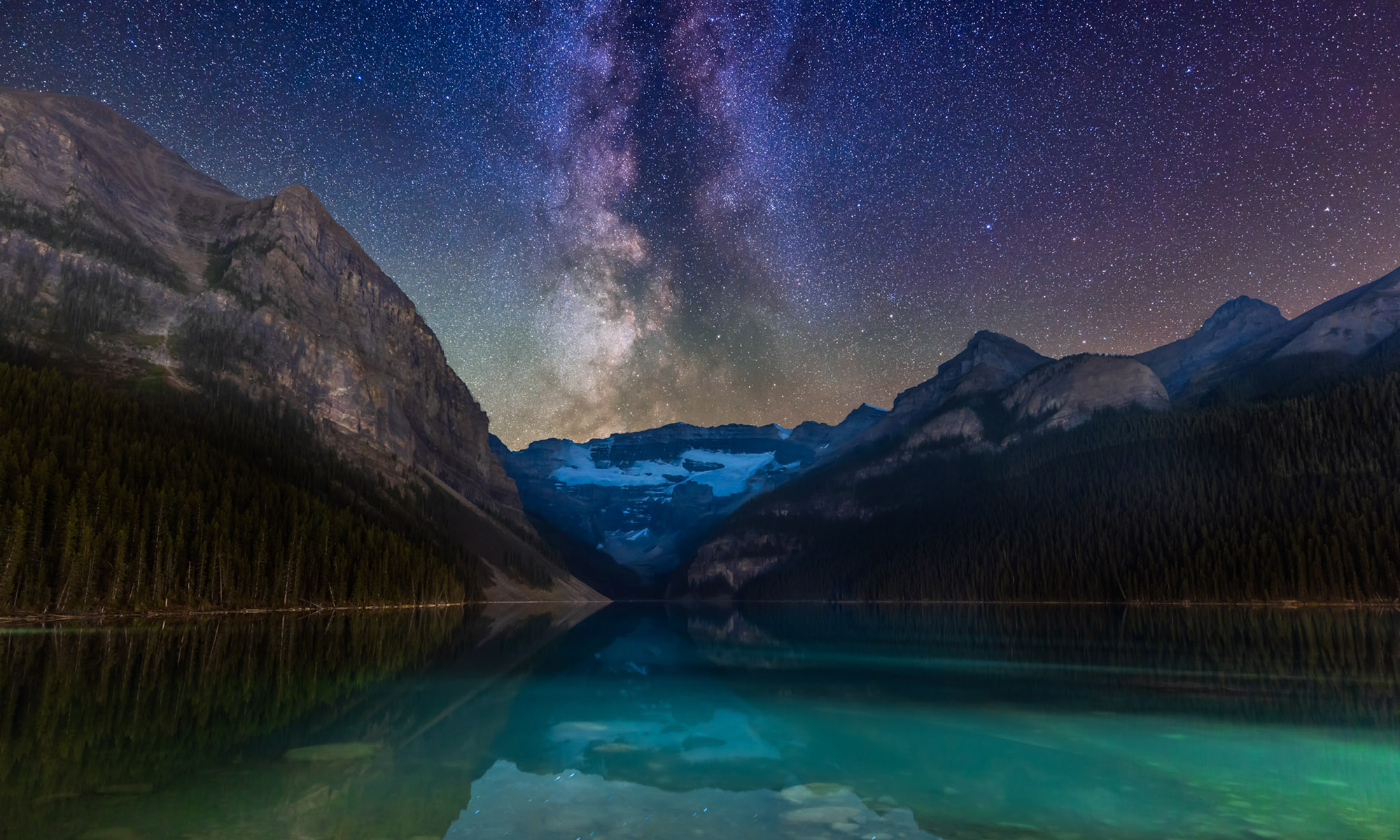
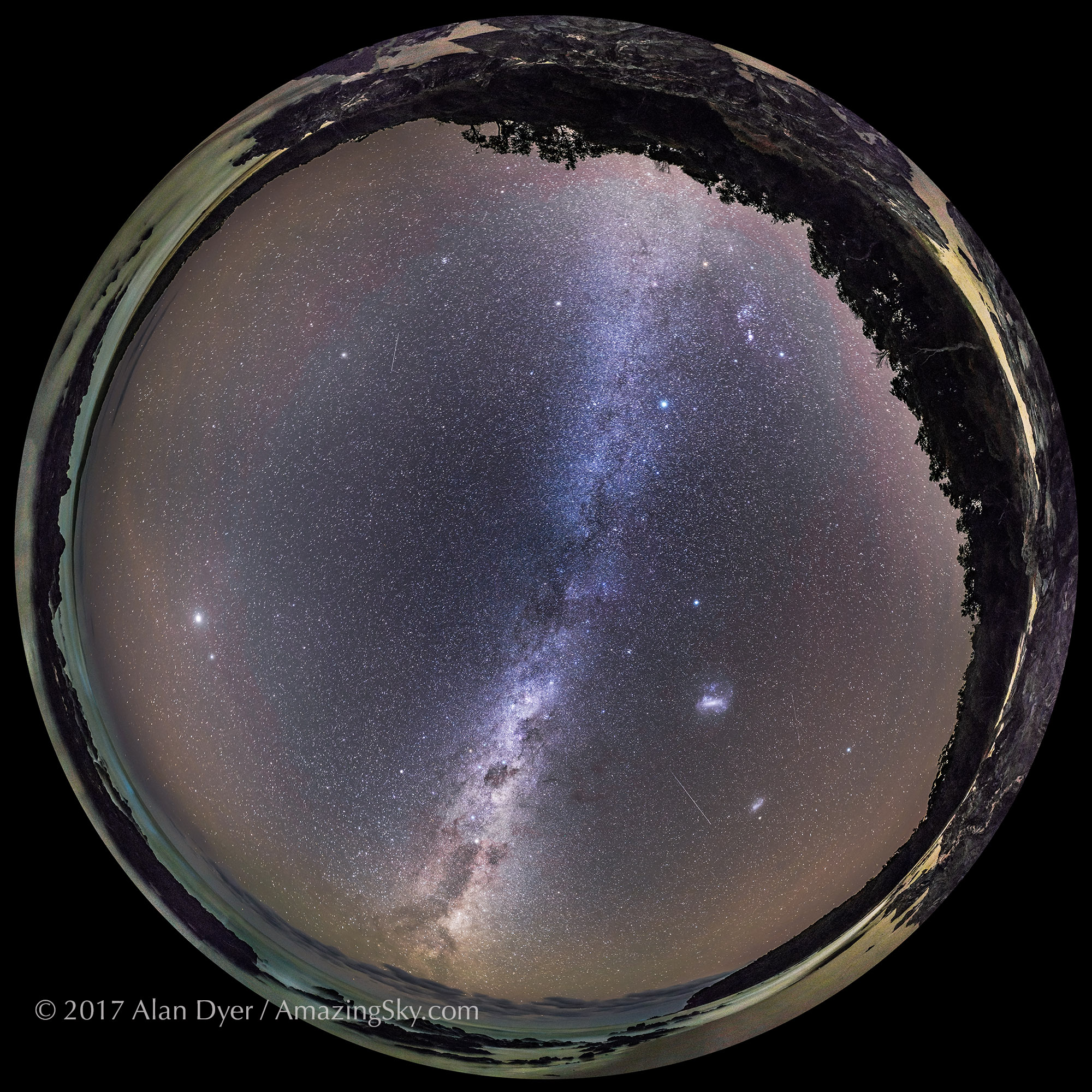
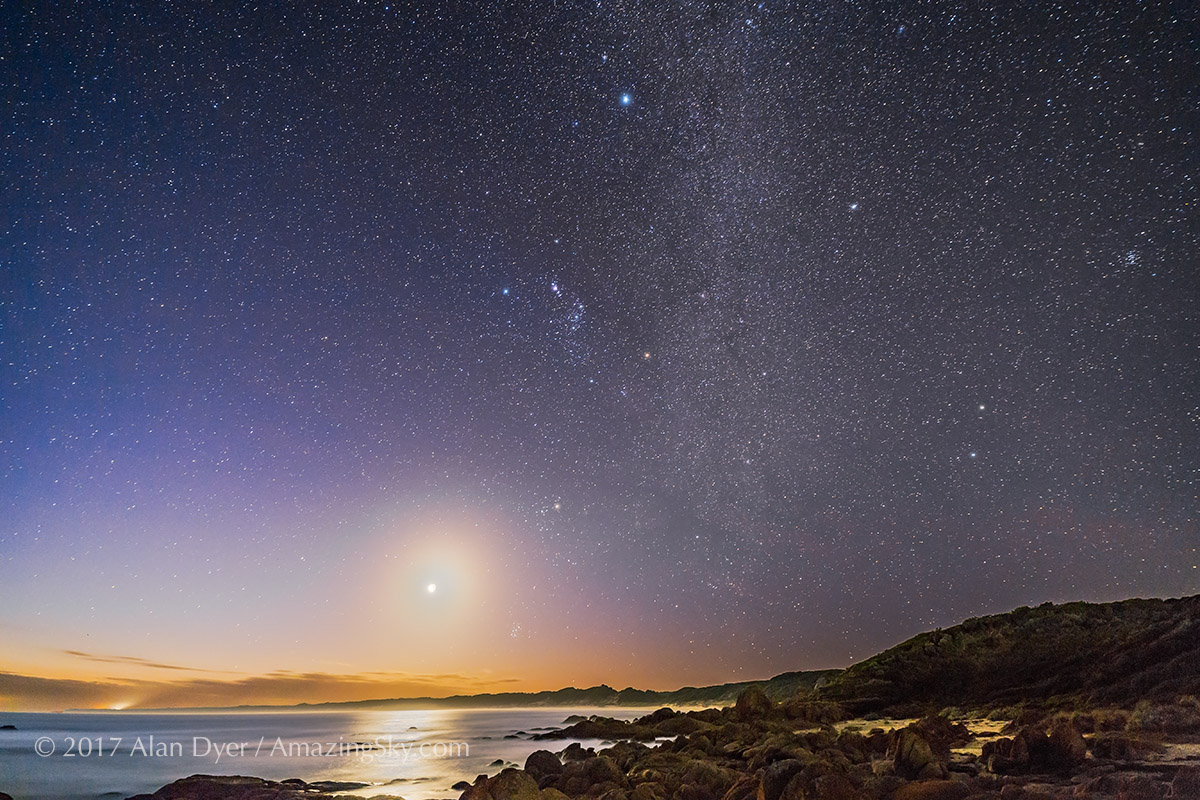
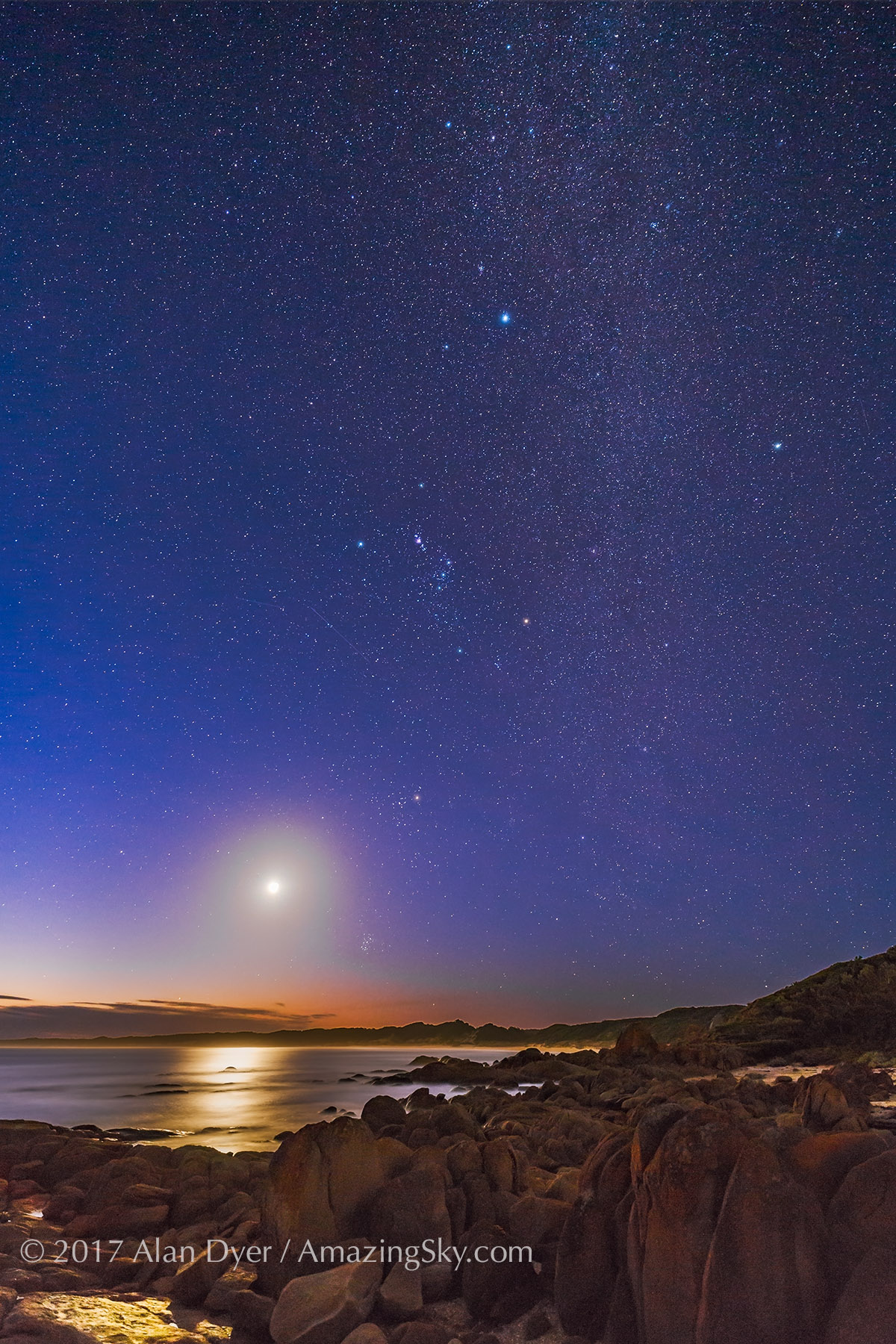
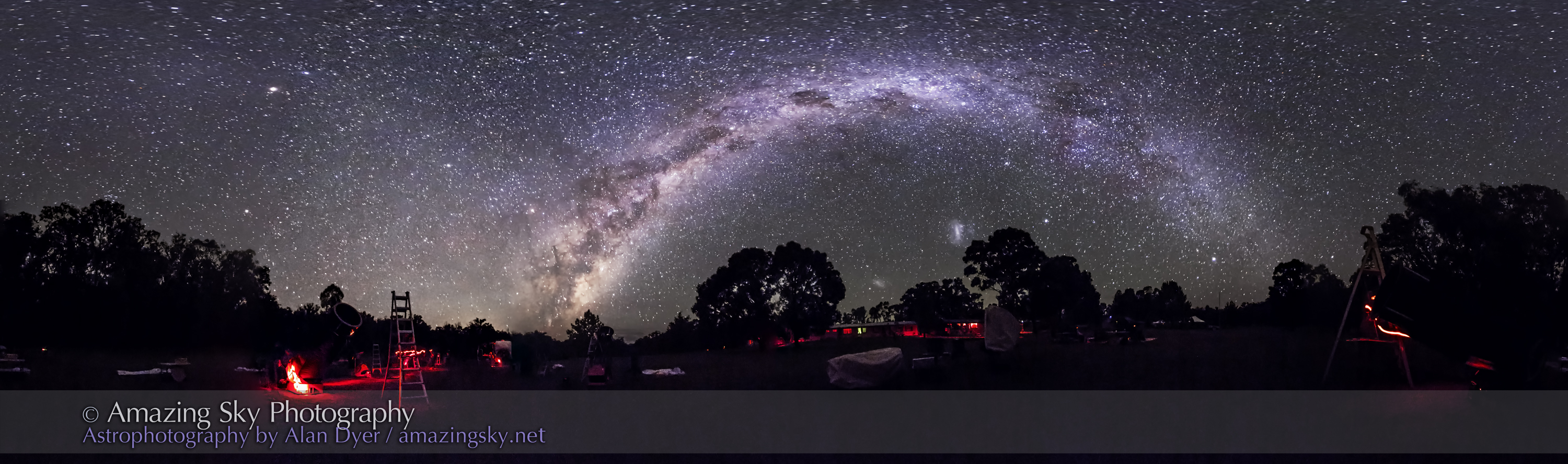
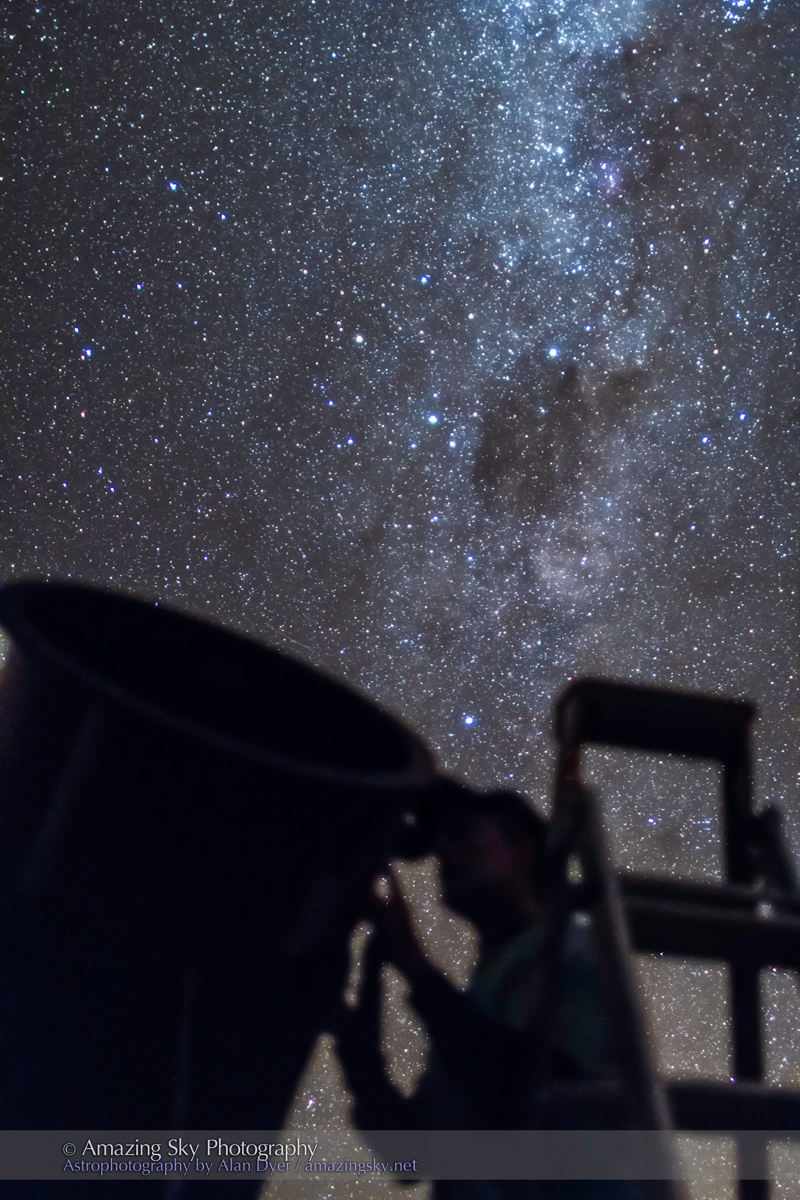
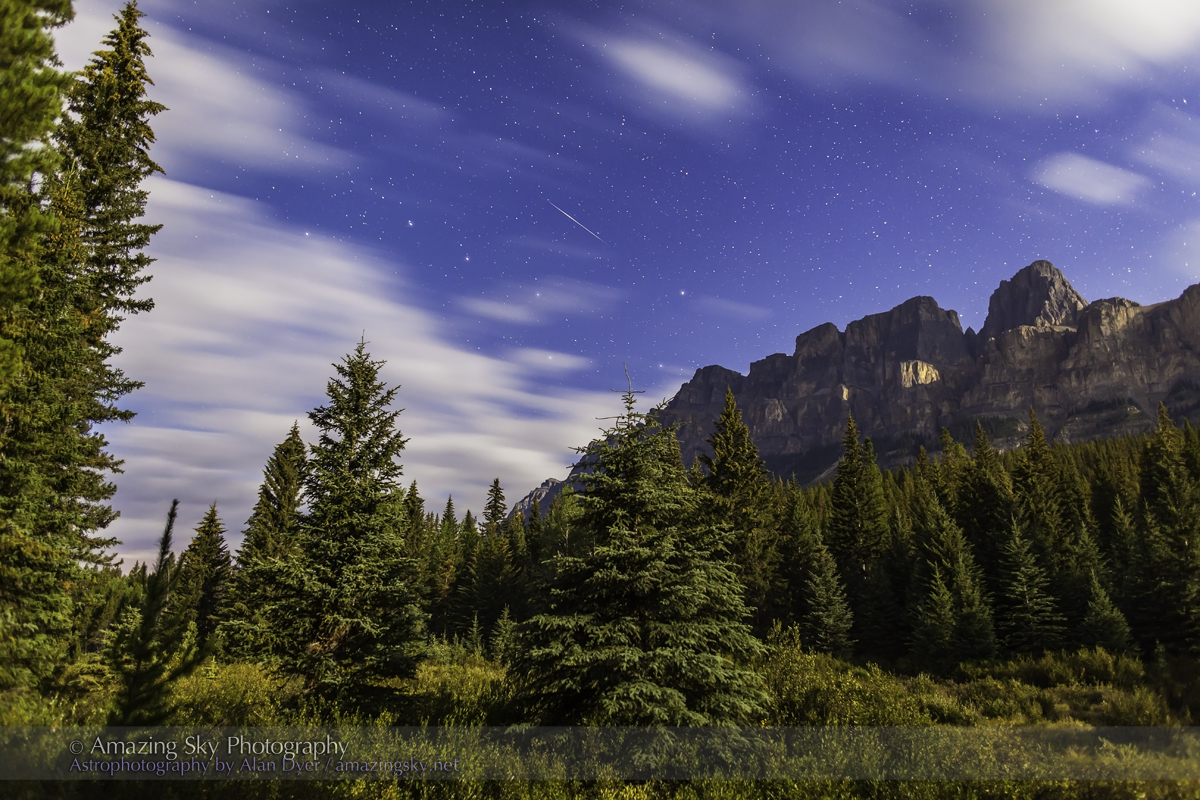
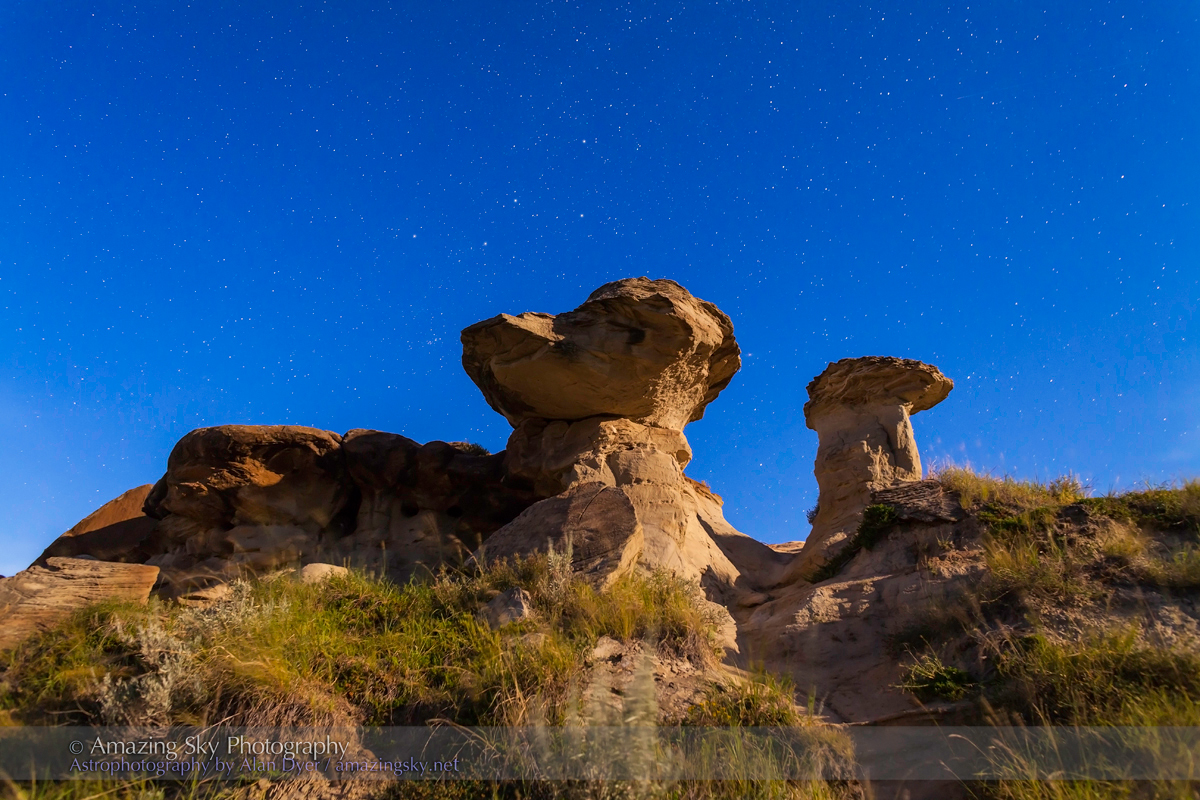
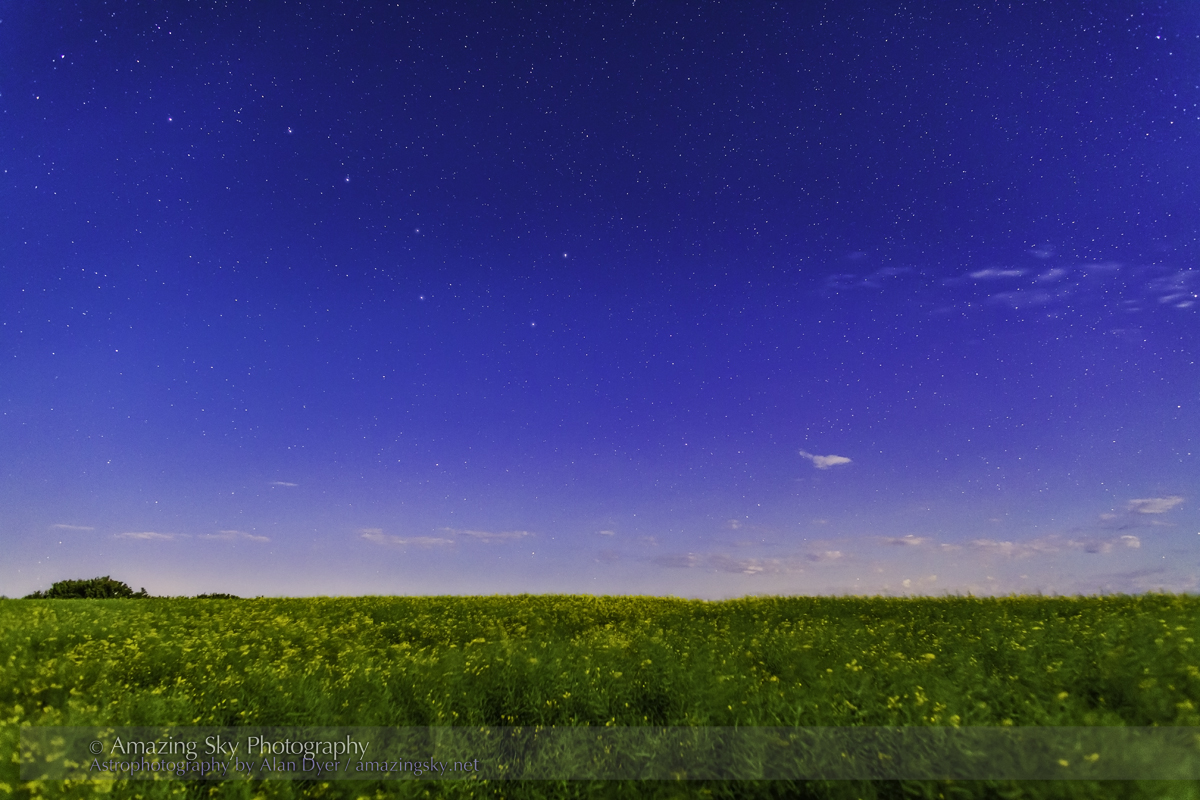
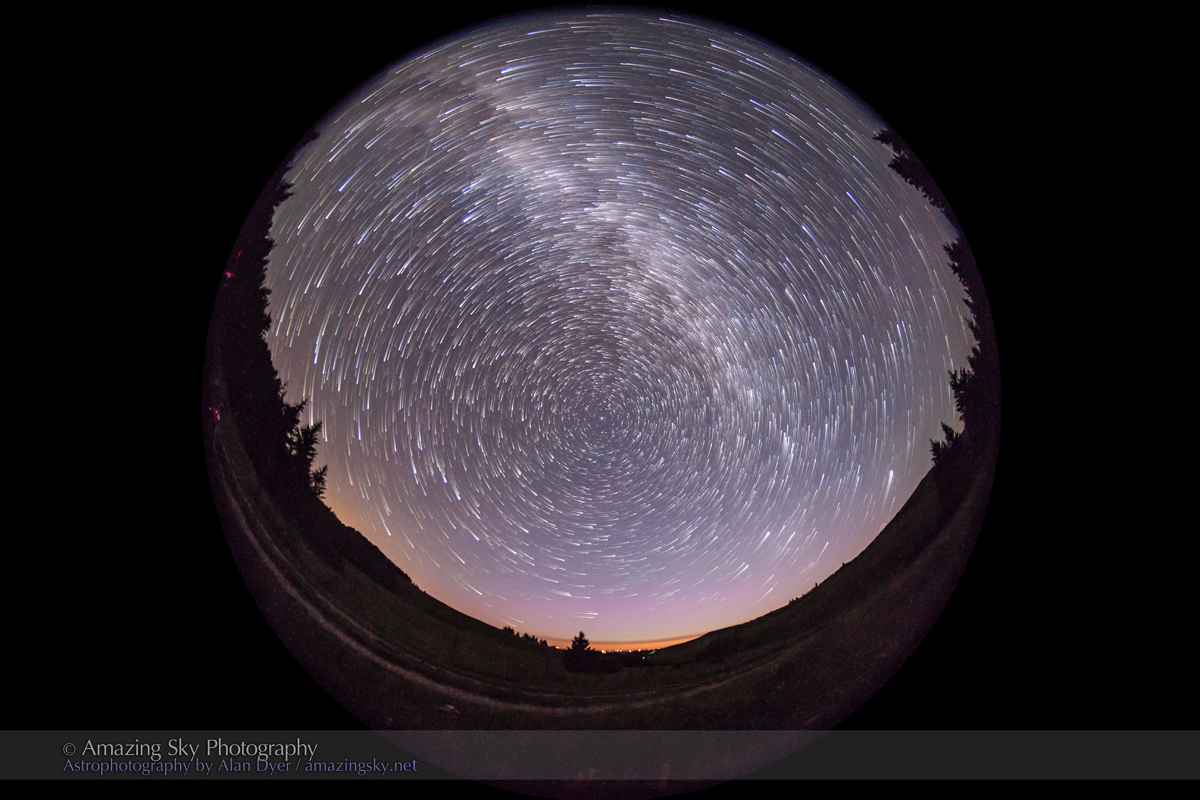
Southern Saskatchewan is a fine place to capture nightscapes of the Milky Way over the grand prairie landscape.
