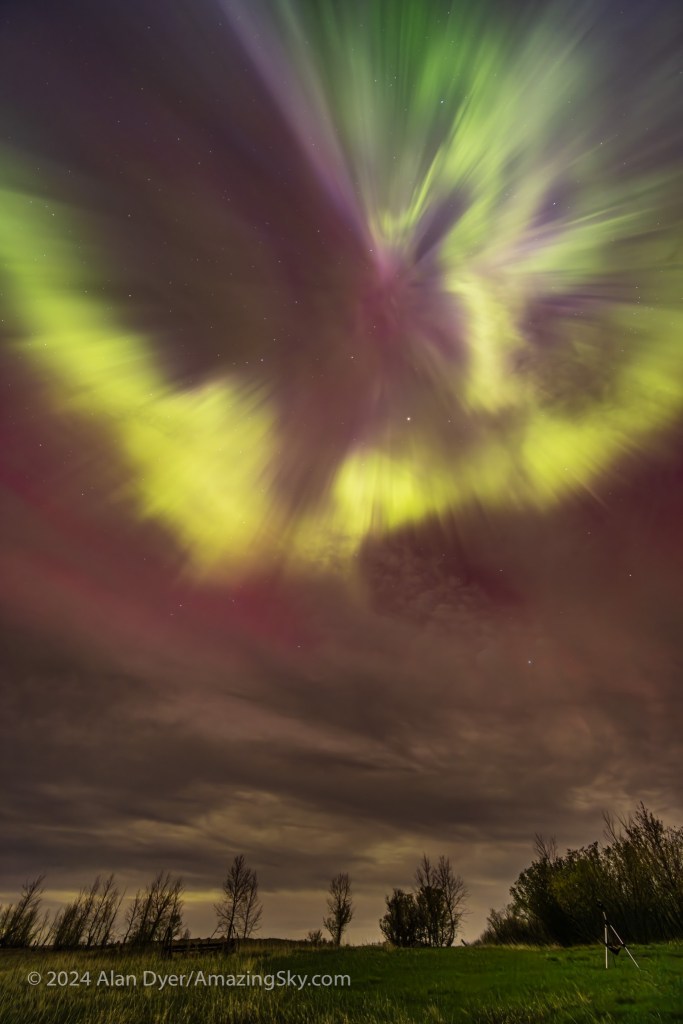
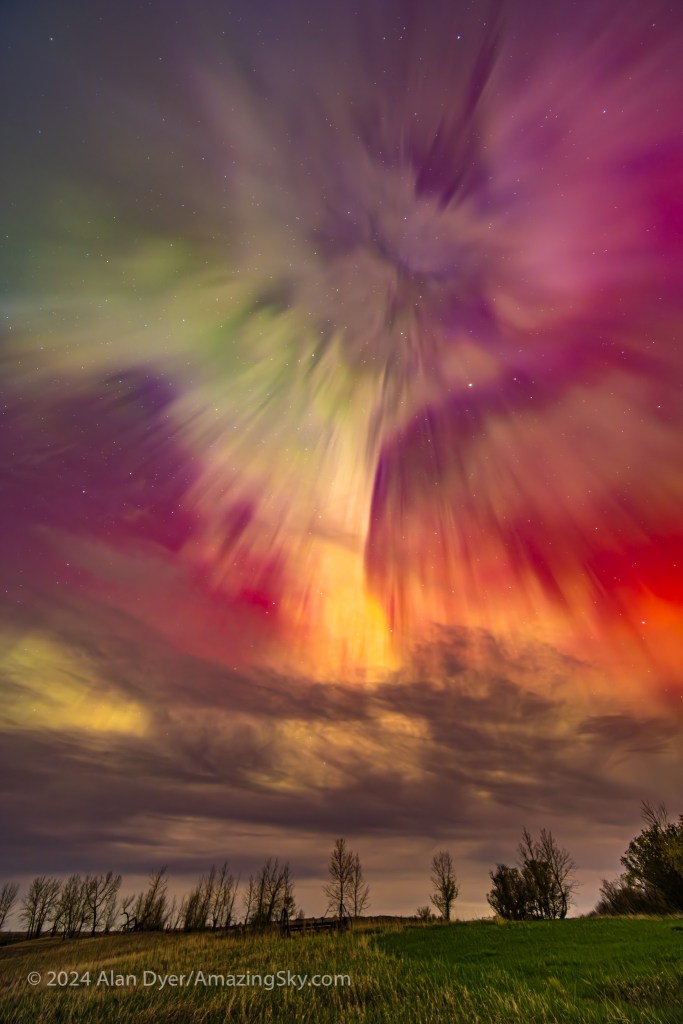
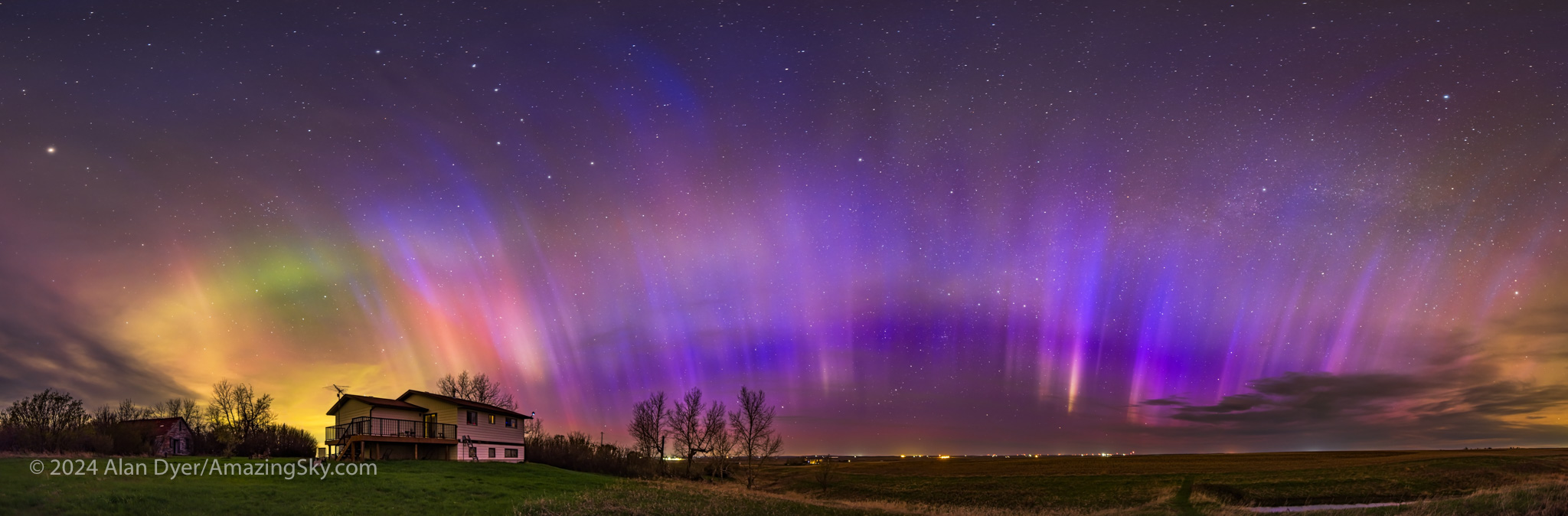
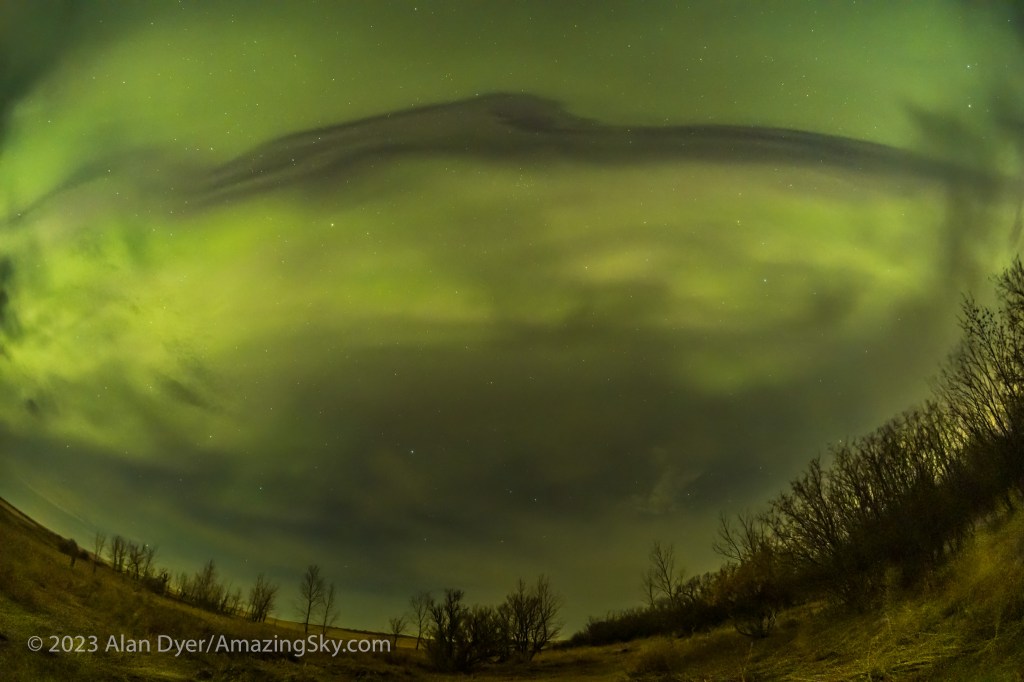
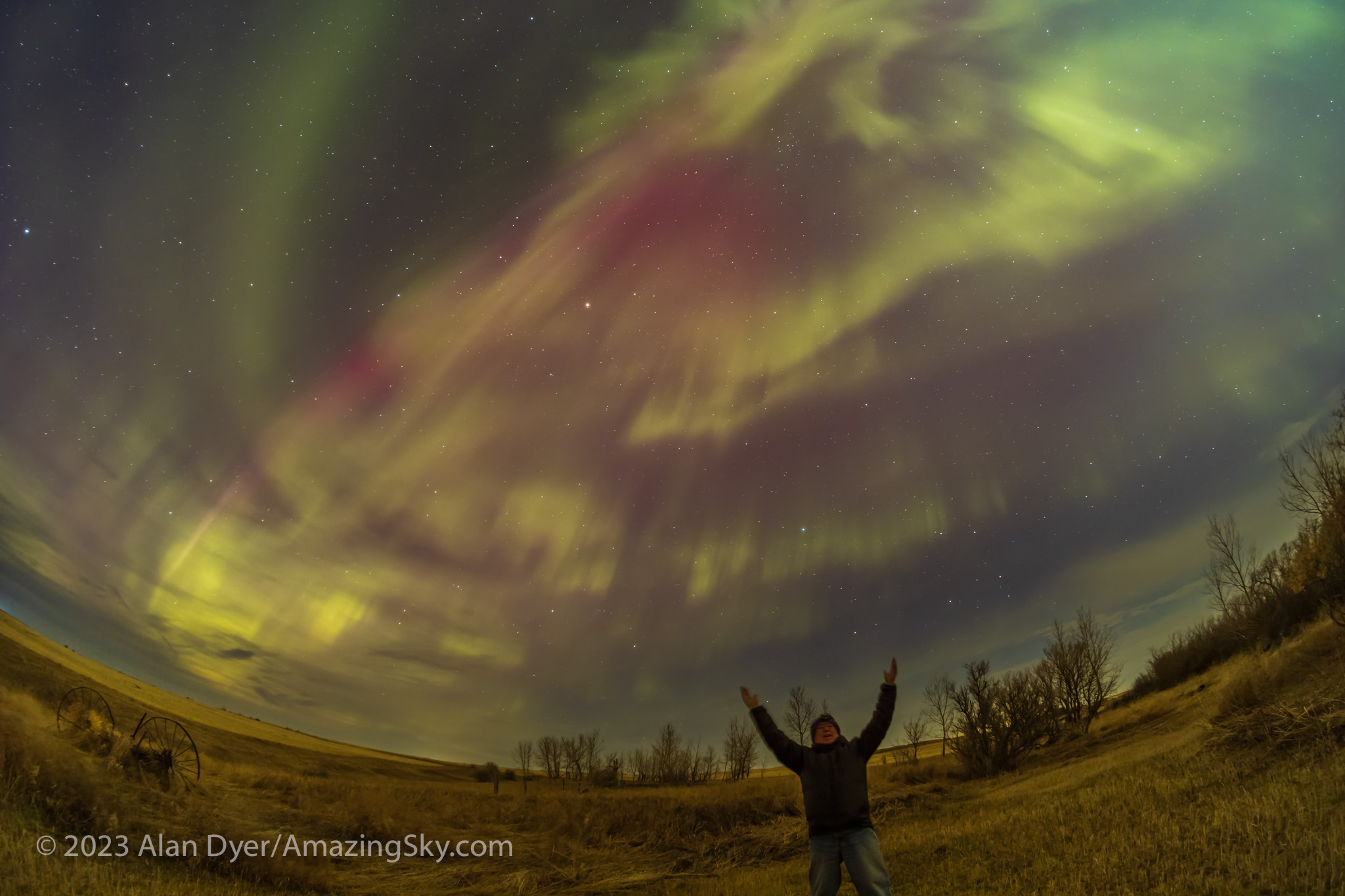
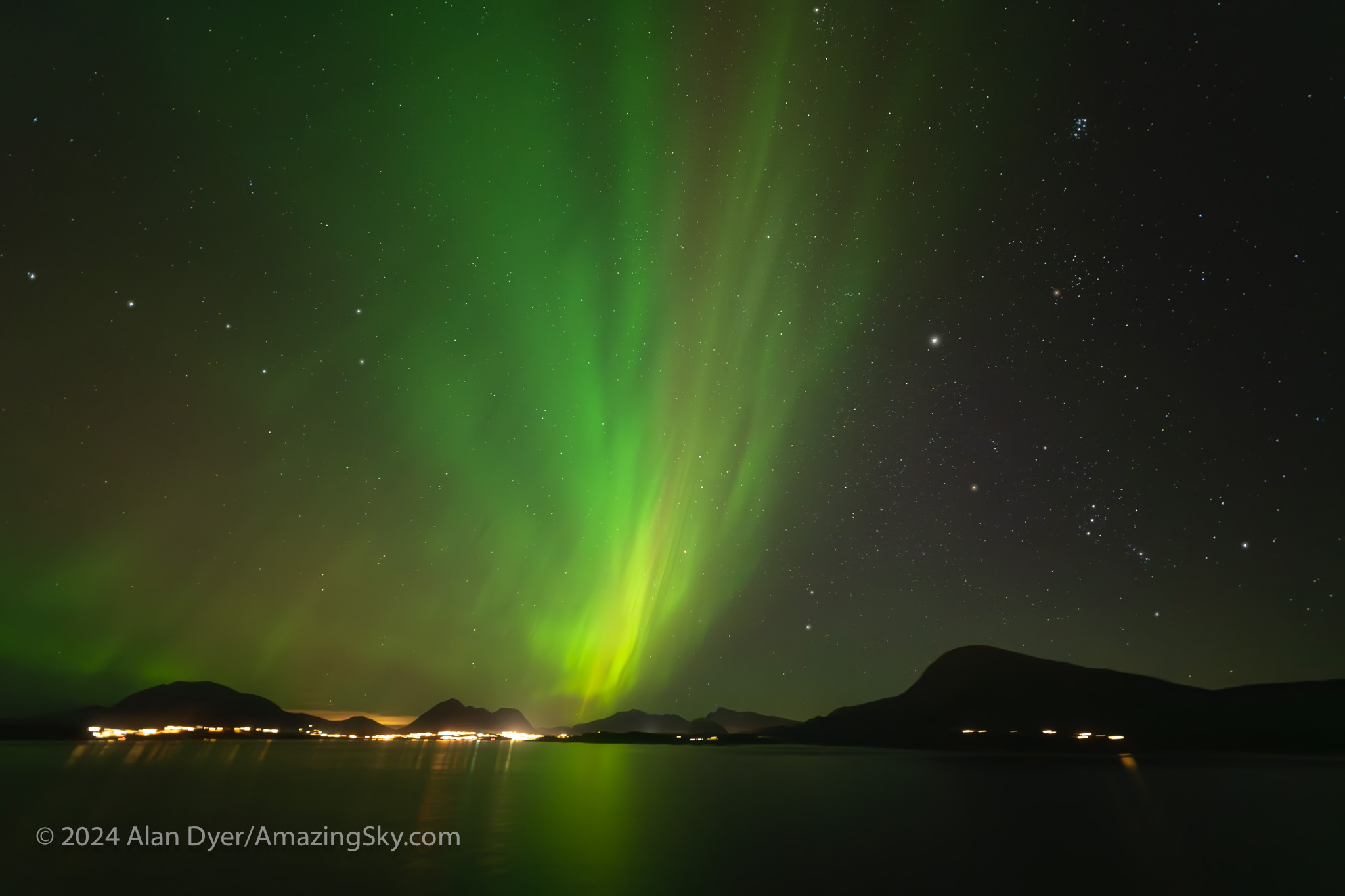
Where the Laowa 10mm really proves its worth is for auroras, as above, which can require as wide a field as you can muster. Note the flat horizon.
For ultra-wide nightscapes in a single image (not a panorama) with a natural looking (not curved) horizon, and for meteor showers, the Laowa is just the ticket.
BONUS TEST: The TTArtisan 7.5mm f/2 Fish-Eye ($140)


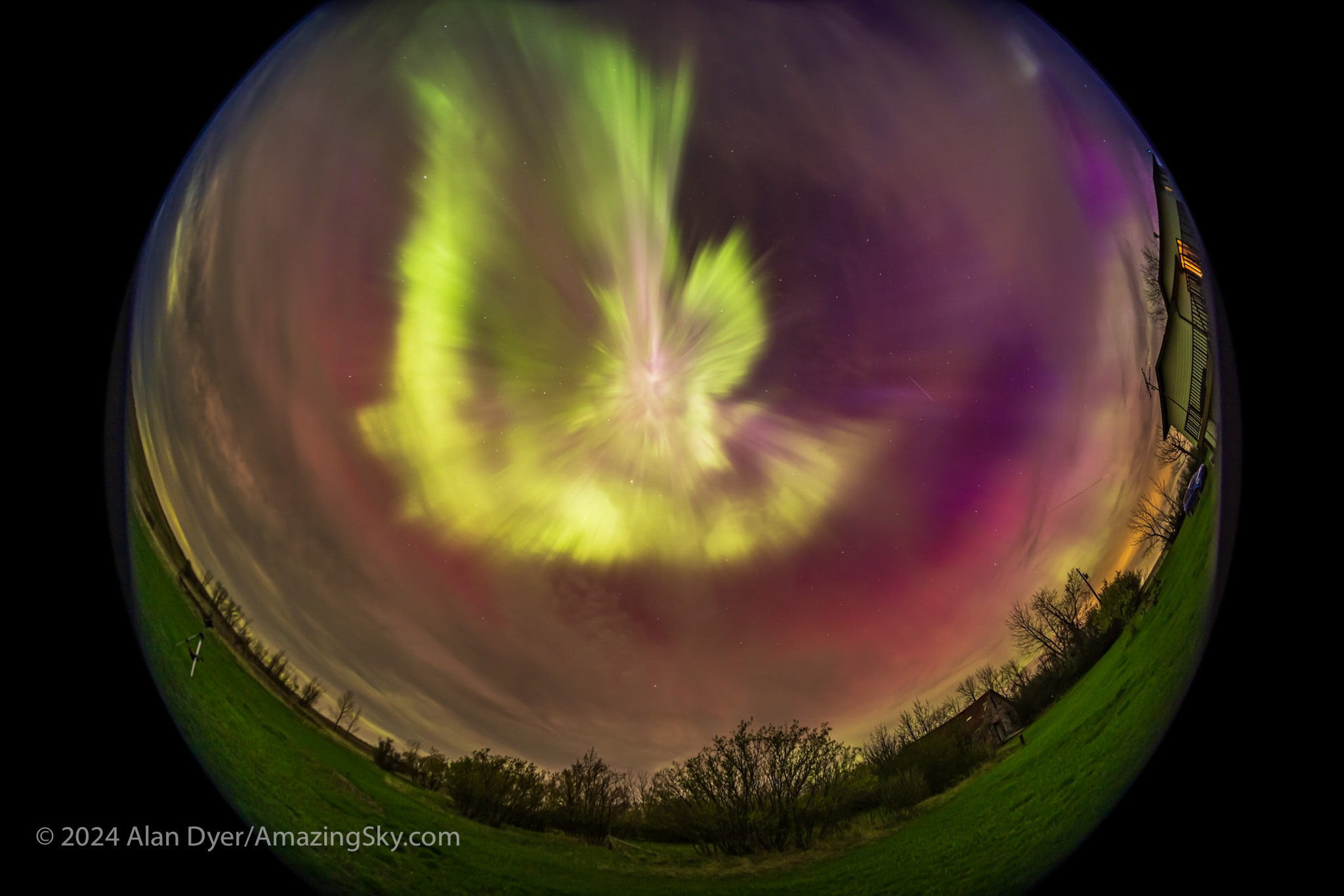
Technically, this lens is designed to be used on cropped-frame (or APS-sensor) cameras where it fills the frame with a curving horizon. But it works on a full-frame camera where it projects a circular image slightly larger in diameter than the short dimension of the frame, so not a complete circle as with a true circular fish-eye like the old Sigma 8mm f/3.5.