In late August 2025 I took a short road trip around southwest Saskatchewan, taking advantage of a run of wonderfully clear nights to shoot “nightscapes” at some of my favourite locations.
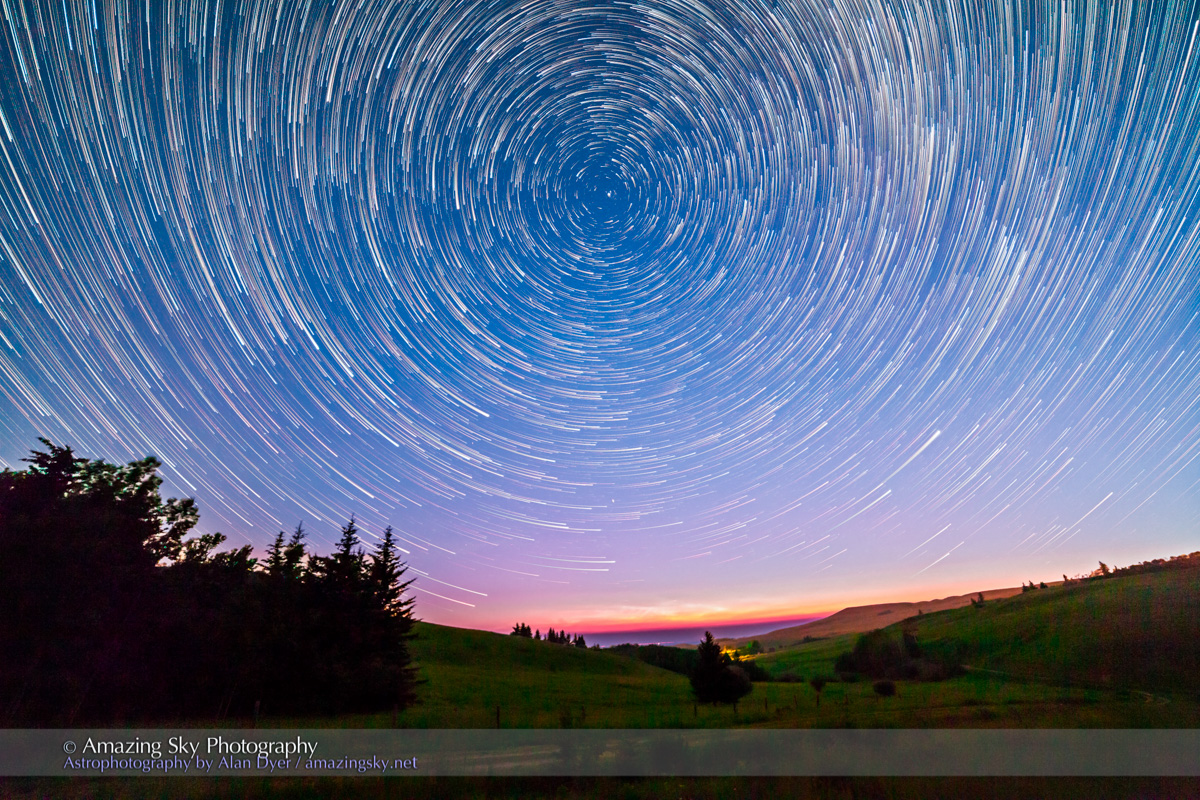
Southern Saskatchewan, and more specifically Southwest Saskatchewan, is a stargazing paradise. The skies are dark and there’s nothing to get in the way of seeing them! Yet, the landscapes have their unique beauty.
And in the case of Grasslands National Park the landscape preserves the endangered realm of original short-grass prairie. It is what the land was like long ago, even including some bison at large.