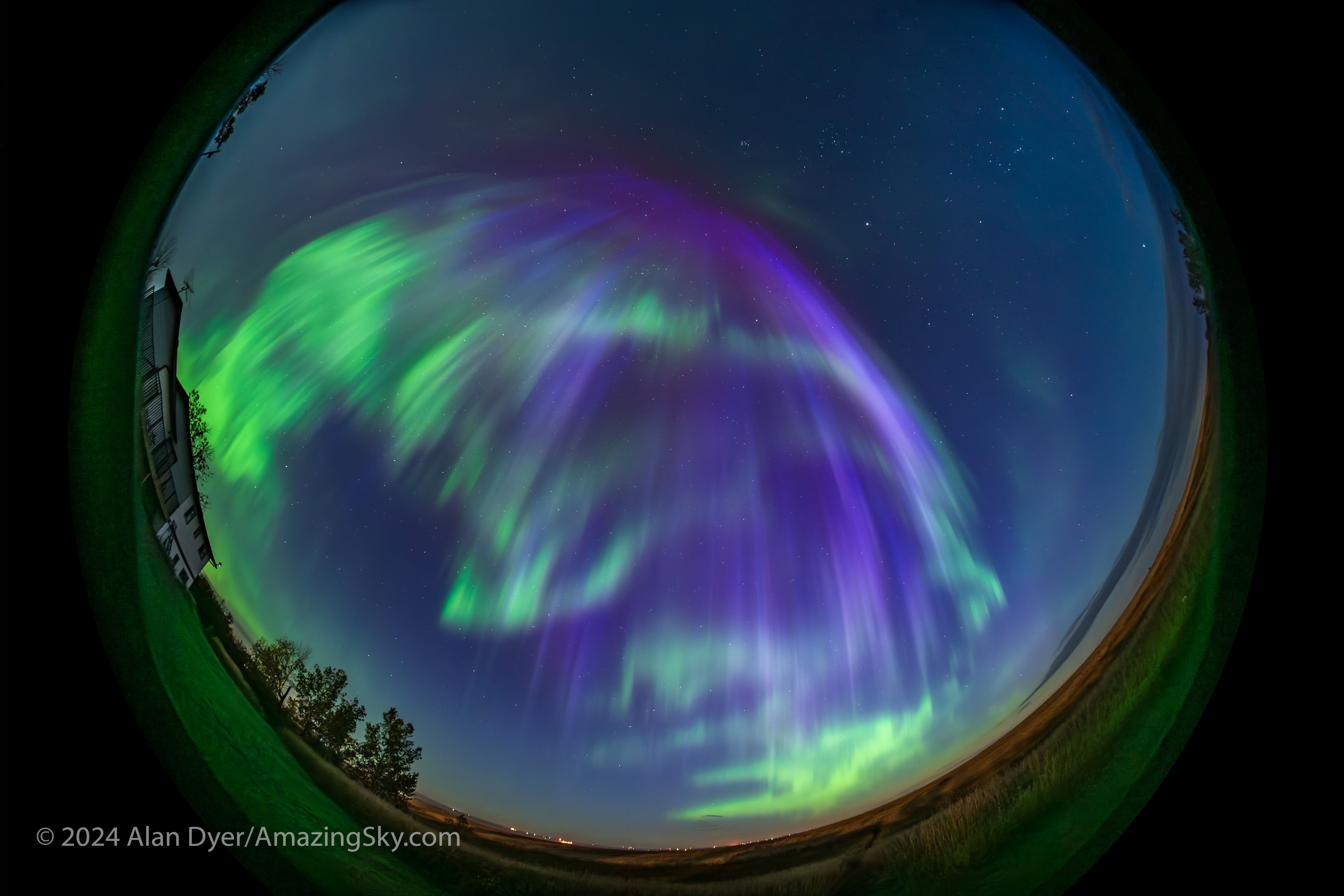

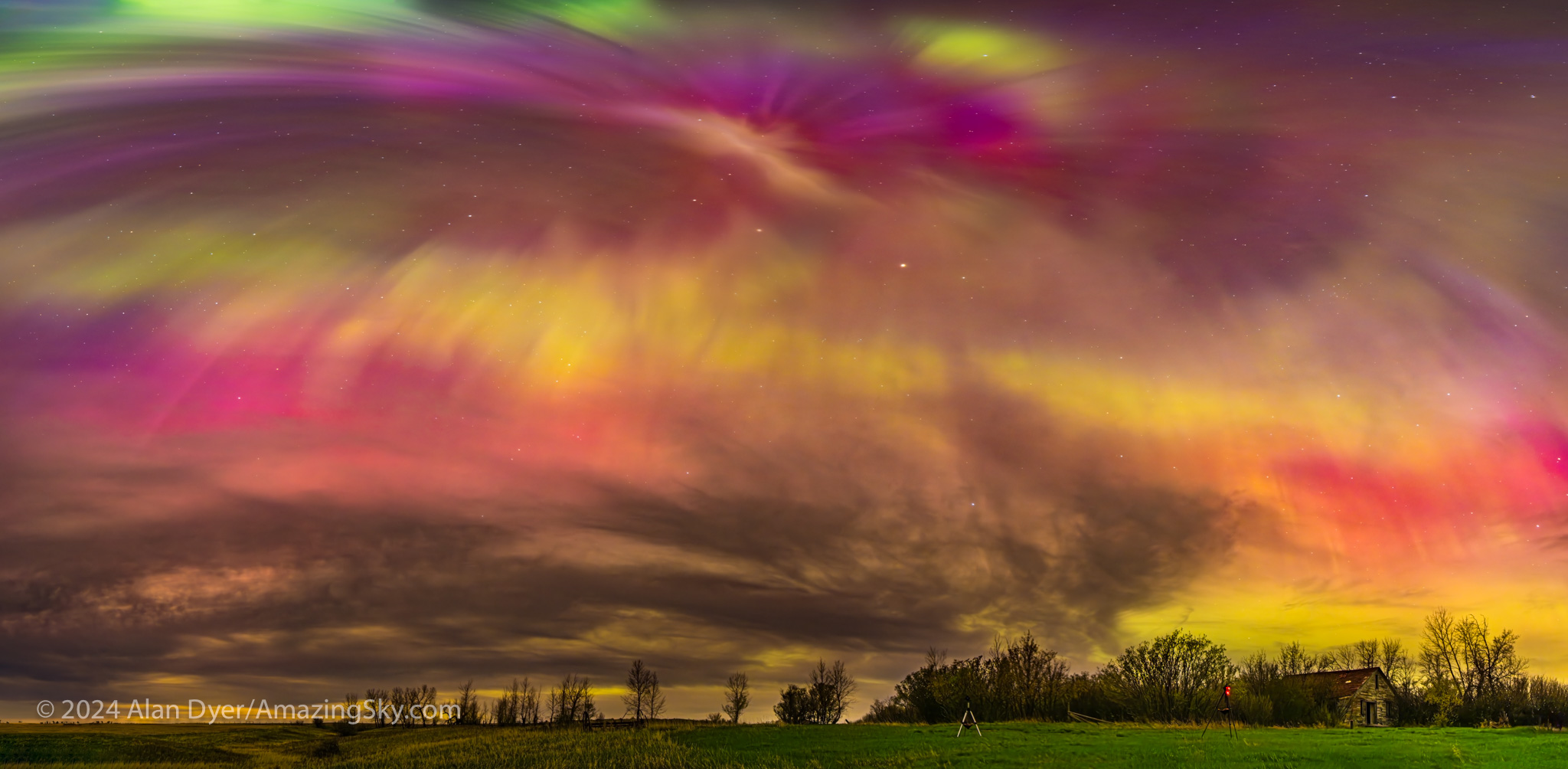
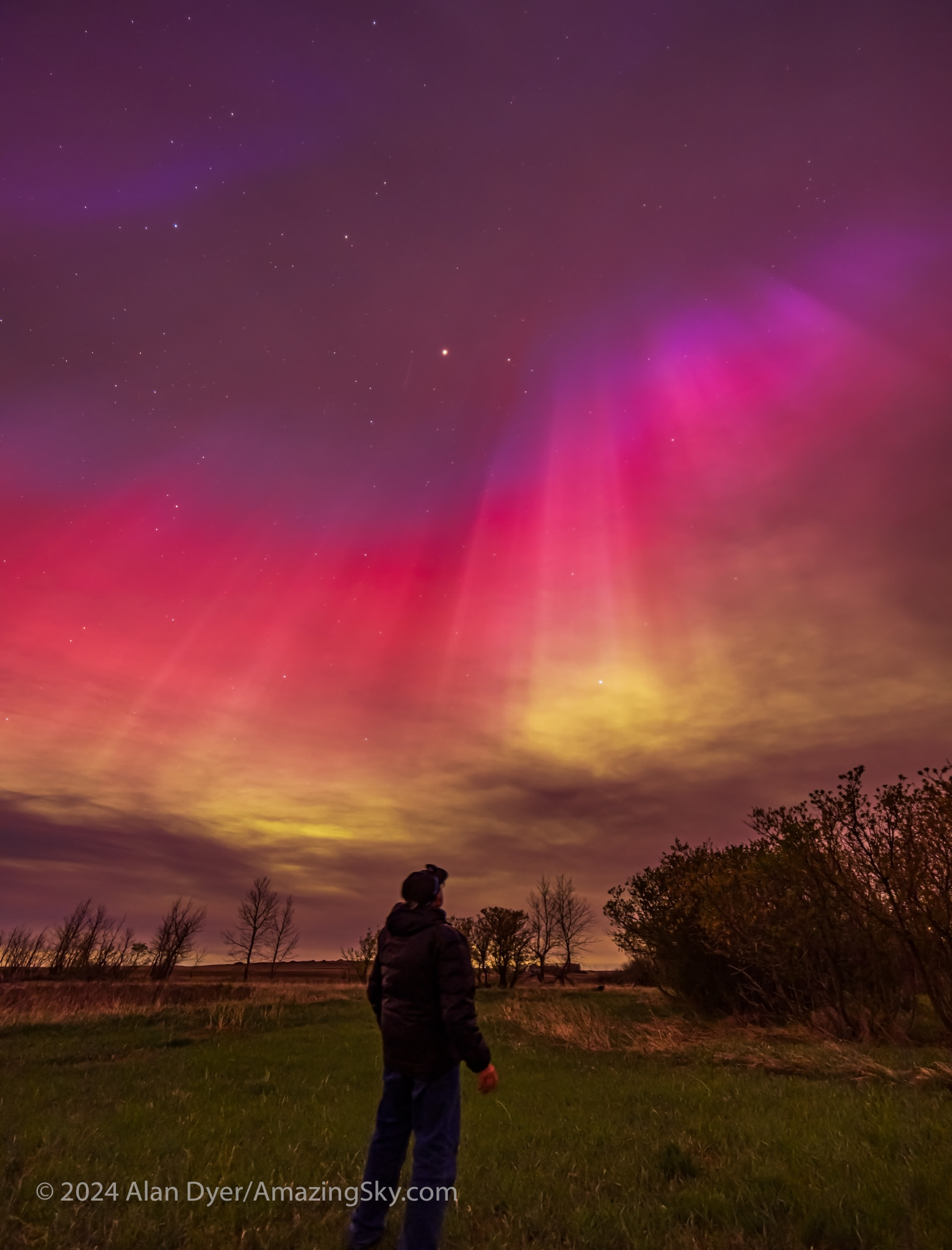
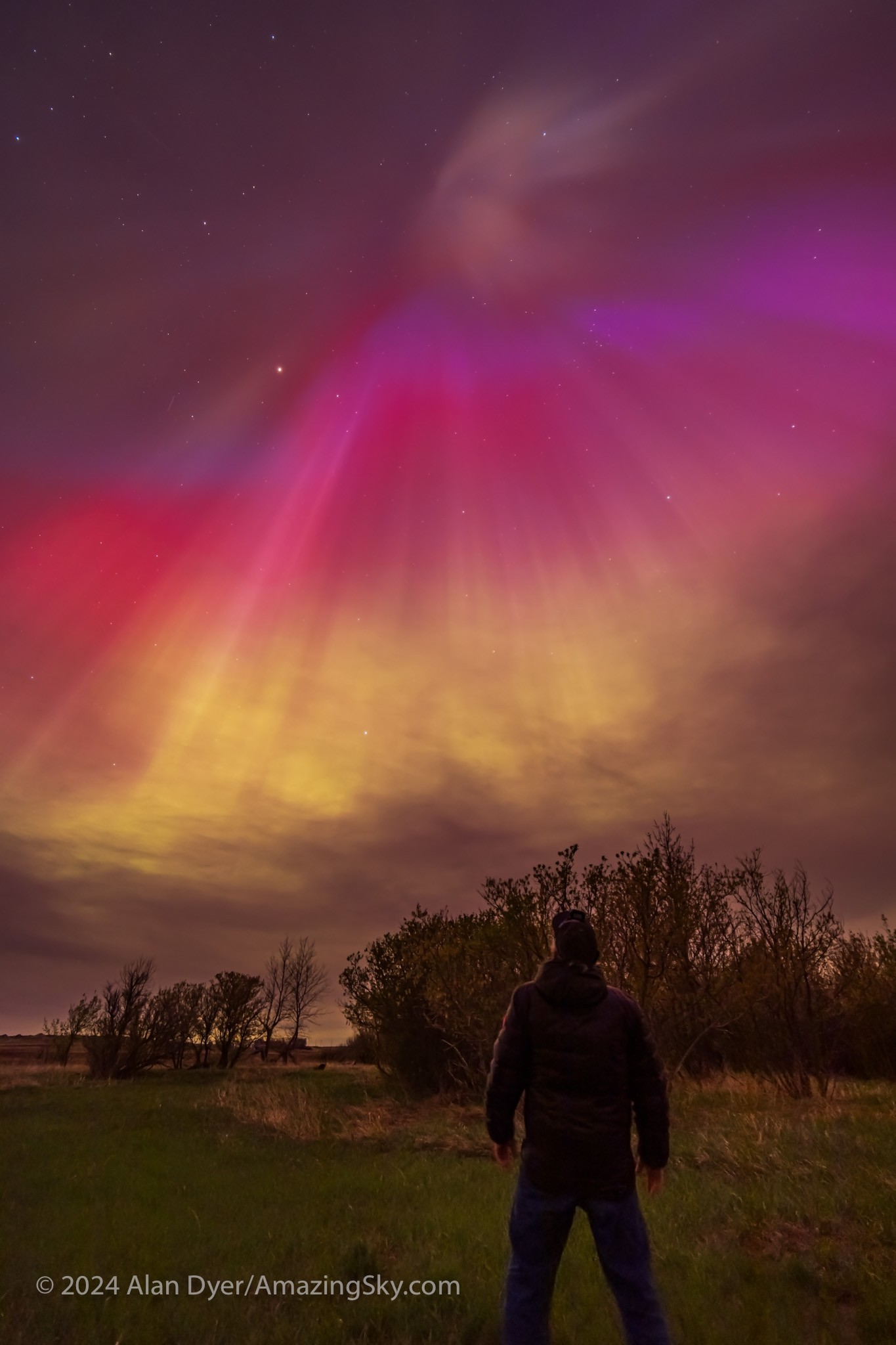