Grasslands National Park
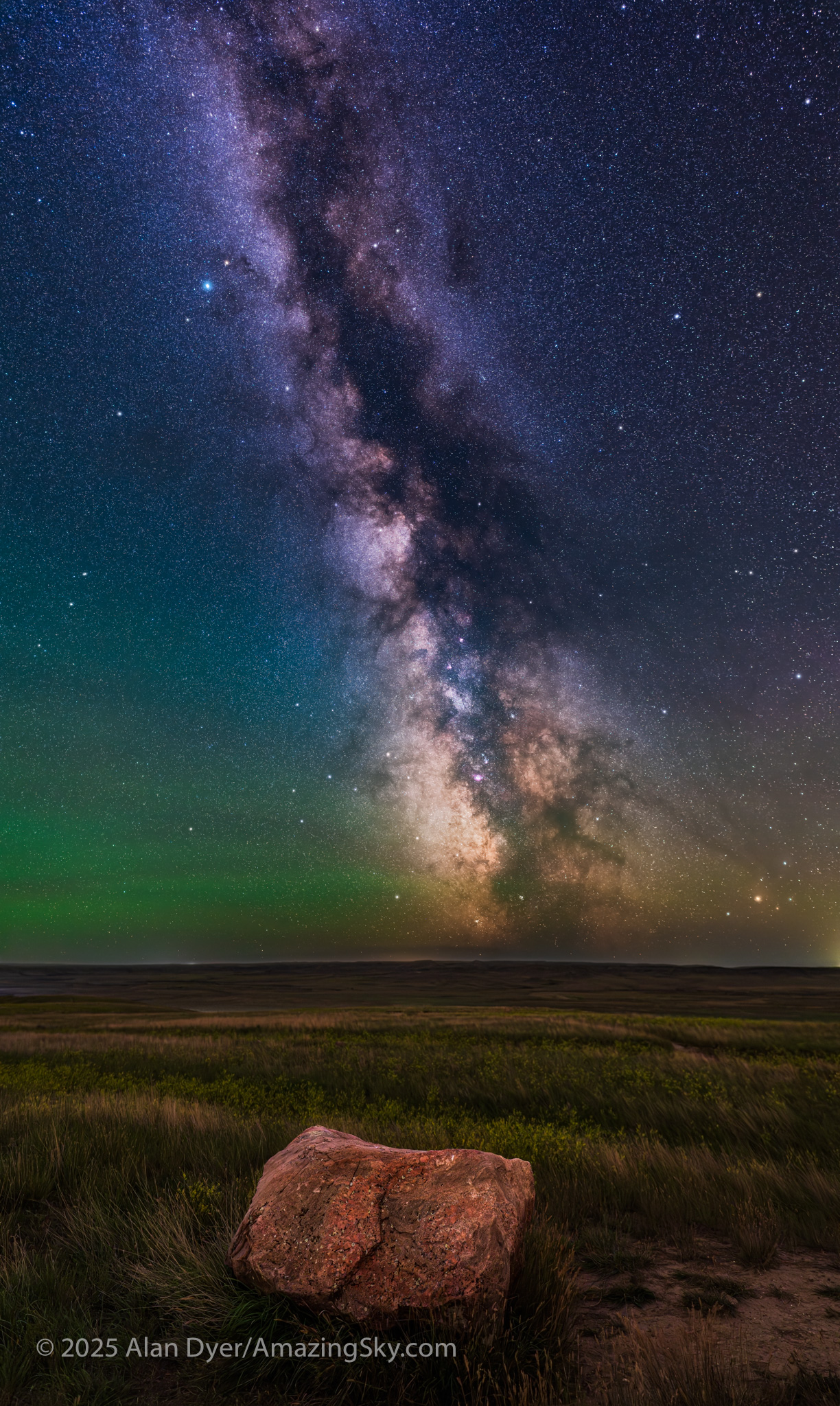

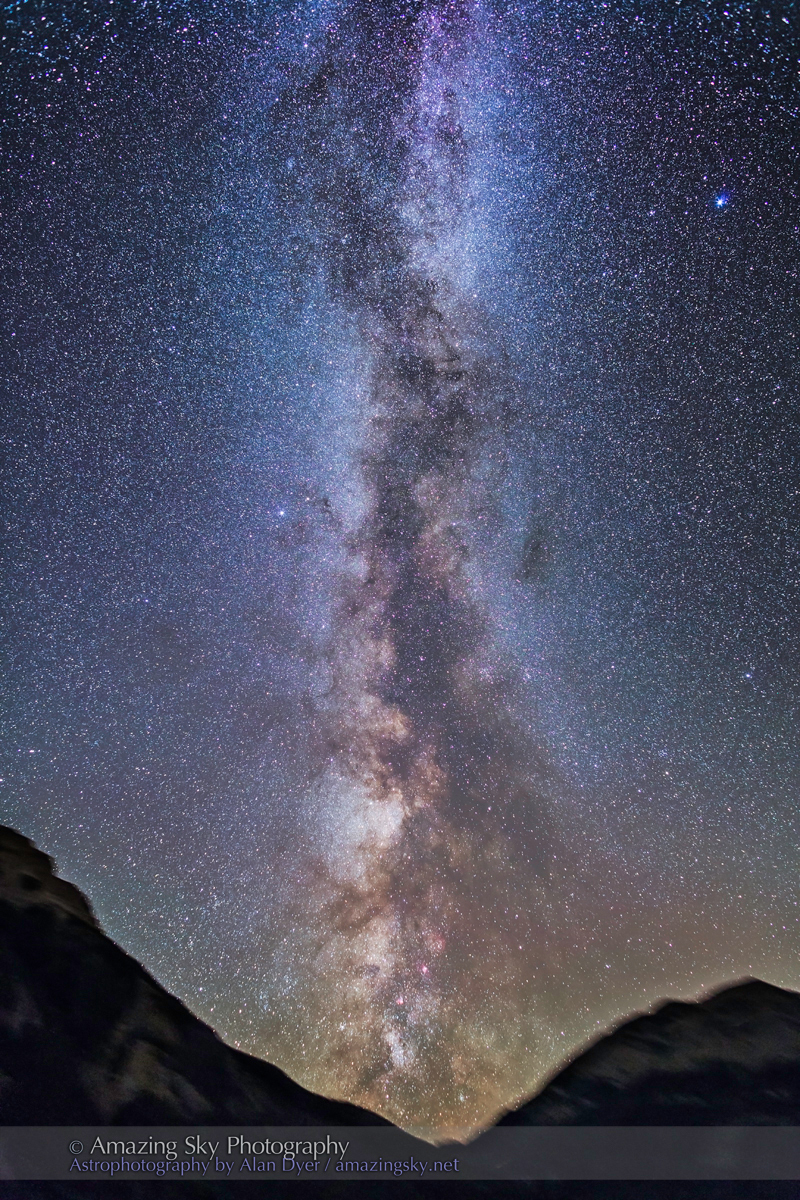
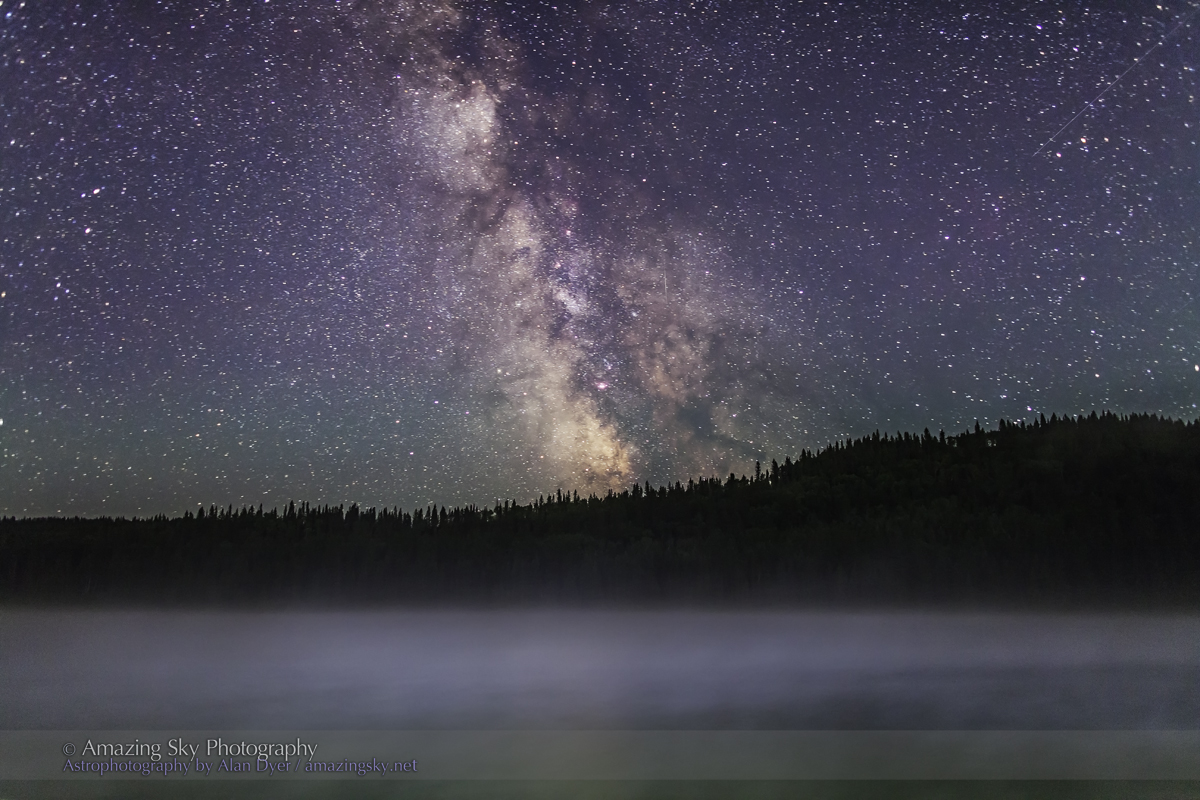
This is a blend of tracked and stacked sky exposures with a single untracked ground exposure:
– 7 x 60 seconds at f/2 tracked and focused for the sky, plus
– 1 x 4 minutes at f/2.8 untracked and focused for the foreground to bring out the details lit only by starlight. No light painting was employed here.
– All with the Nikon Z8 at ISO 800 and Nikkor 20mm S lens, on the MSM Nomad tracker. And all from the same tripod position. However, the camera was reframed upward for the sky shots.
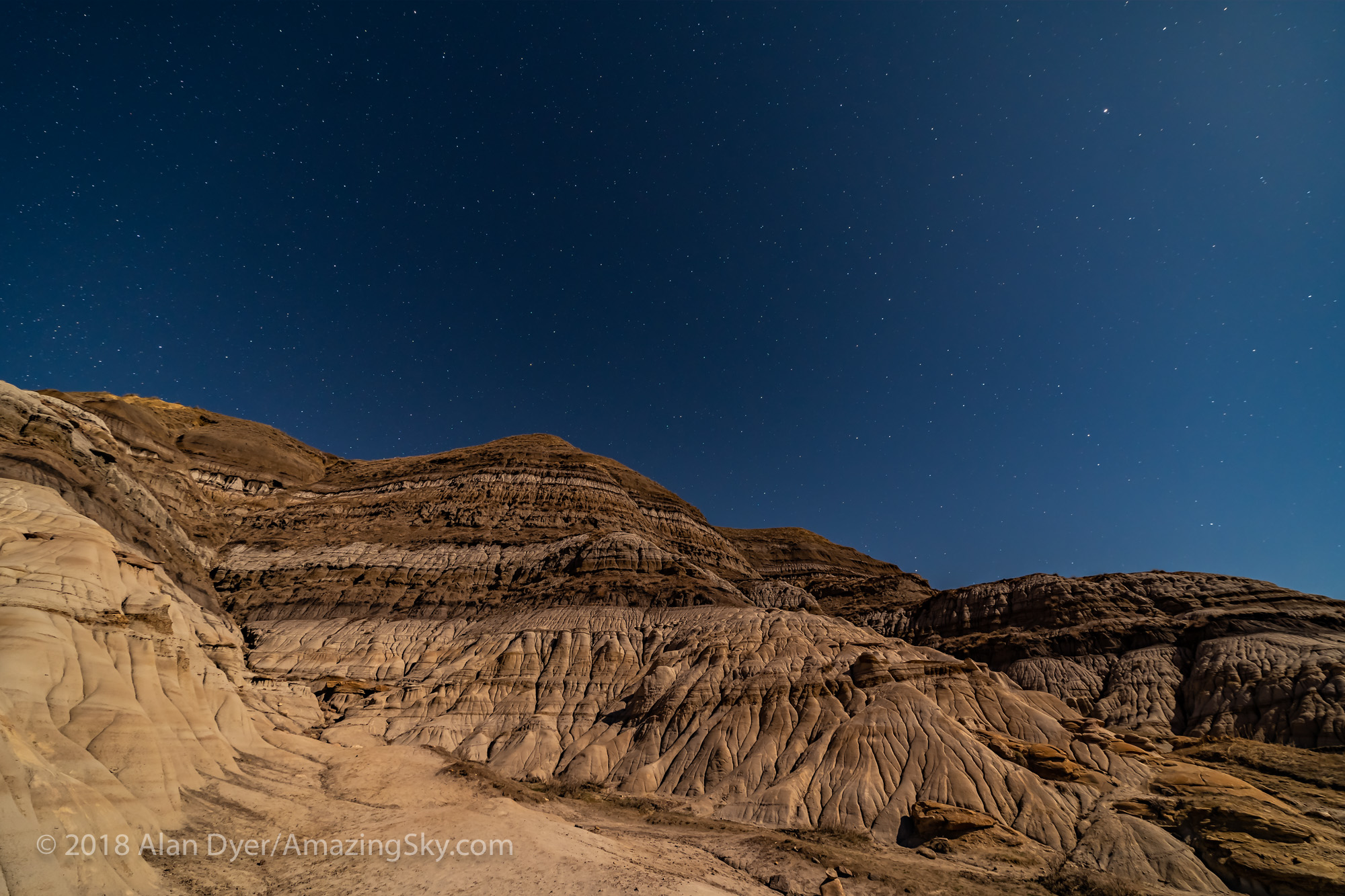
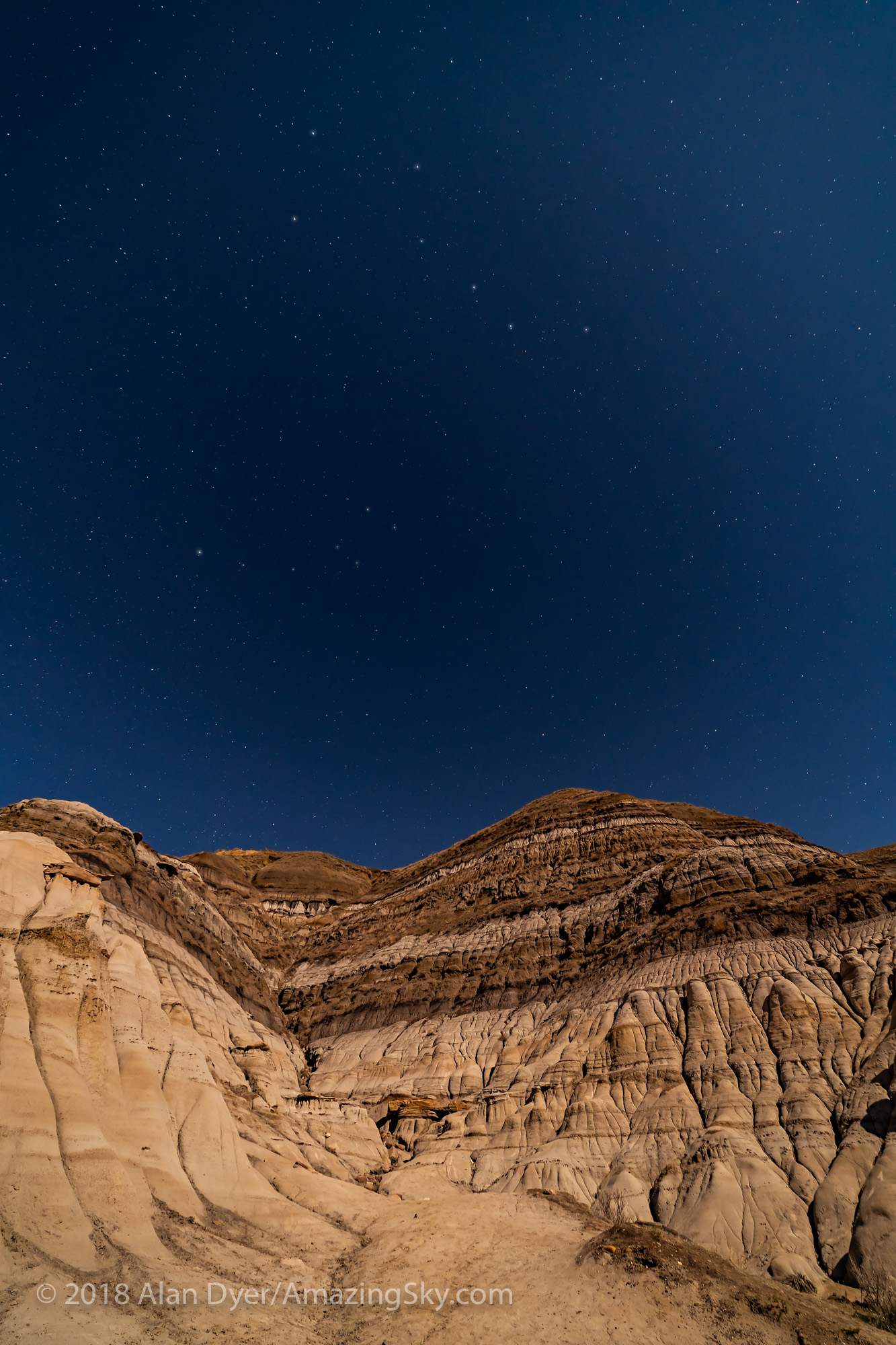
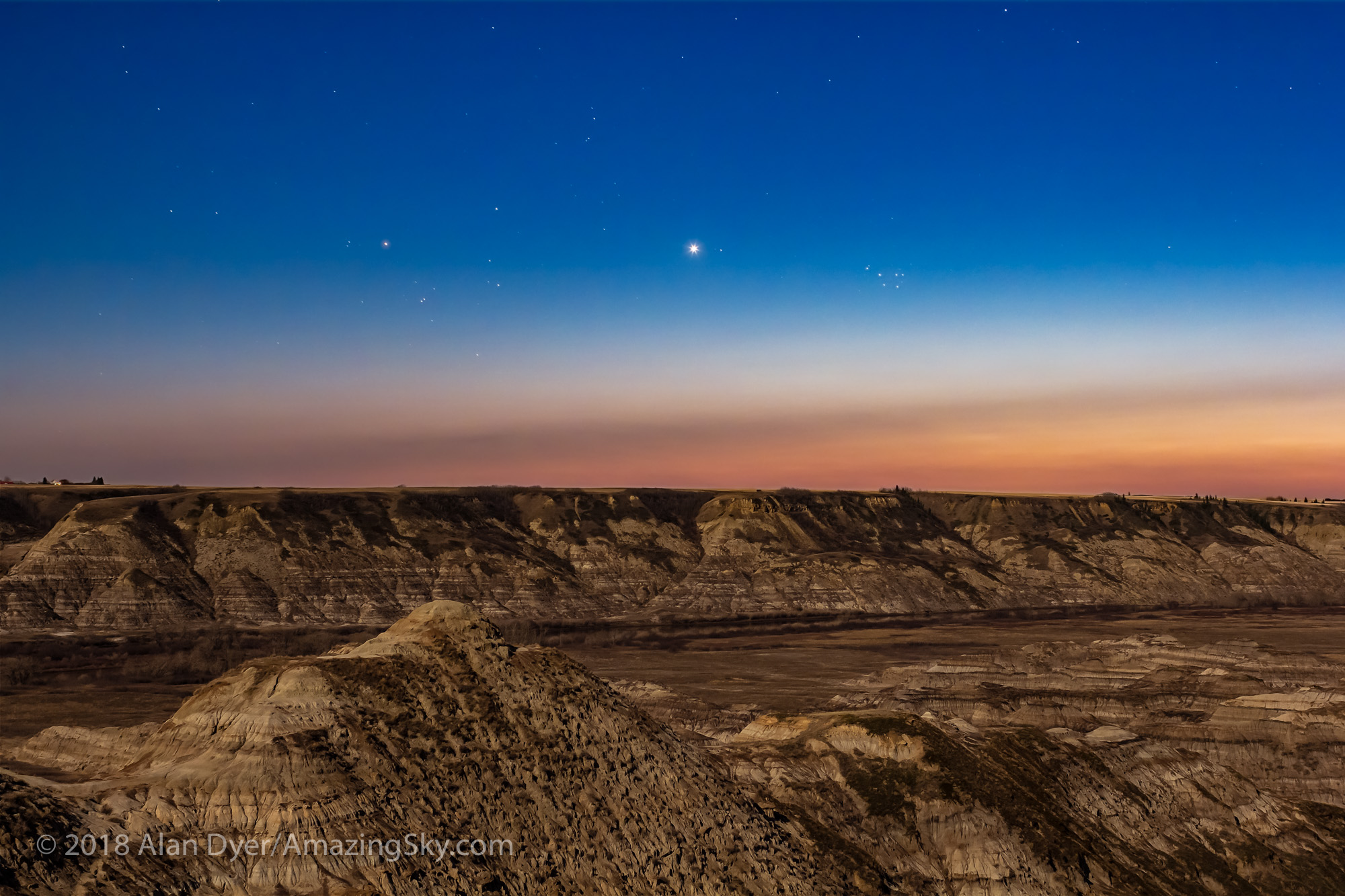
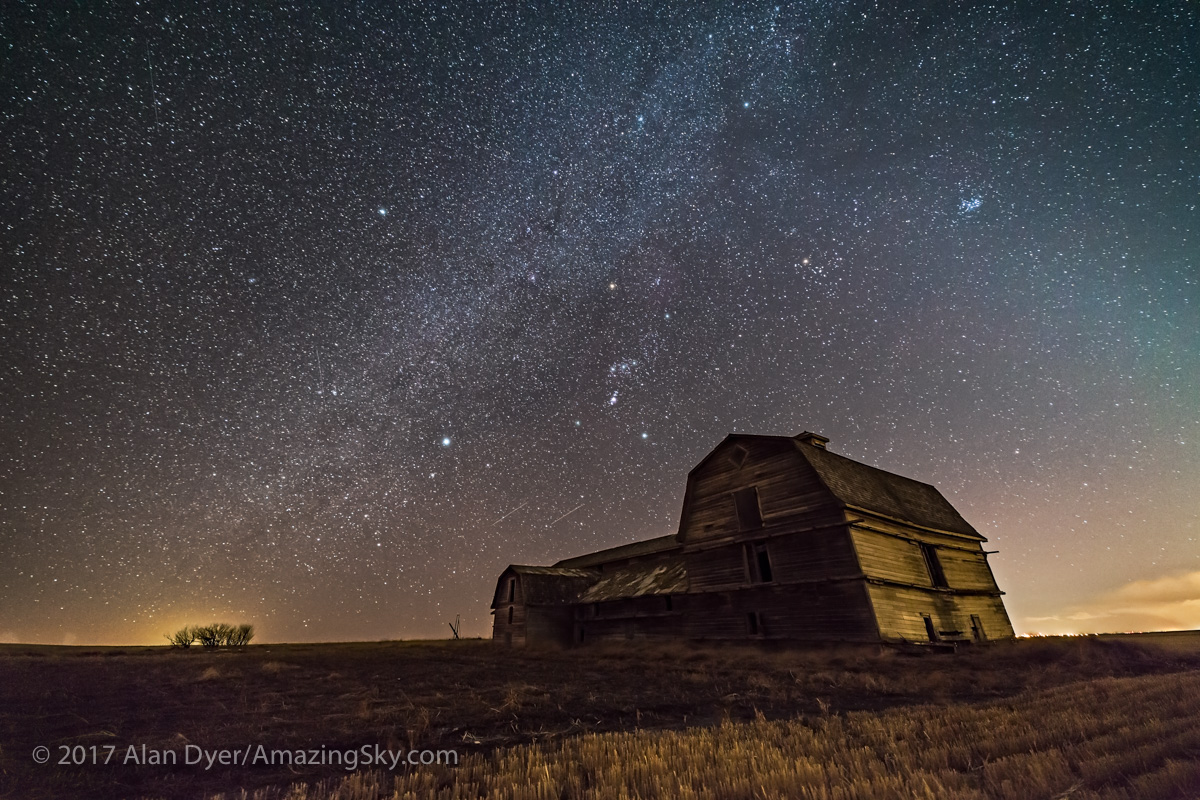
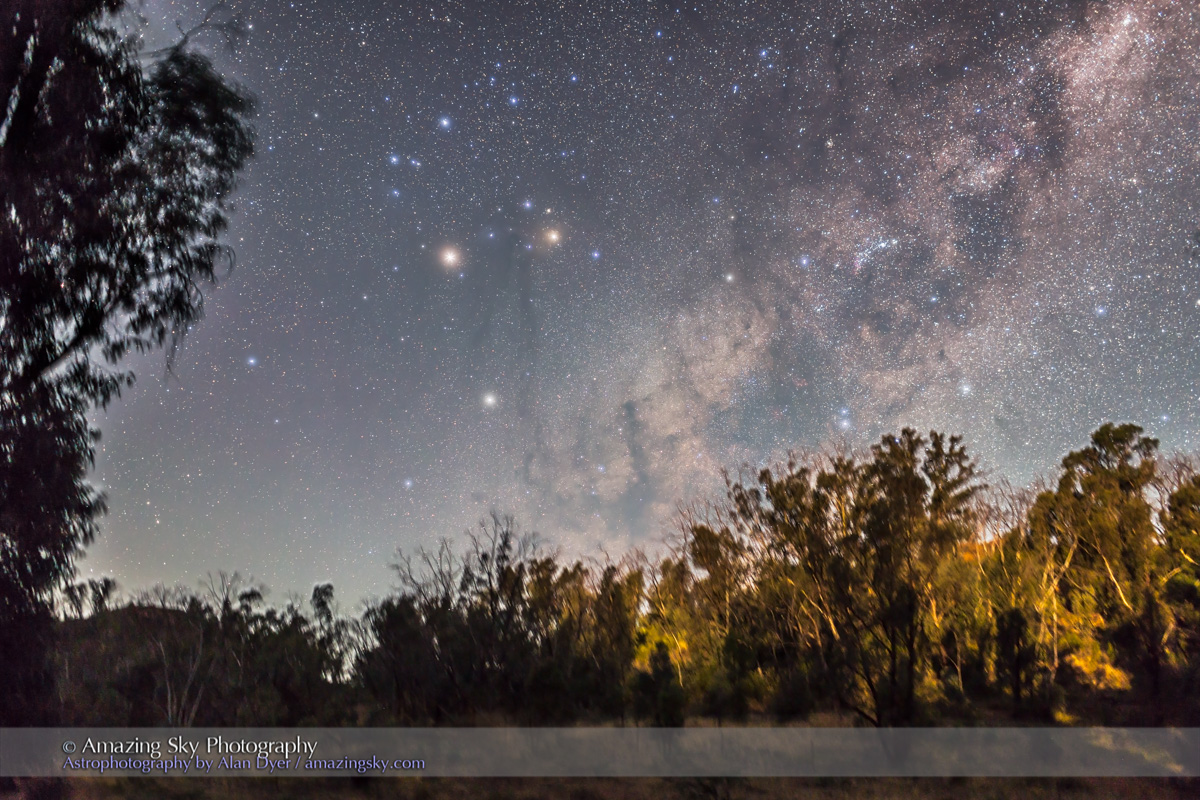
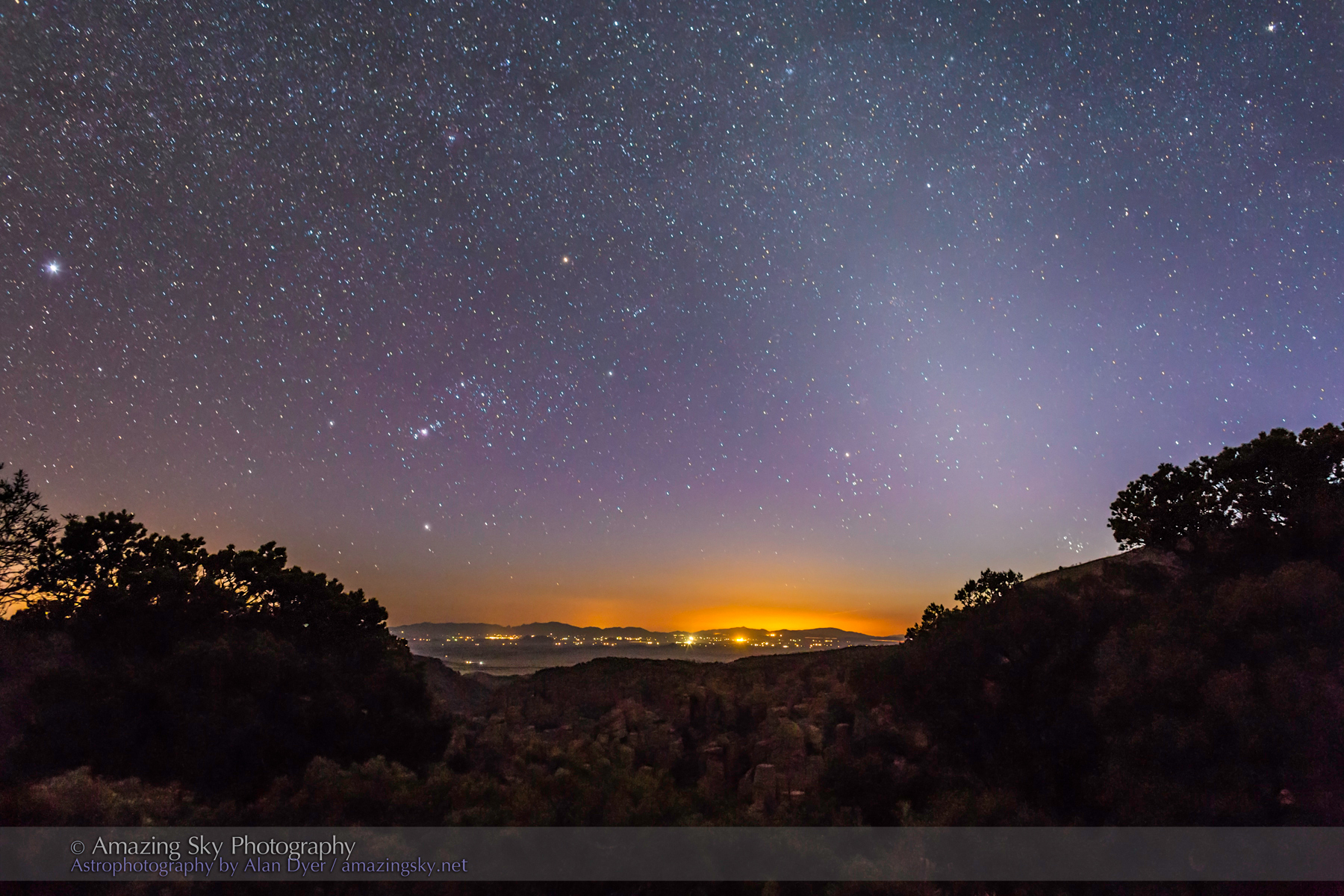
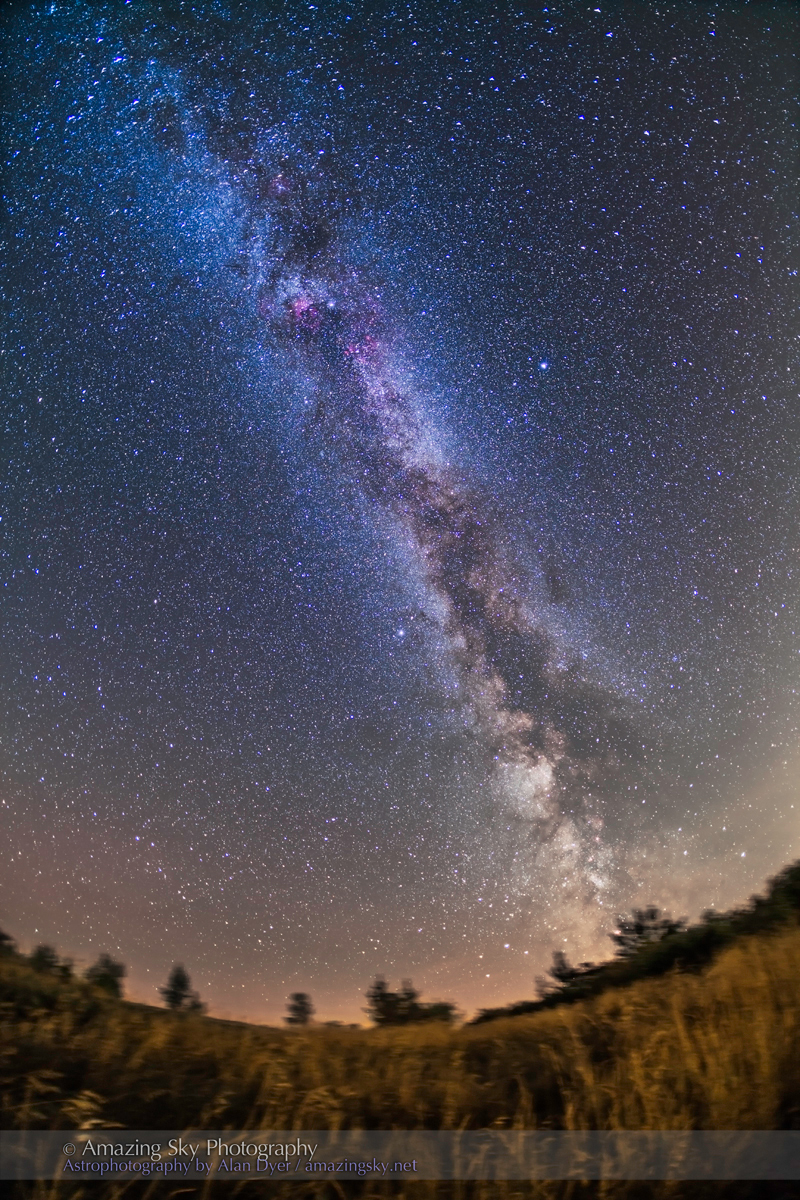
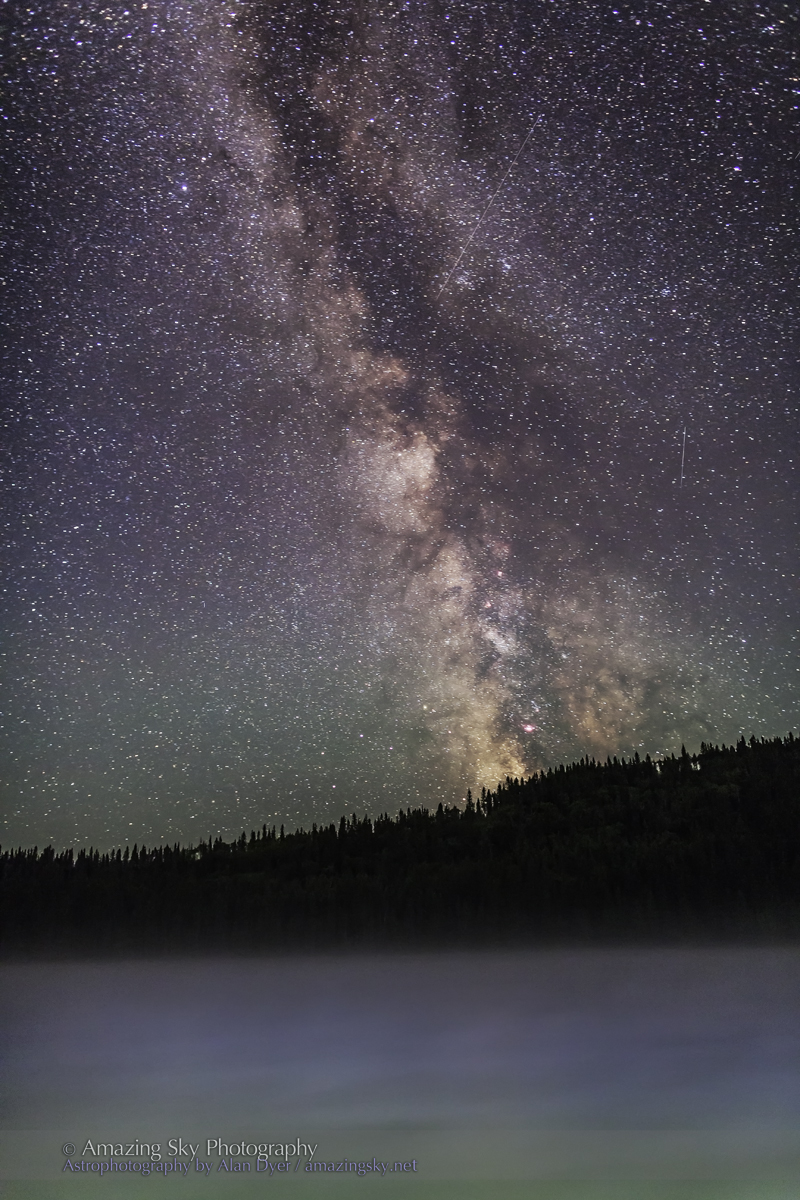
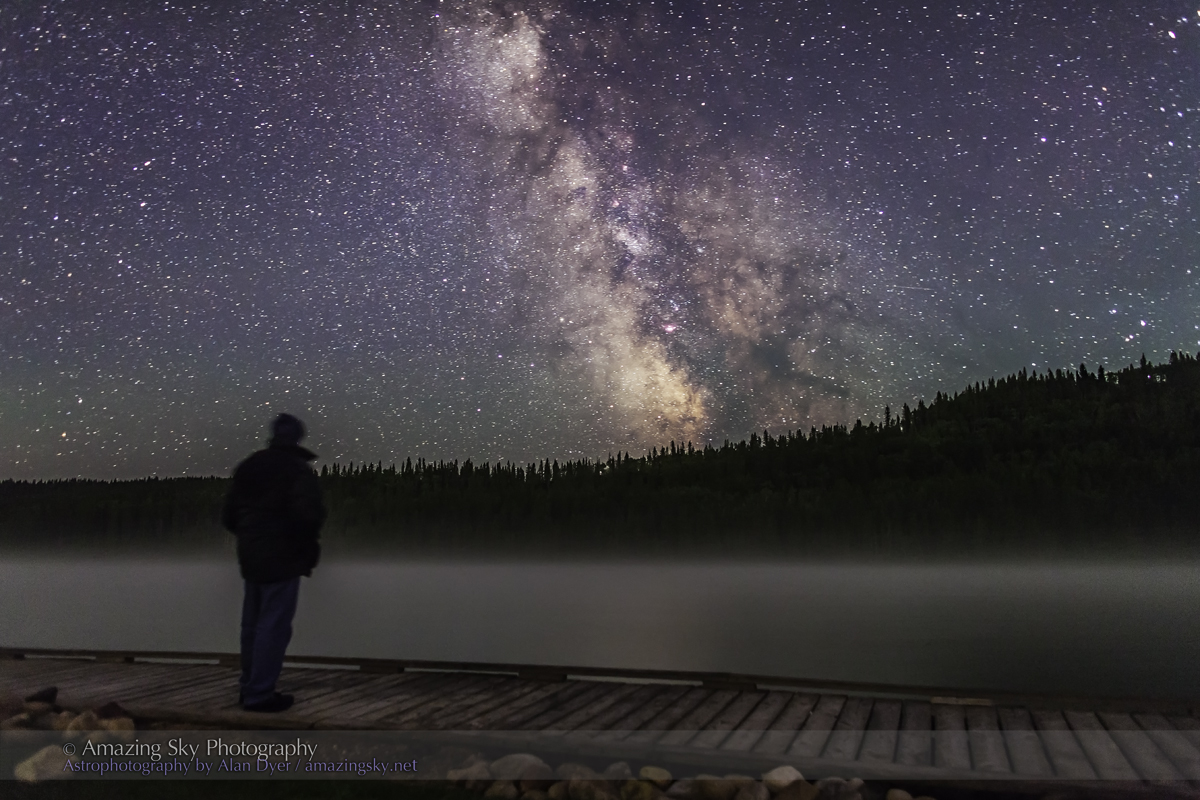
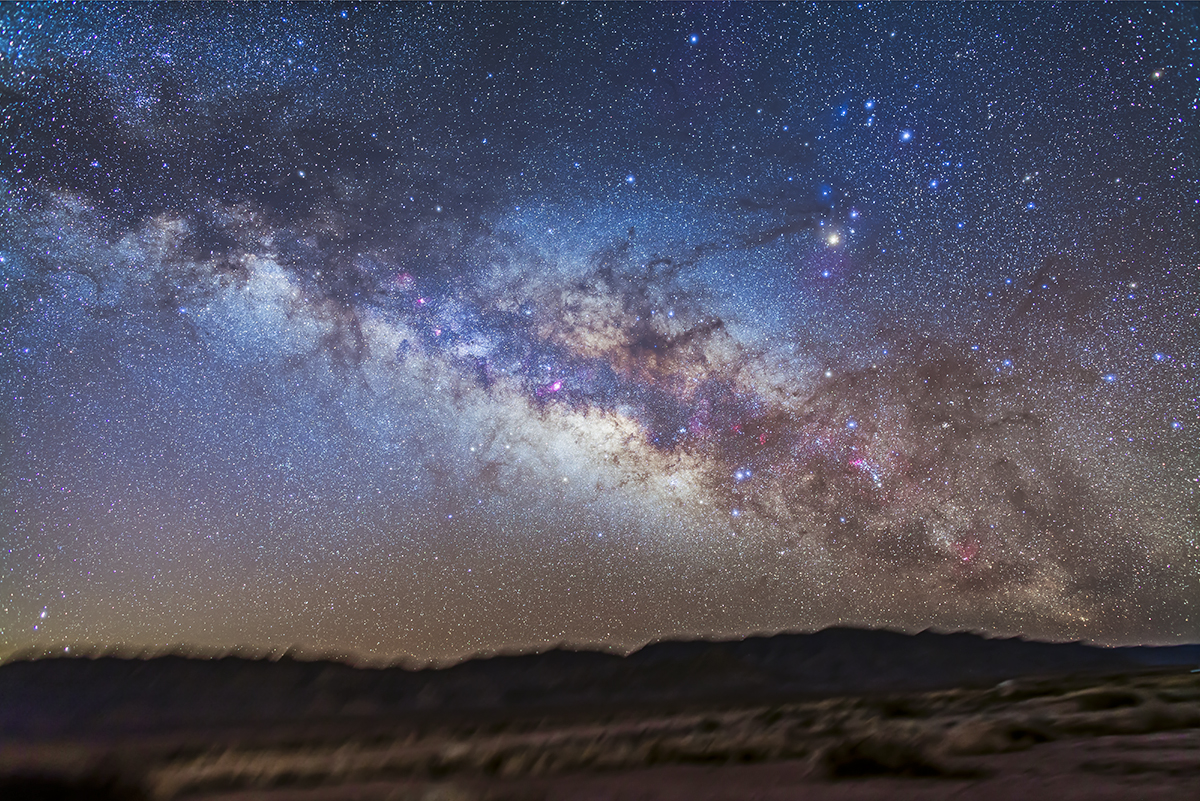
In fact, my main destination on my visit to Grasslands this year was to revisit a site I had intended to shoot from in 2019 – the Bison Rubbing Stone overlooking the Frenchman Creek Valley, with the Milky Way as a backdrop.
In 2019 I had to drive through the herd of bison to get there. With the herd only a few hundred metres away, I thought better of setting up at their scratching post. So that year I headed down into the valley to shoot at the 76 Ranch Corral. You can see some images from that location taken on an earlier trip to Grasslands here.
This year I was assured the bison were in the outback, so I set up at their rubbing stone. This is one of the many glacial erratic boulders the Ice Age left scattered across the