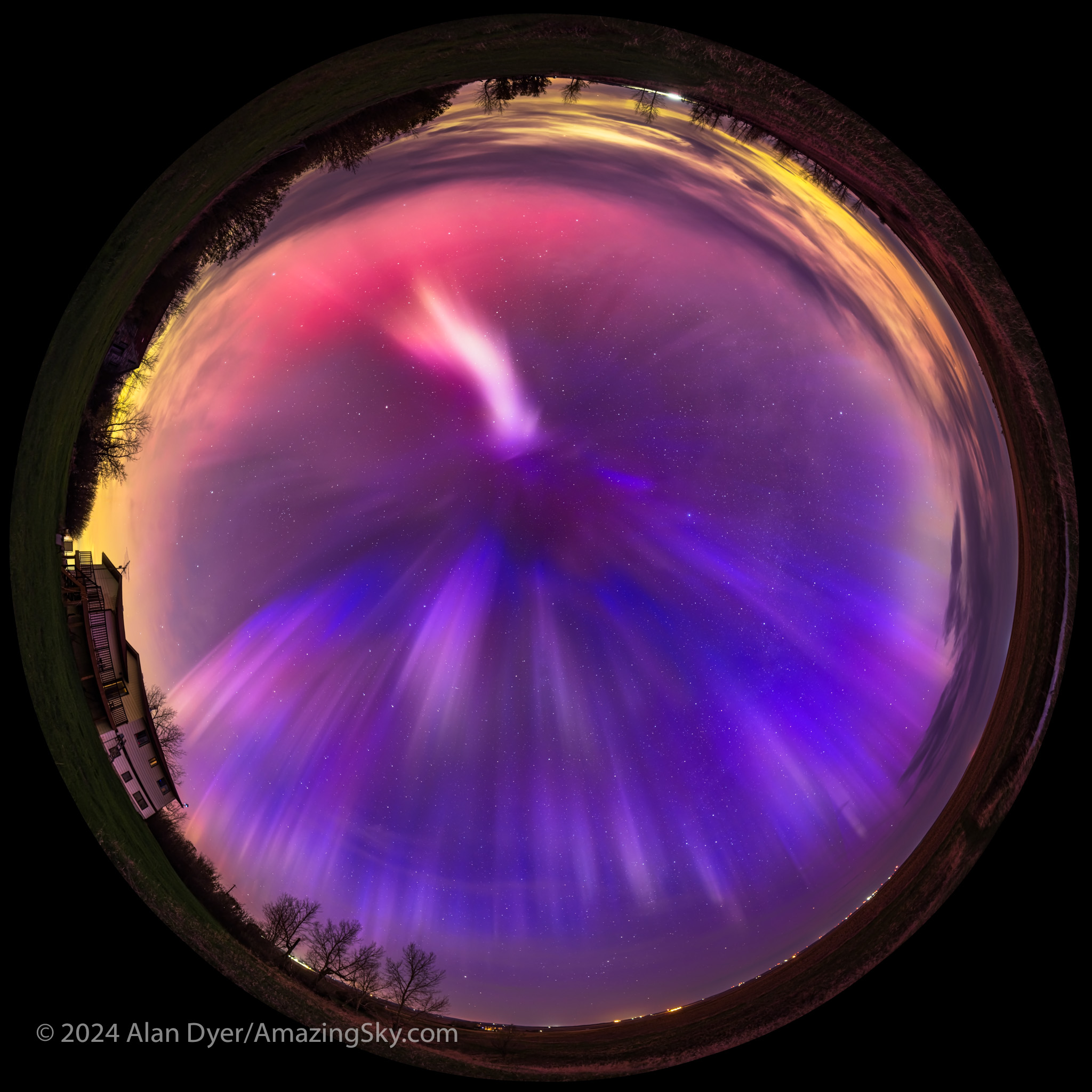
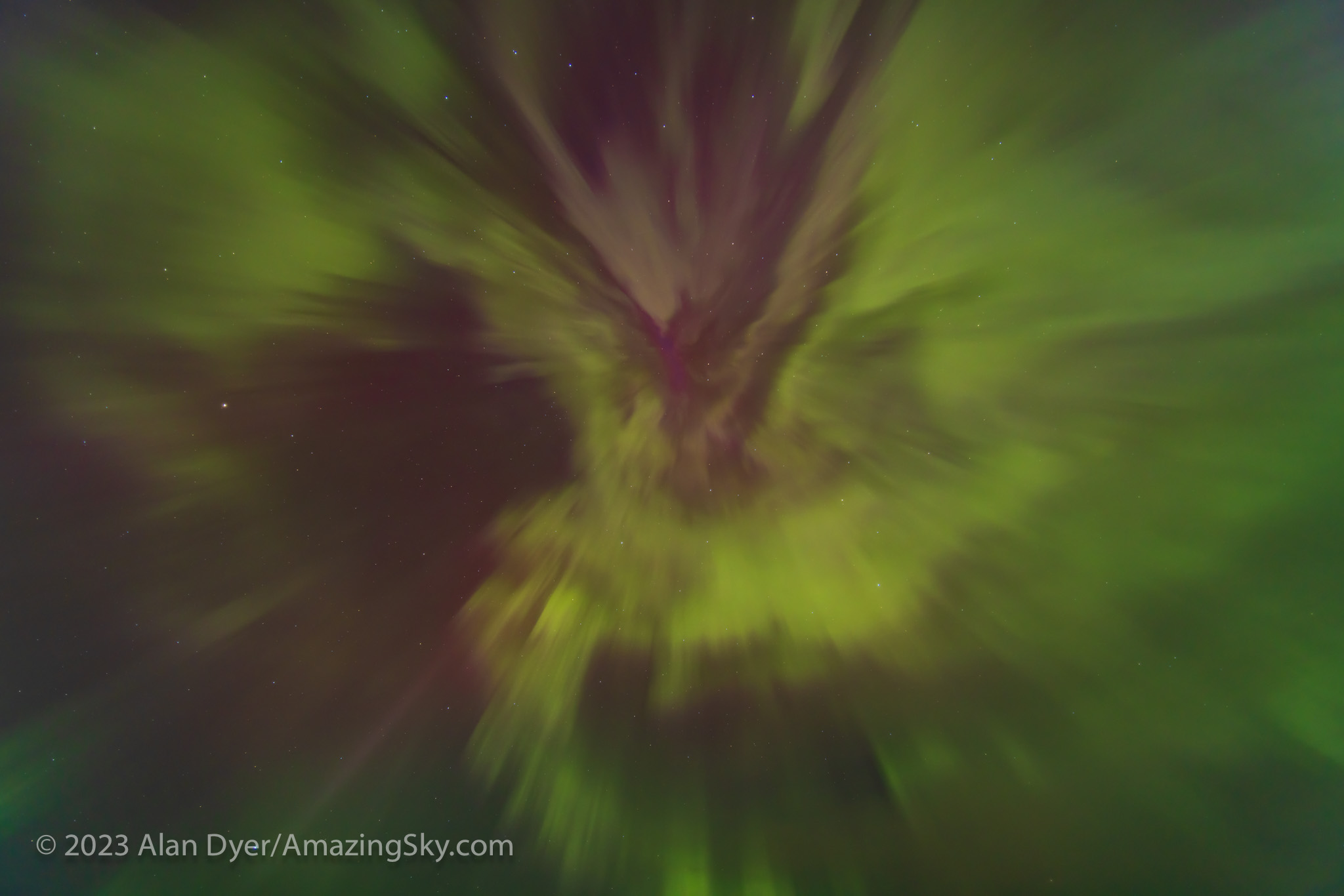
For all-sky auroras, this is ideal, where the TTArtisan’s fast f/2 speed is unprecedented in a fish-eye lens. That makes rapid-cadence time-lapses possible, as well as real-time movies. An example is here on my YouTube channel.
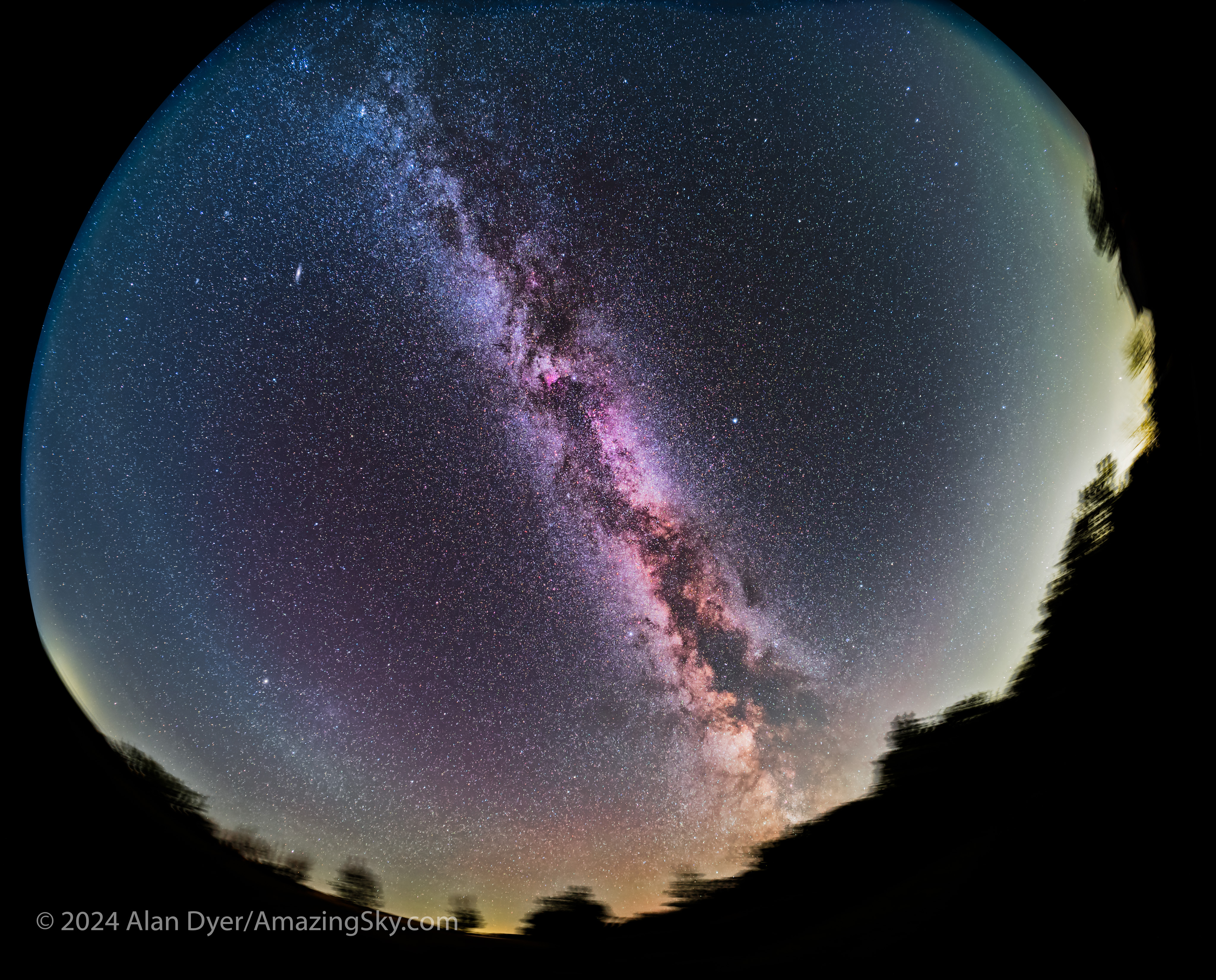

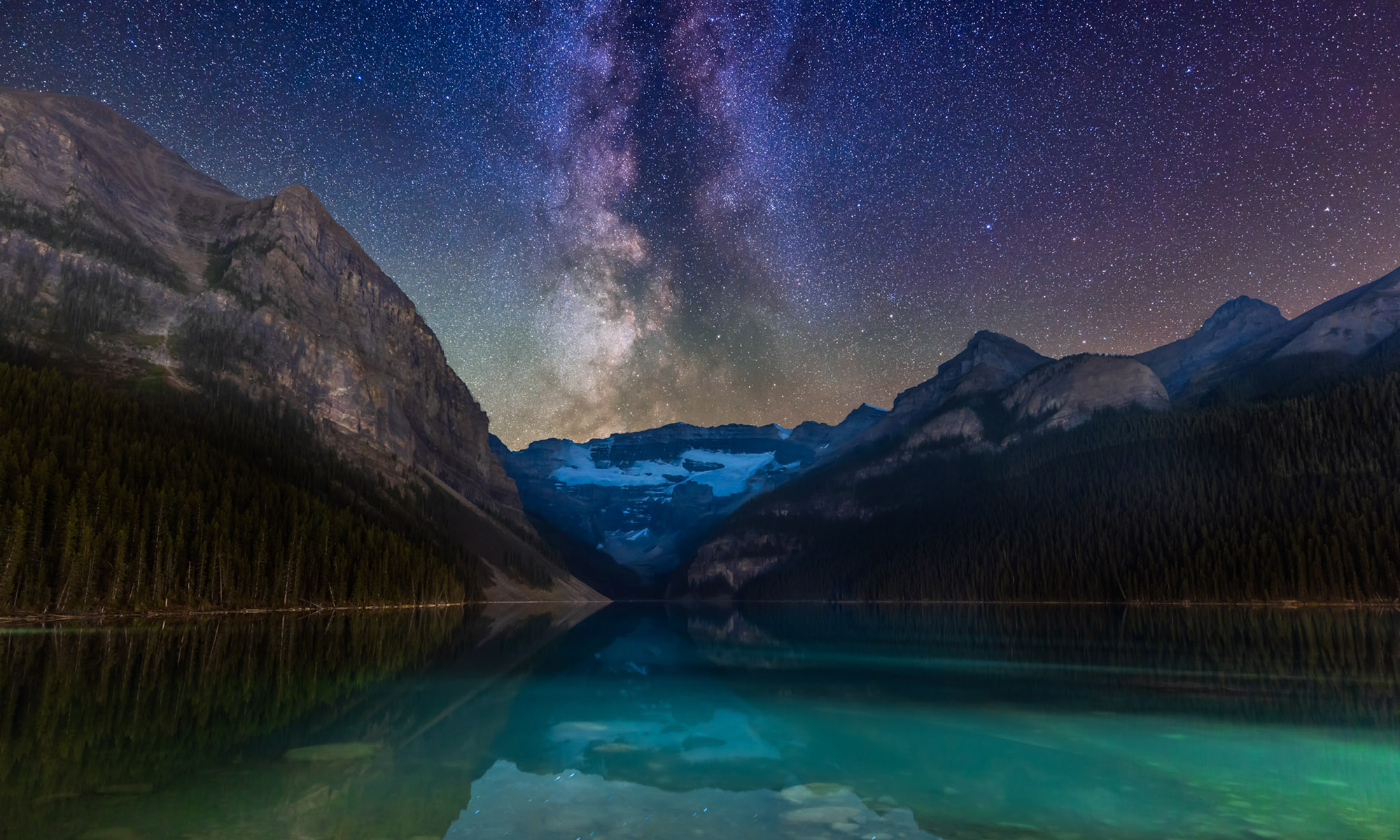
Or you can just capture the Milky Way from horizon to horizon, as above. For the latter, having stars sharp across the circular field is still desirable.