prairies. With no trees about, the bison have long loved to use them to scratch an itch. But the connection with the stars is that one legend of the sky told by Blackfoot First Nations describes the Milky Way as the “Buffalo Trail,” the dust left by a cosmic herd of bison.
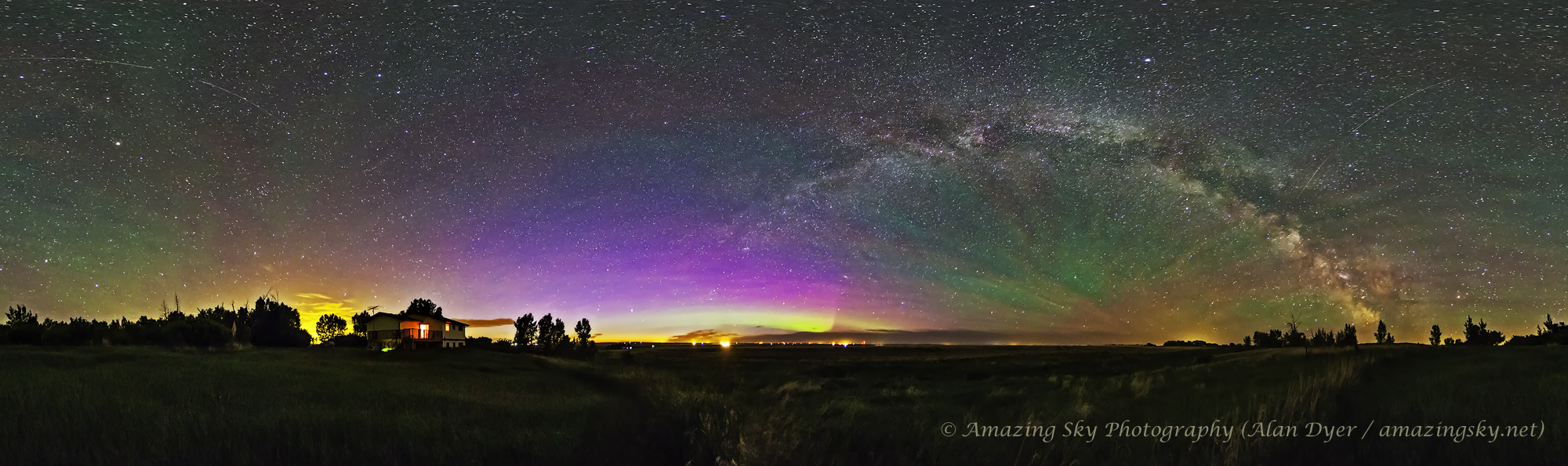
I got the shot! Then all I had to do was turn the camera around to face north to get this scene.
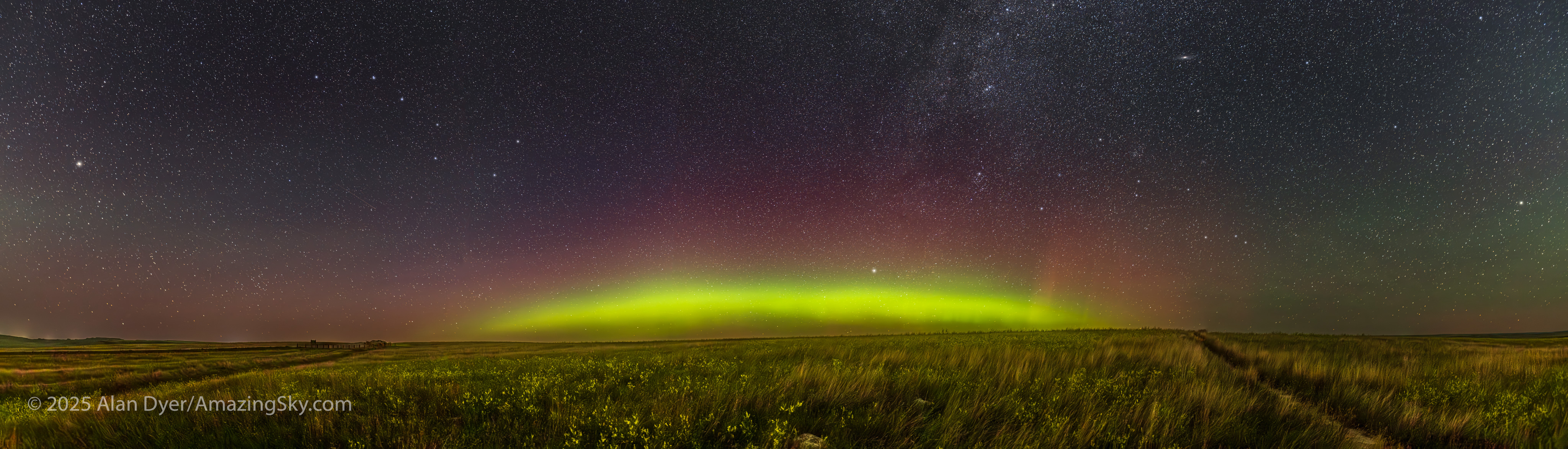

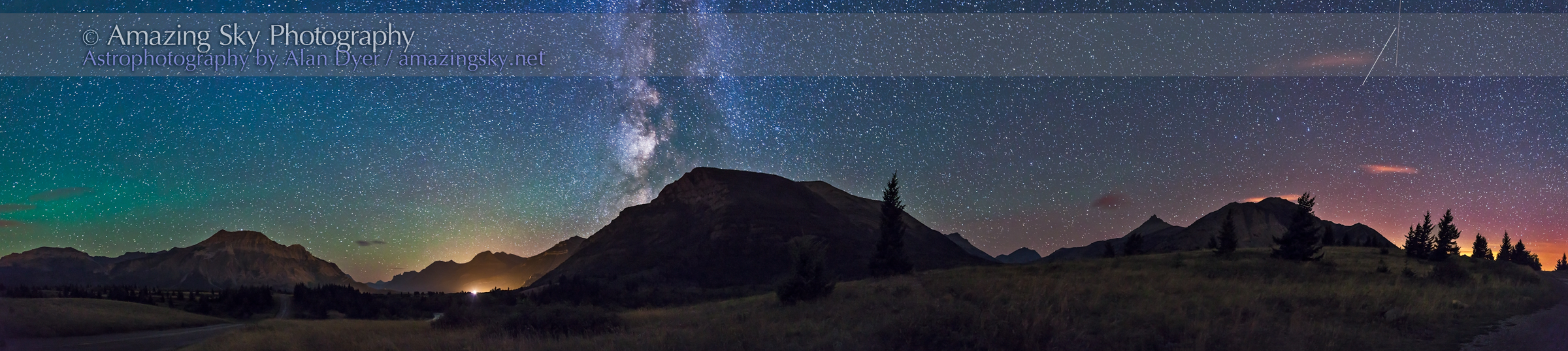
This is a panorama of 5 segments, each 30 seconds untracked at f/2 with the Nikkor 20mm S-Line lens and Nikon Z8 at ISO 1600. Stitched with Adobe Camera Raw. I removed aircraft trails, but at left I retained the many faint satellite trails in the northwest still lit by twilight, as this was early at about 10:30 pm CST. I did not focus stack these frames. Nor was the camera tracking the stars.
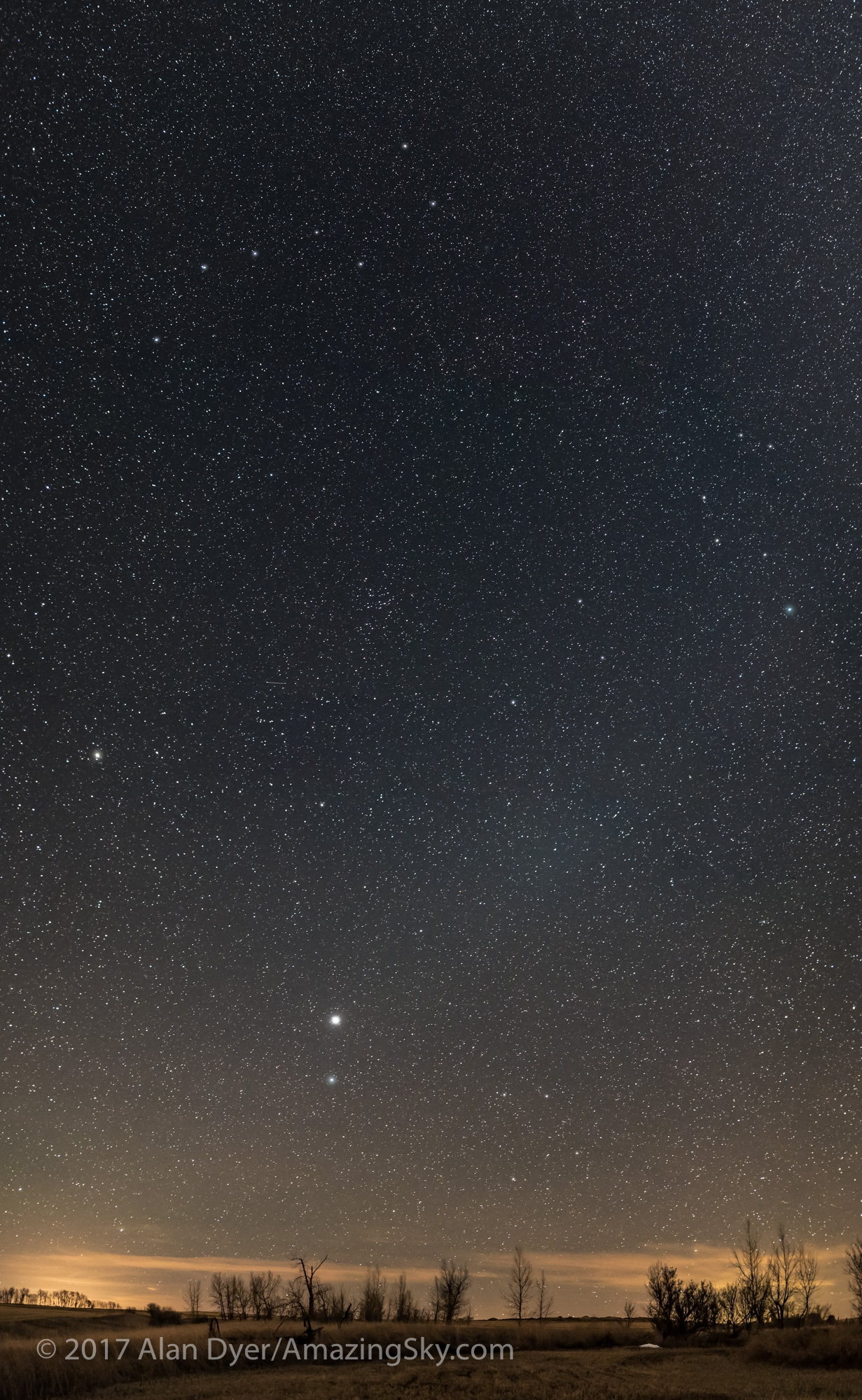
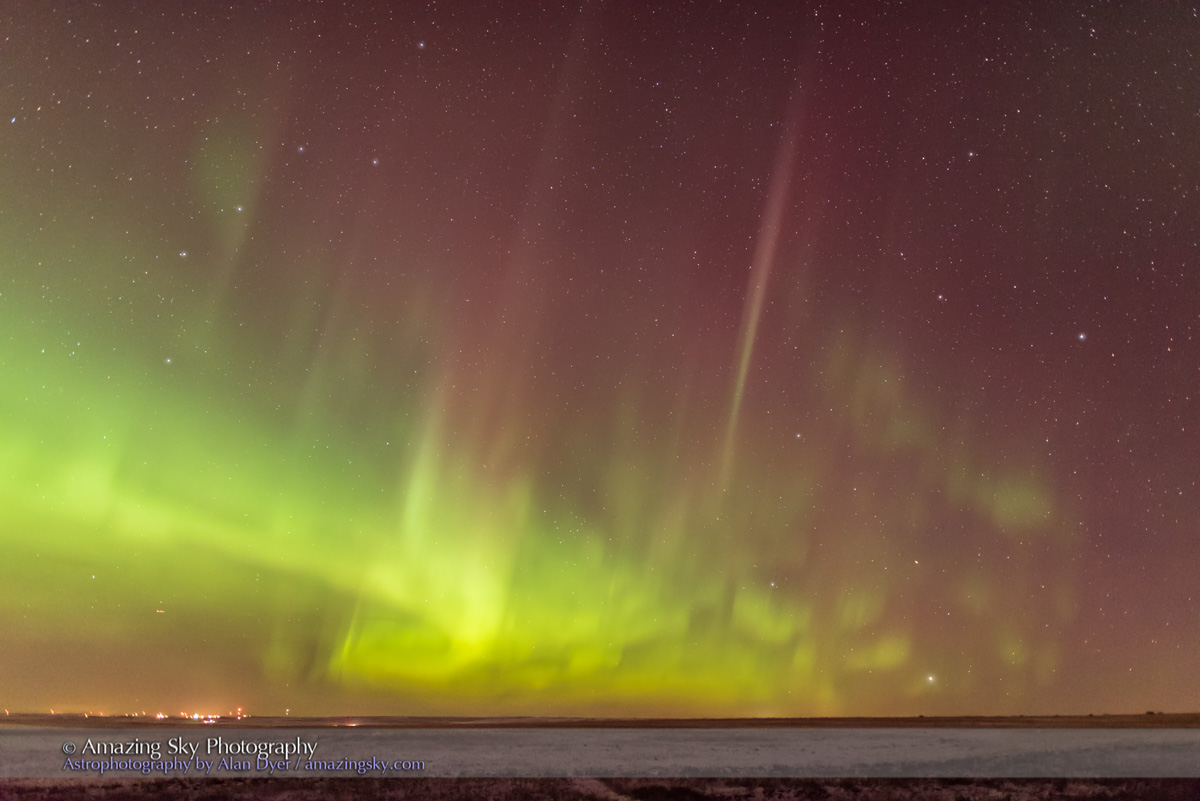
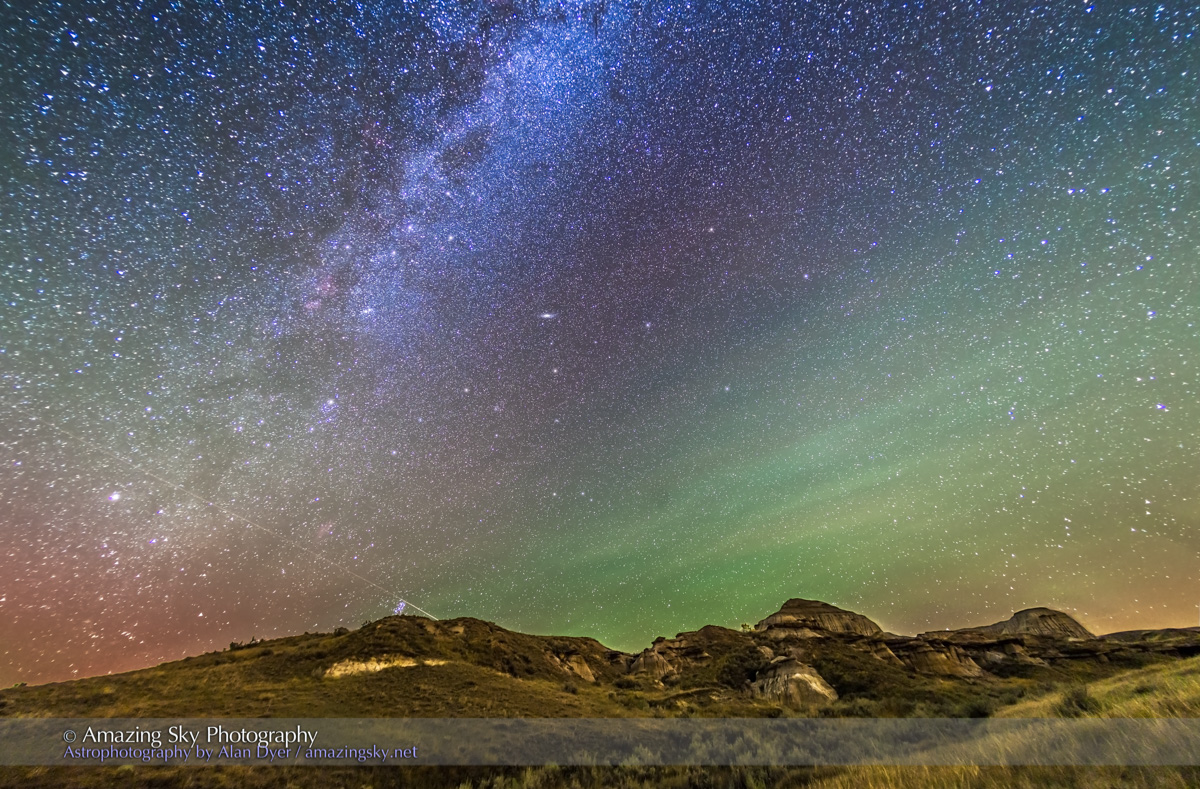
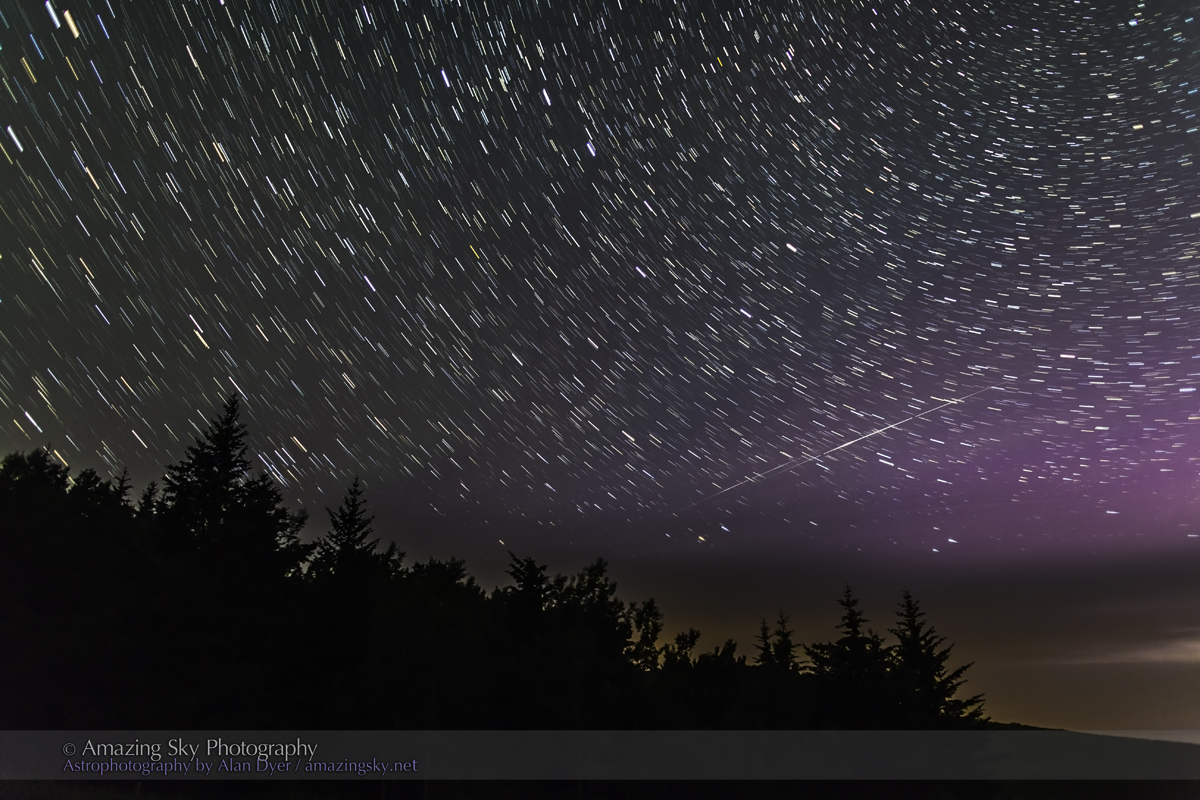
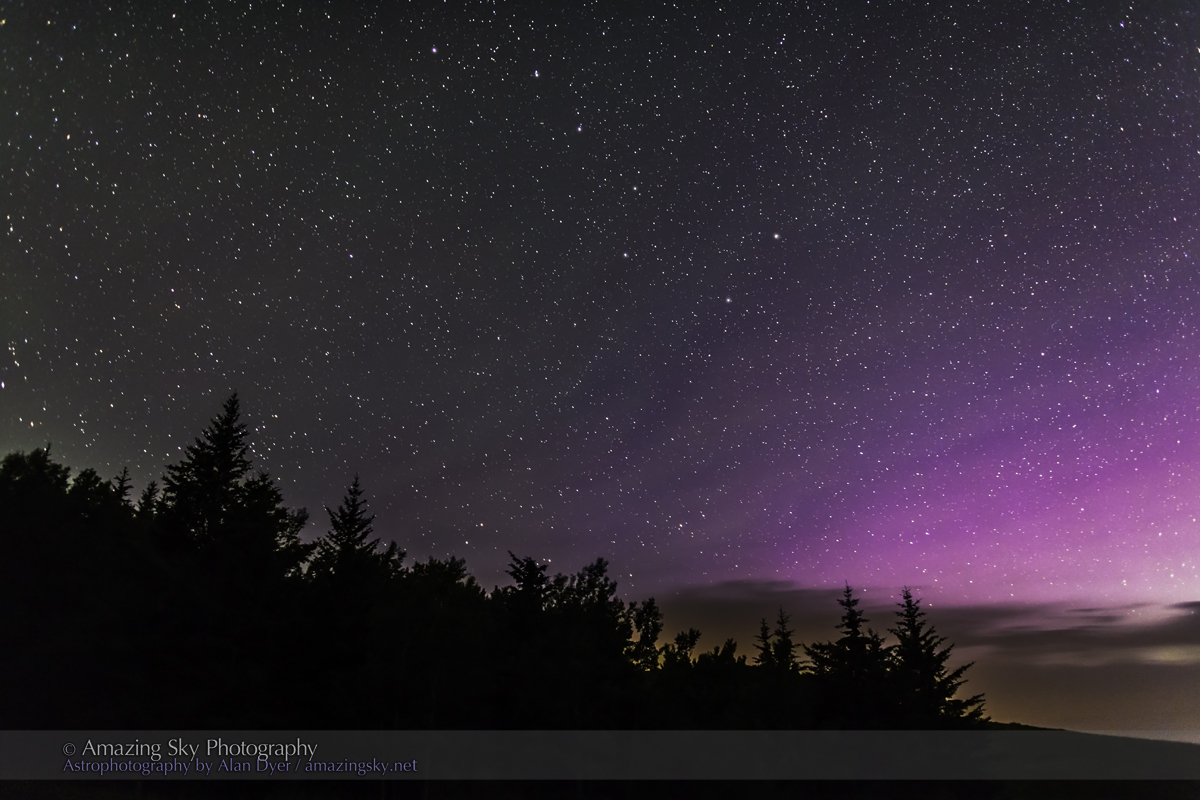
A mild aurora appeared in a classic arc across the north, and framed between the hiking trail, with the Big Dipper to the left and the Milky Way rising to the right. This is the wonderful sky that awaits in the “big sky” country of Grasslands. On the horizon only 3 distant lights could be seen. Grasslands is a Dark Sky Preserve. May it always be so!
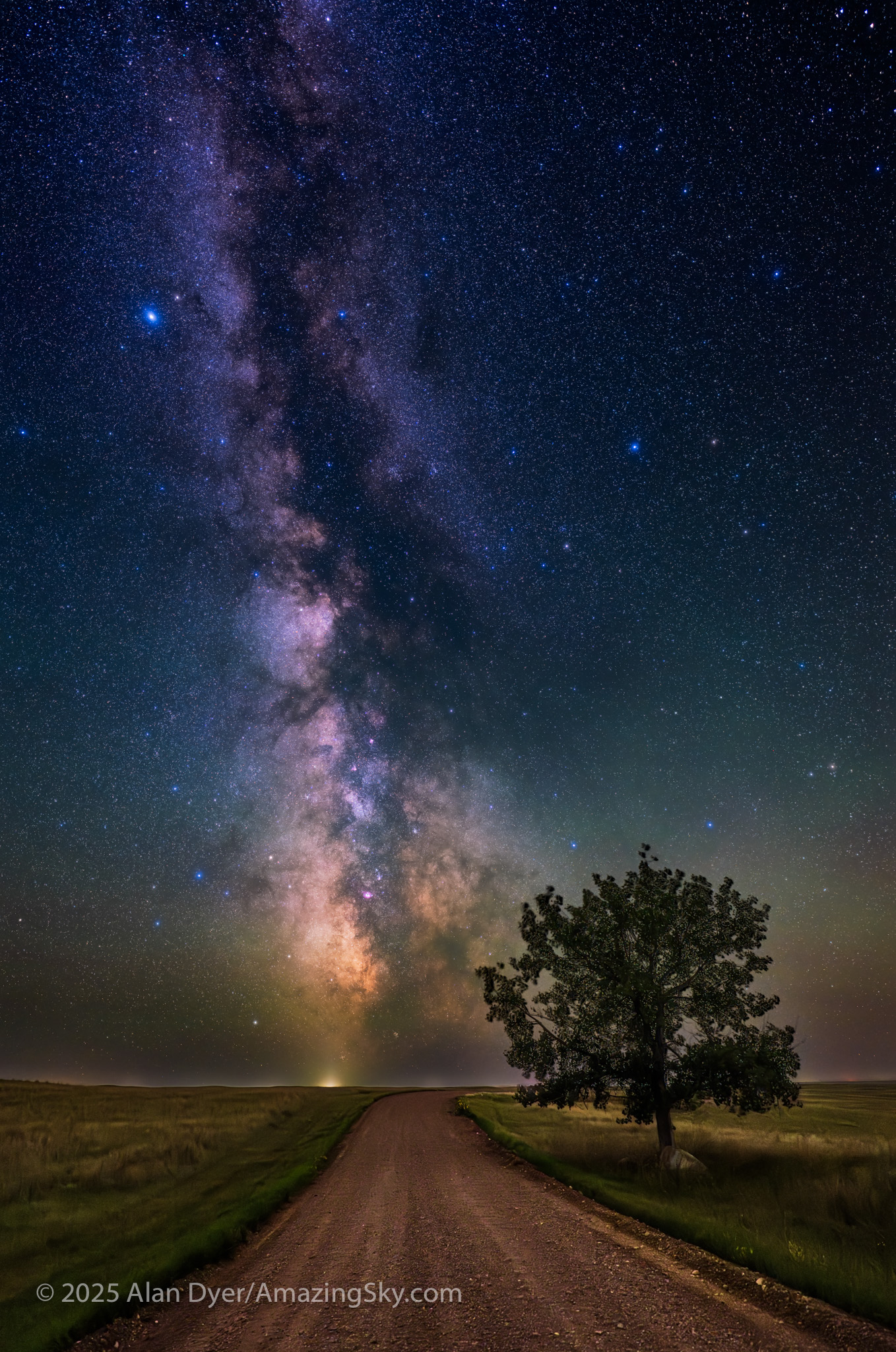

This is a blend of tracked and stacked sky exposures with a single untracked ground exposure:
– 4 x 30 seconds at f/2 tracked for the sky, plus
– 1 x 2 minutes at f/2.8 untracked for the ground to bring out the details lit by starlight, plus
– A single 30-second tracked exposure through a Tiffen Double Fog 3 filter layered in, to add the star glows.
– All with the Nikon Z8 at ISO 800 and Nikkor 20mm S lens, on the MSM Nomad tracker. And all from the same tripod position. The camera was not moved for the sky photos.