I have this lens for Canon RF as well, but that unit shows a noticeable softening of the left edge with defocused stars, likely from lens de-centering. I was told by TTArtisan that was a normal unit-to-unit variation and not a defect warranting replacement. Annoying!
I hesitated to buy one for my Nikon. But this is such a unique lens, and so affordable, I took the chance. The Nikon Z-mount version proved much better.
TTArtisan 7.5mm Edge Performance
There is no corner performance or vignetting to test here.
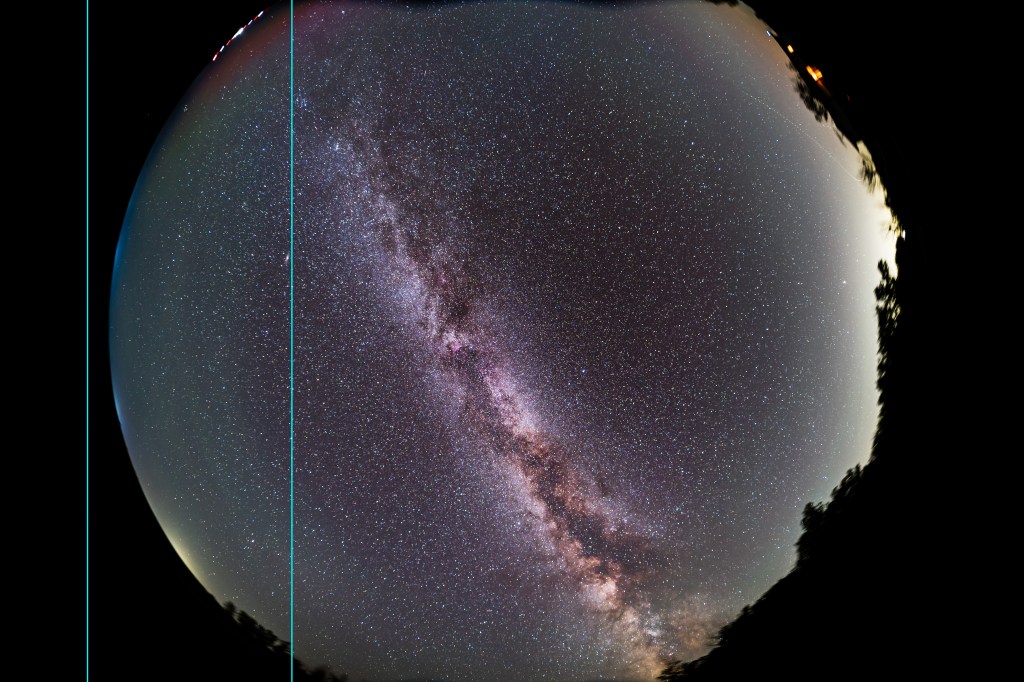

Instead, I’m inspecting the same side on the Nikon Z version that caused a problem on my Canon version.

The Nikon version looks fine, with stars sharp along the edge even at f/2, showing just a low level of astigmatism, to be expected in such a fast, wide lens. Stars tighten up a bit more at f/2.8. Most critically, the field was flat and in focus across the frame. There was no evidence of lens de-centering or optical defects.
The edges do show some discolouration and a soft edge to the image area. I also see two odd dark protrusions at the top of the frame. Looking through the lens, there’s nothing obvious intruding into the light path.
Keep in mind when used on a full-frame camera you’re seeing more of the projected image than was intended in the design.

The TTArtisan 7.5mm is a specialty lens to be sure. But at its low price it isn’t a big outlay to include in your lens arsenal, for unique all-sky images, of auroras, satellite passages, sky colours, and the Milky Way. And it is terrific for time-lapses and movies of the whole sky. It is a no-frills manual lens available for most camera mounts.
Recommendations
The Viltrox 16mm, Laowa 10mm and TTArtisan 7.5mm are all available for Sony E-mount. The Laowa and TTArtisan are available for Canon RF, but the Viltrox 16mm is not, as it is an auto-focus, full-frame lens, the class of lenses Canon has yet to allow on their RF mounts, much to the disdain of all concerned but Canon management it seems.
Viltrox 16mm — For nightscape use, the Viltrox 16mm might be the single best choice, as being the most versatile and affordable of the trio of wide-angle lenses. Its focal length is a good balance between the usual 14mm and what I think is a more useful 20mm.
Nikkor 20mm — I like the Nikkor 20mm for its lower level of vignetting, slightly tighter framing, and very sharp stars. I think a 20mm is an ideal focal length for many nightscapes and Milky Way scenes. But it is the most expensive lens tested here.
Laowa 10mm — While nearly as costly as the Nikkor 20mm, the Laowa 10mm is much more specialized and, I think, not as useful as the others for general nightscape and Milky Way shooting. But it is superb for auroras, if you are in a place where they are common, as they are here in Alberta. Otherwise, I think you’d find the 10mm a costly lens that might not see a lot of use for astrophotography. Its real forté is architecture and real-estate interiors.
TTArtisan 7.5mm — Ditto on its limited use. But it is so affordable it’s easy to justify even if it doesn’t get a lot of use. The astro images, time-lapses, and movies it can produce are unique and impossible to create any other way. Be sure to buy it from a source where you can return it easily if you find your sample defective.
Reason To Go Mirrorless
The quality of these and other premium lenses from Nikon, and also from Canon, Sony and third-party makers like Sigma and Viltrox, is one of the major benefits of migrating to mirrorless cameras. DSLRs, and the lenses made for them, are now effectively dead as new gear choices.
Yes, mirrorless cameras can be better in many aspects of their operation than DSLRs. But it is the lenses made for mirrorless that show the greatest improvement over their DSLR equivalents, many of which date back to the forgiving film days.
— Alan, December 6, 2024 (amazingsky.com)