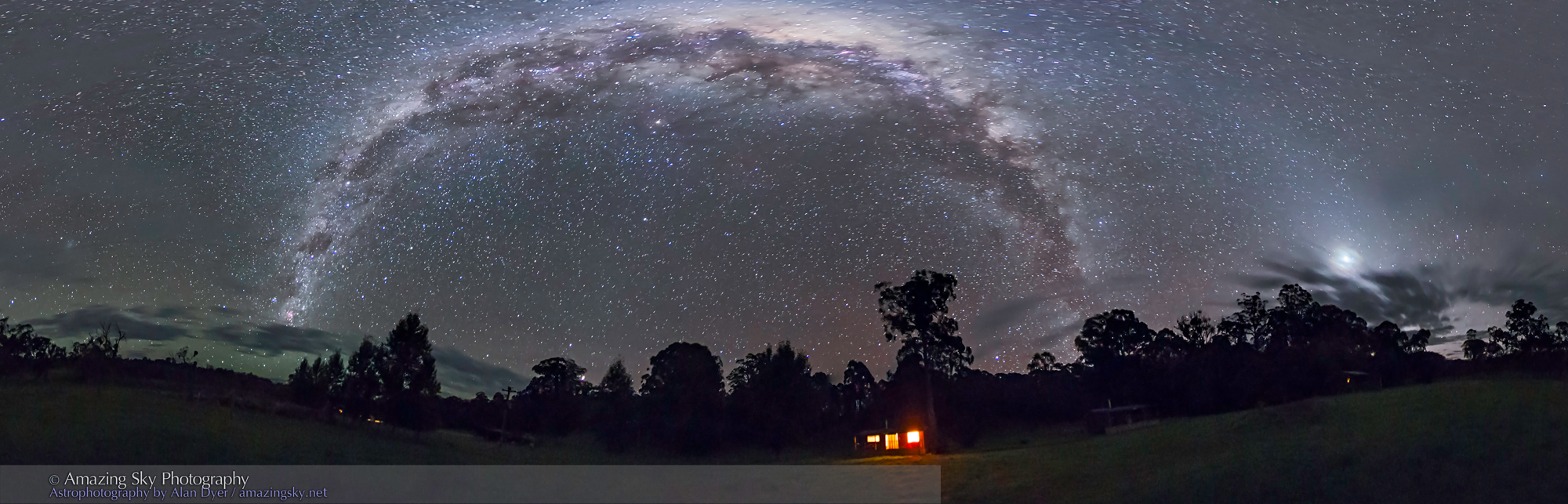
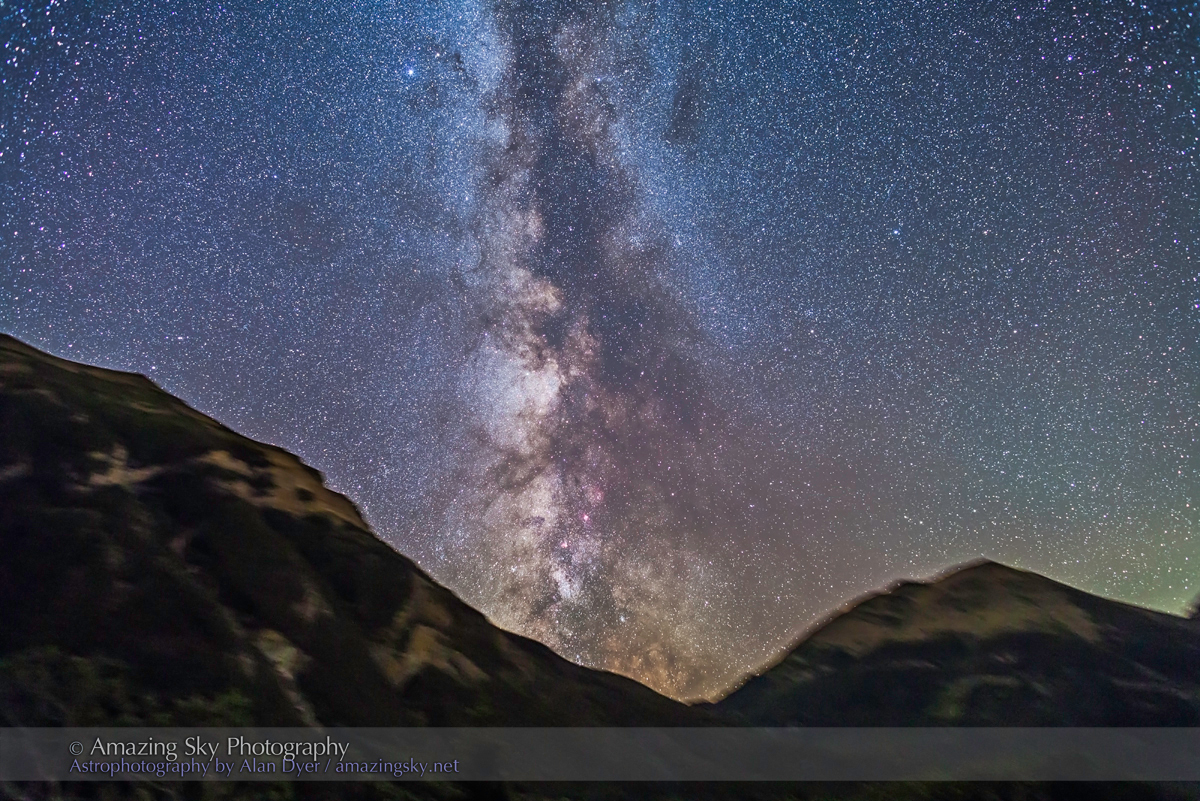
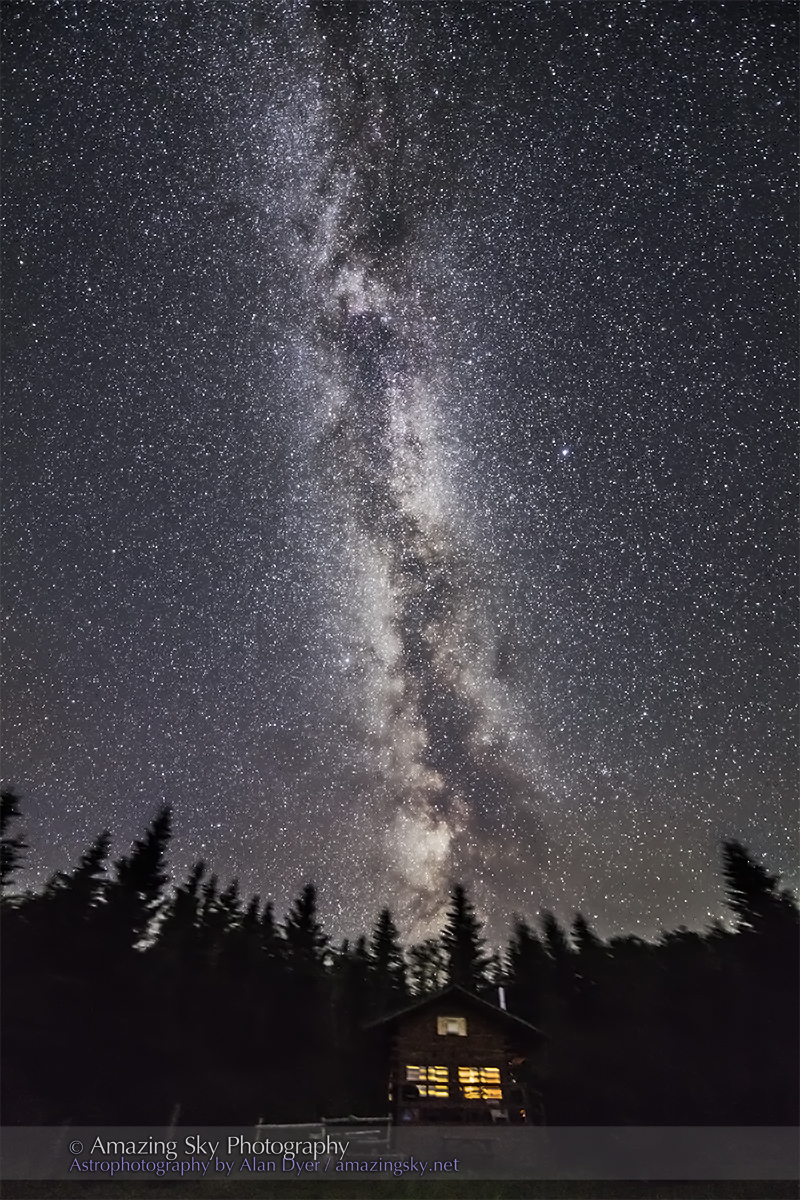
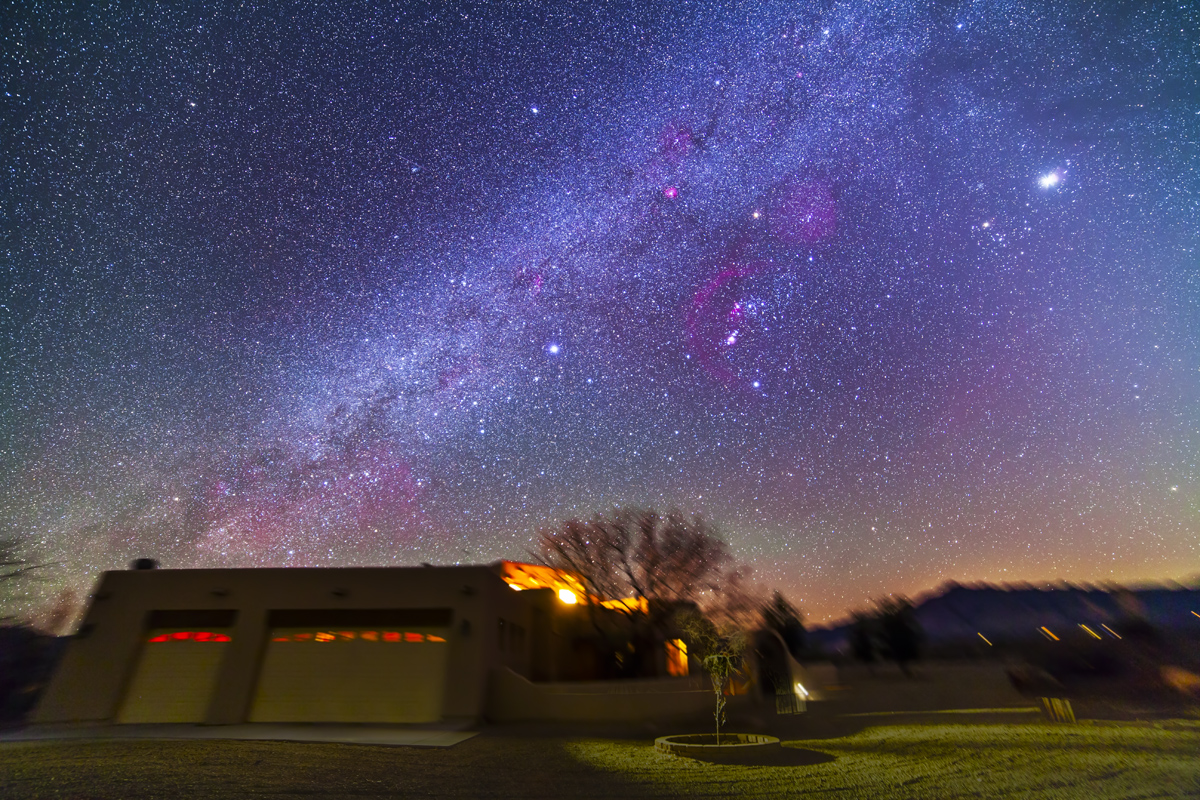
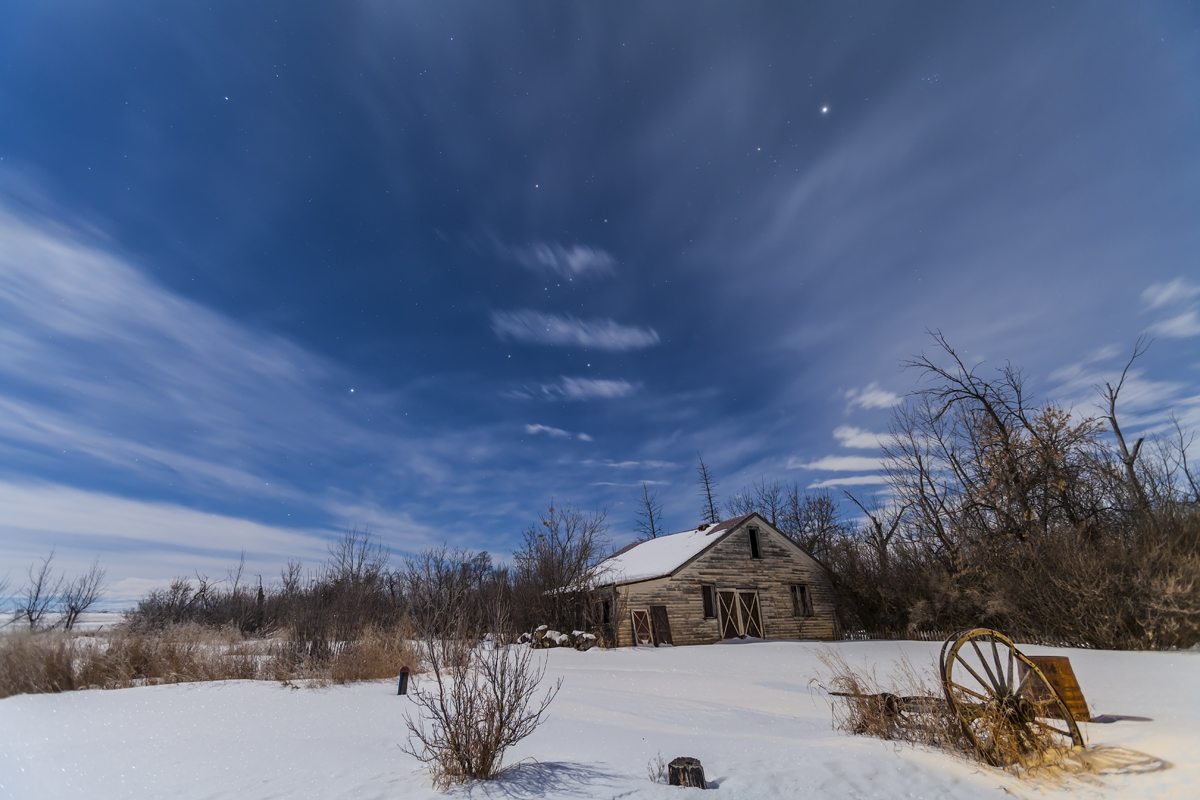
The night before I headed south out of the little town of Val Marie to a favourite spot high on the hill overlooking the Park. It is called Two Trees, but now only one tree remains! It made a fine foreground for the classic “lone tree and Milky Way” nightscape.
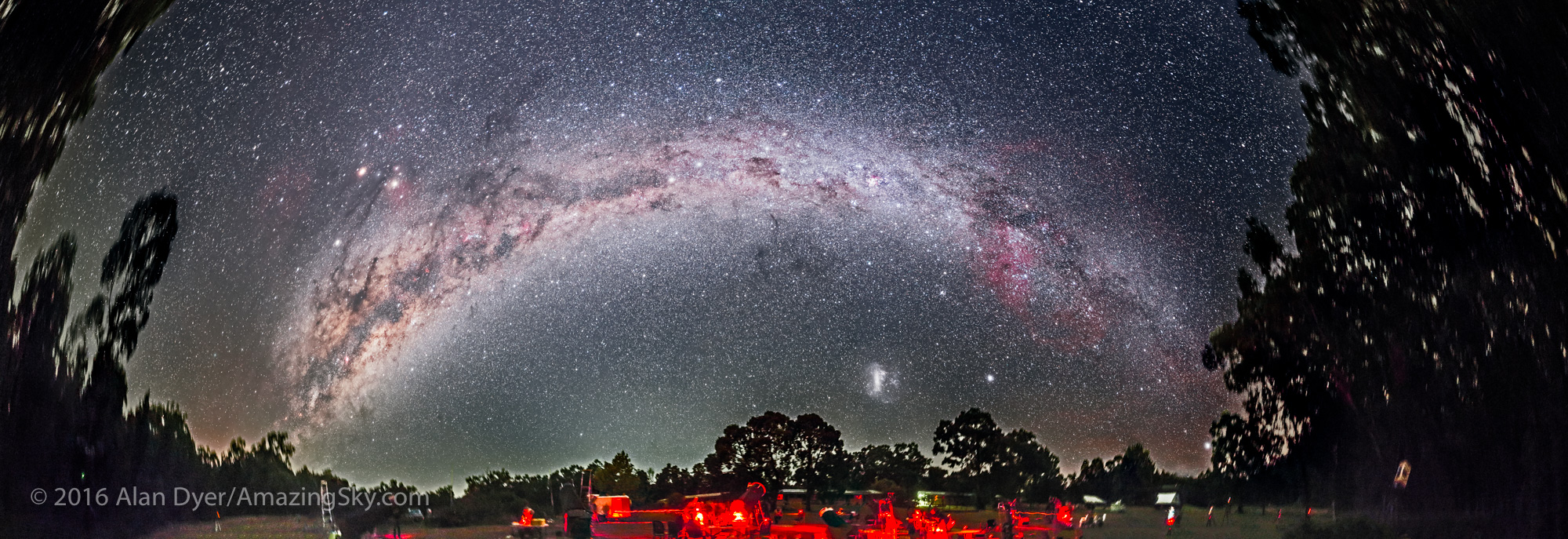
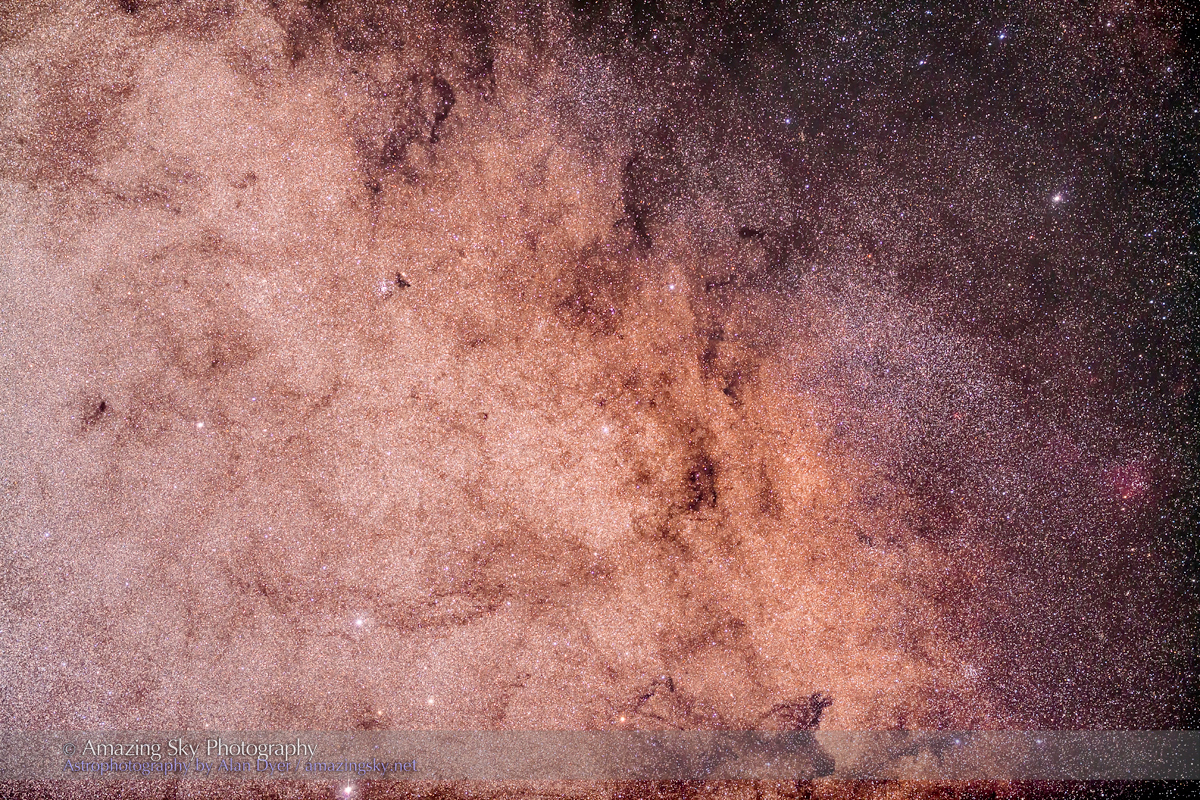
In August the galactic centre lies in the southwest quickly setting in the early evening. But from this latitude of 49º N even with it at its highest, the Milky Way core lies low in the south, making for good compositions with foregrounds below.
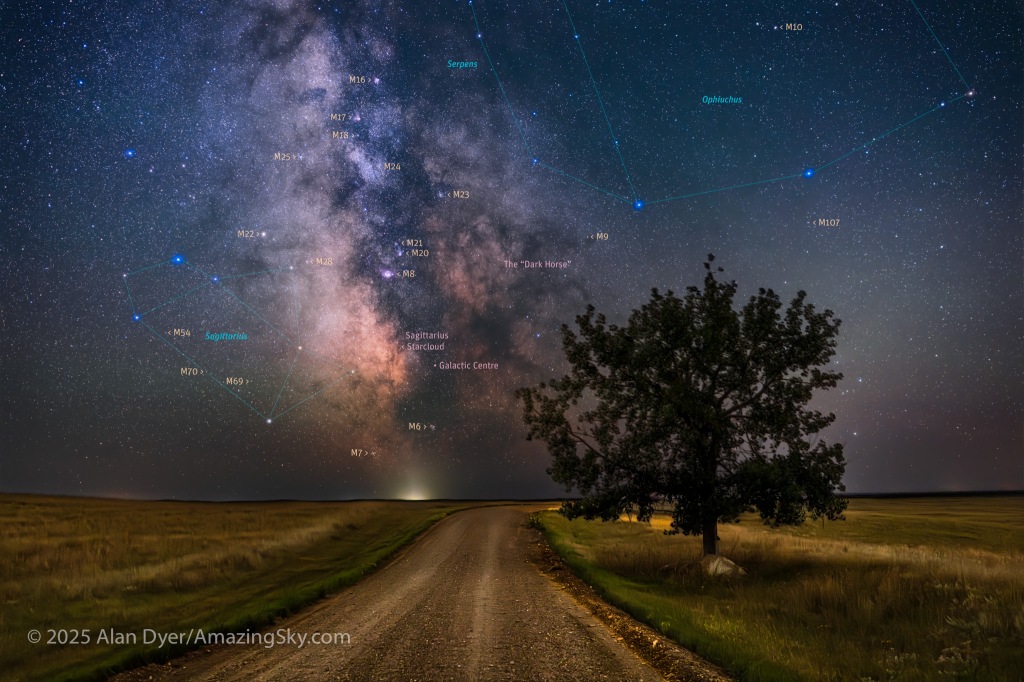
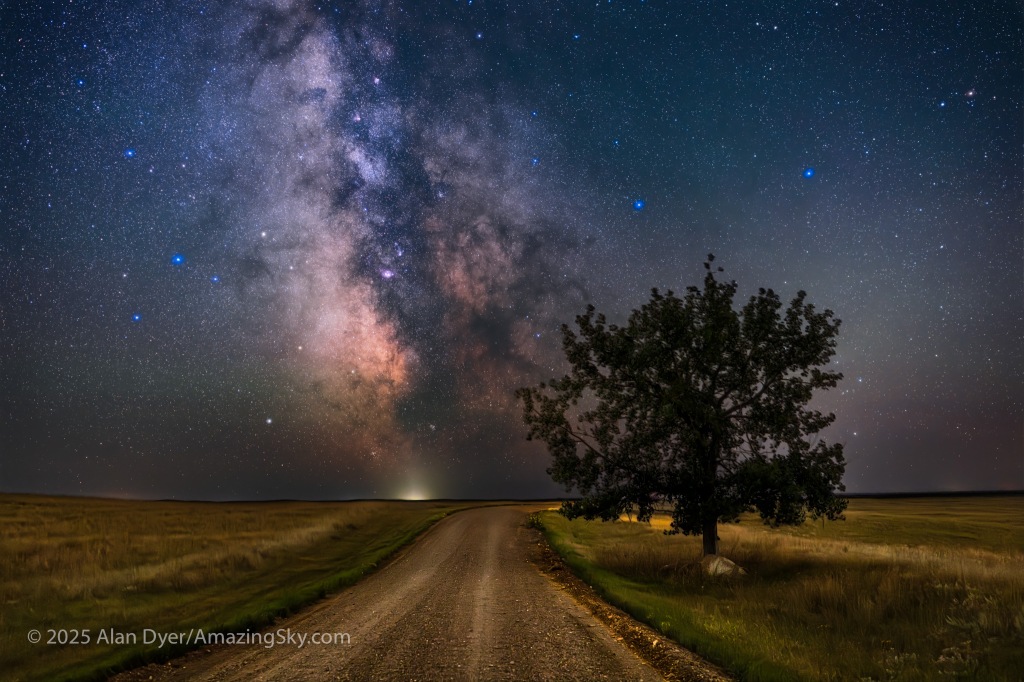


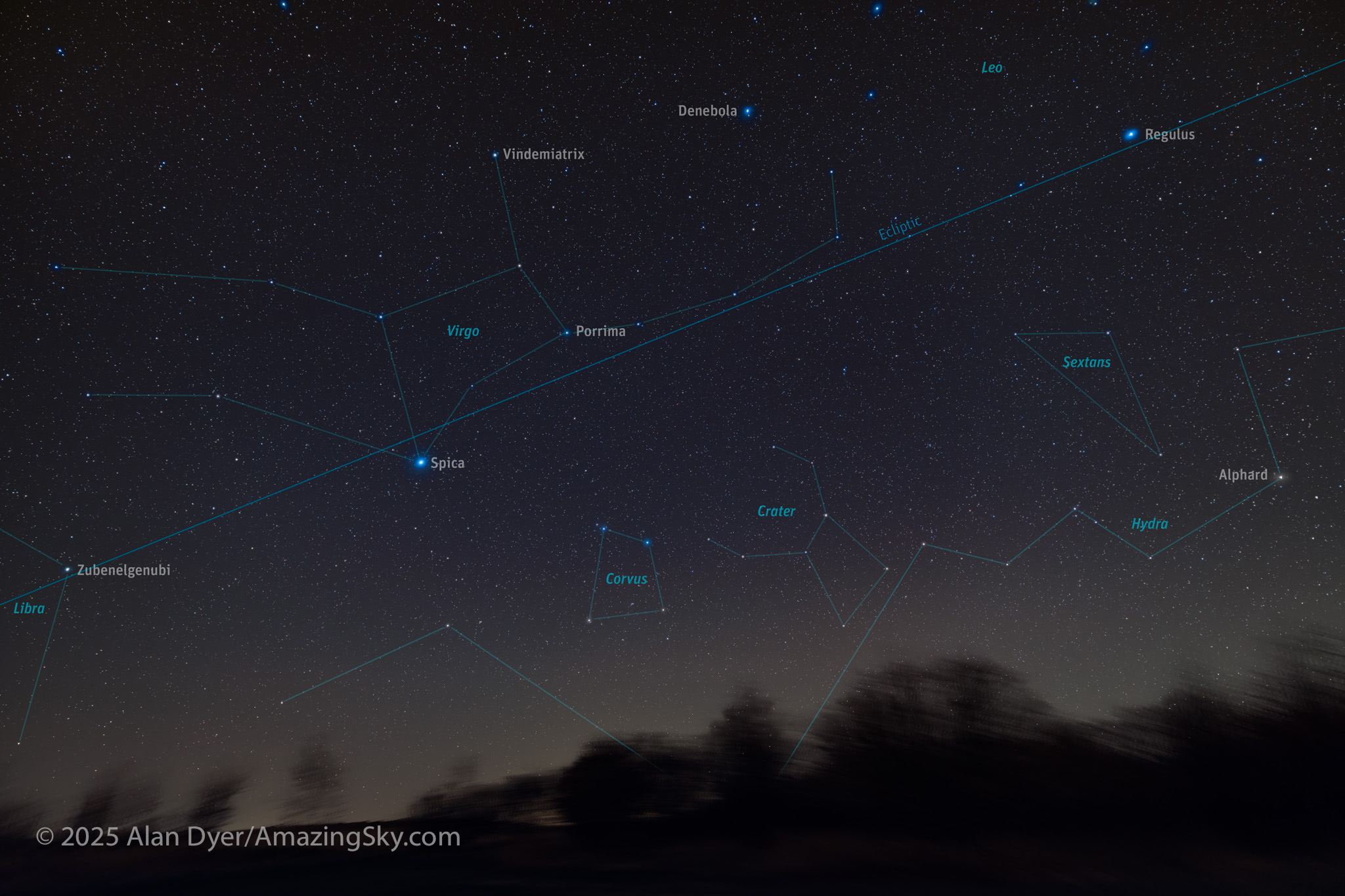
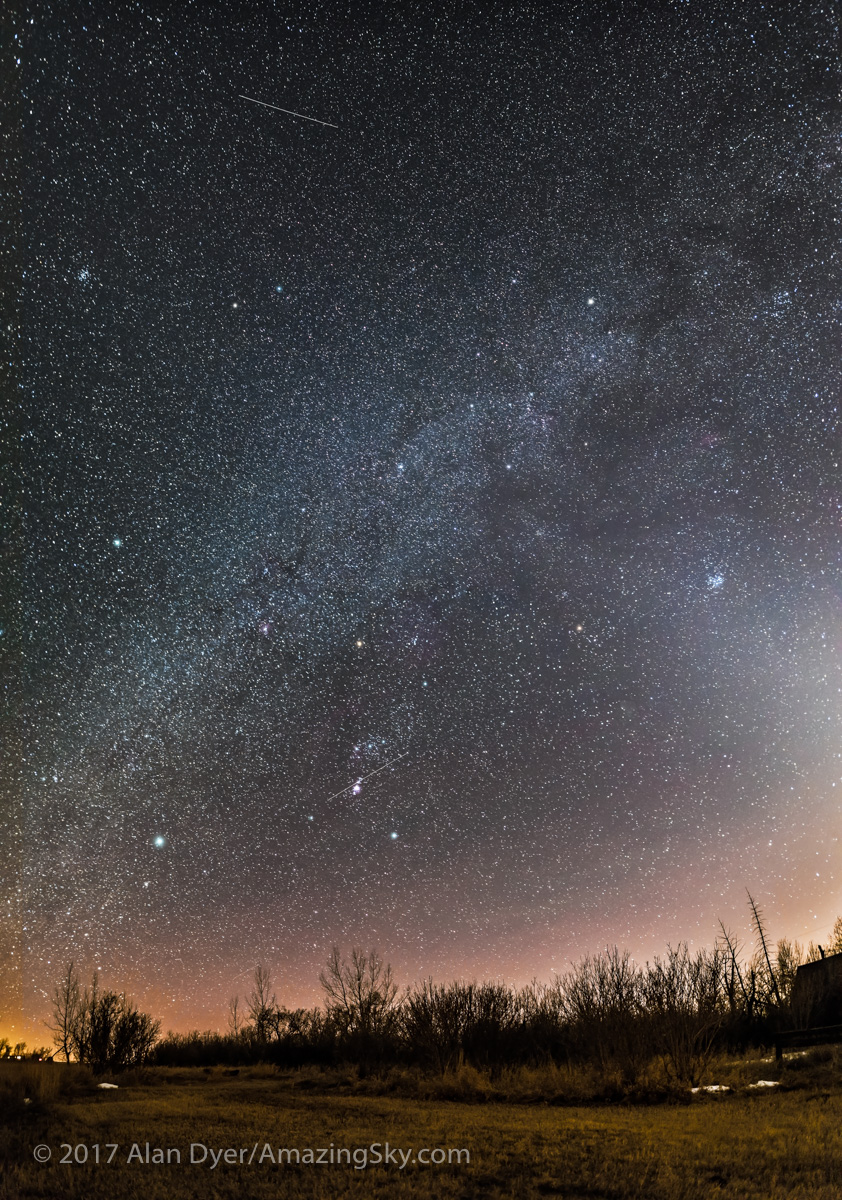
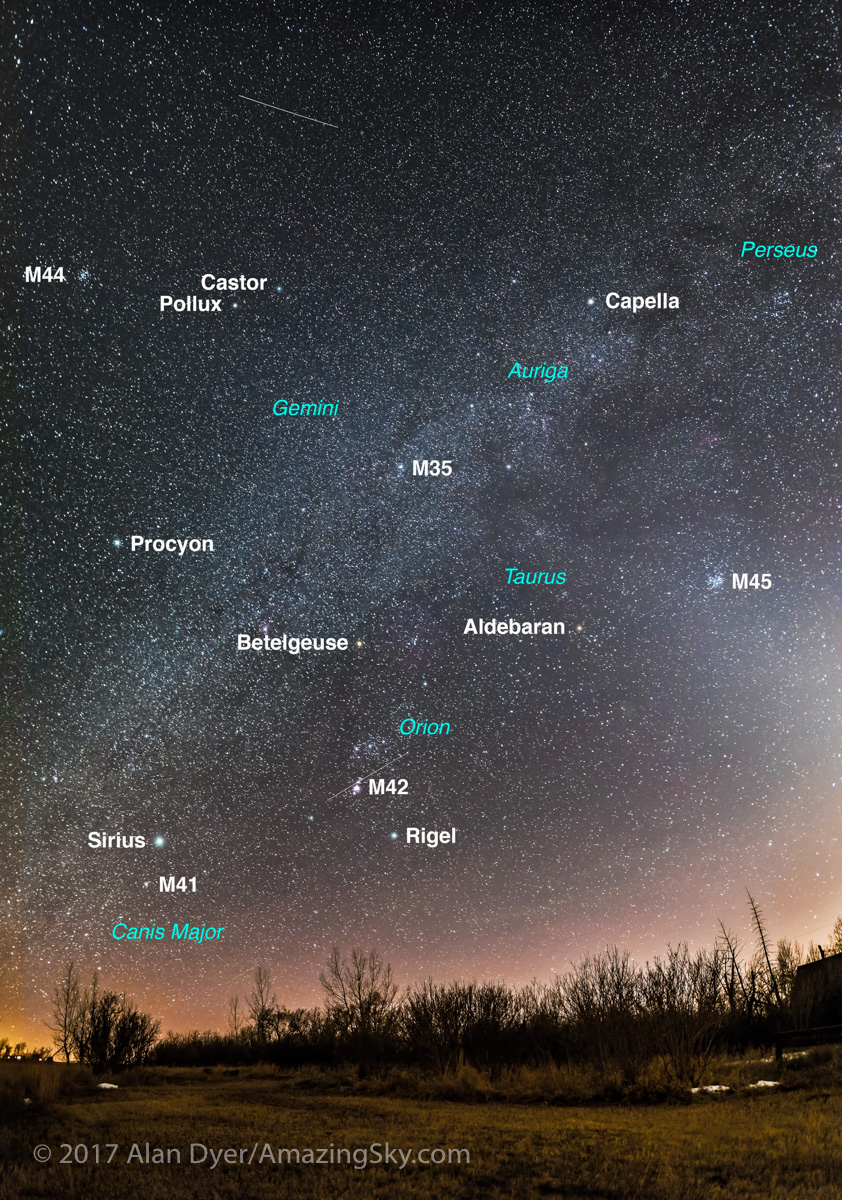
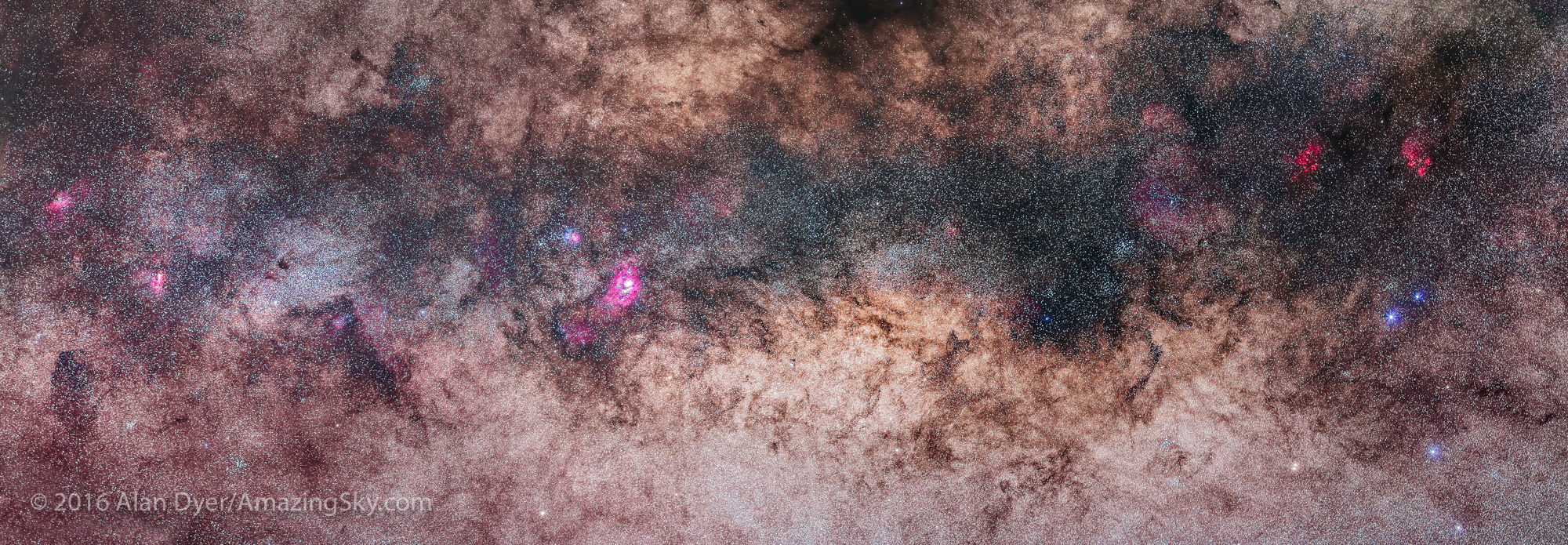
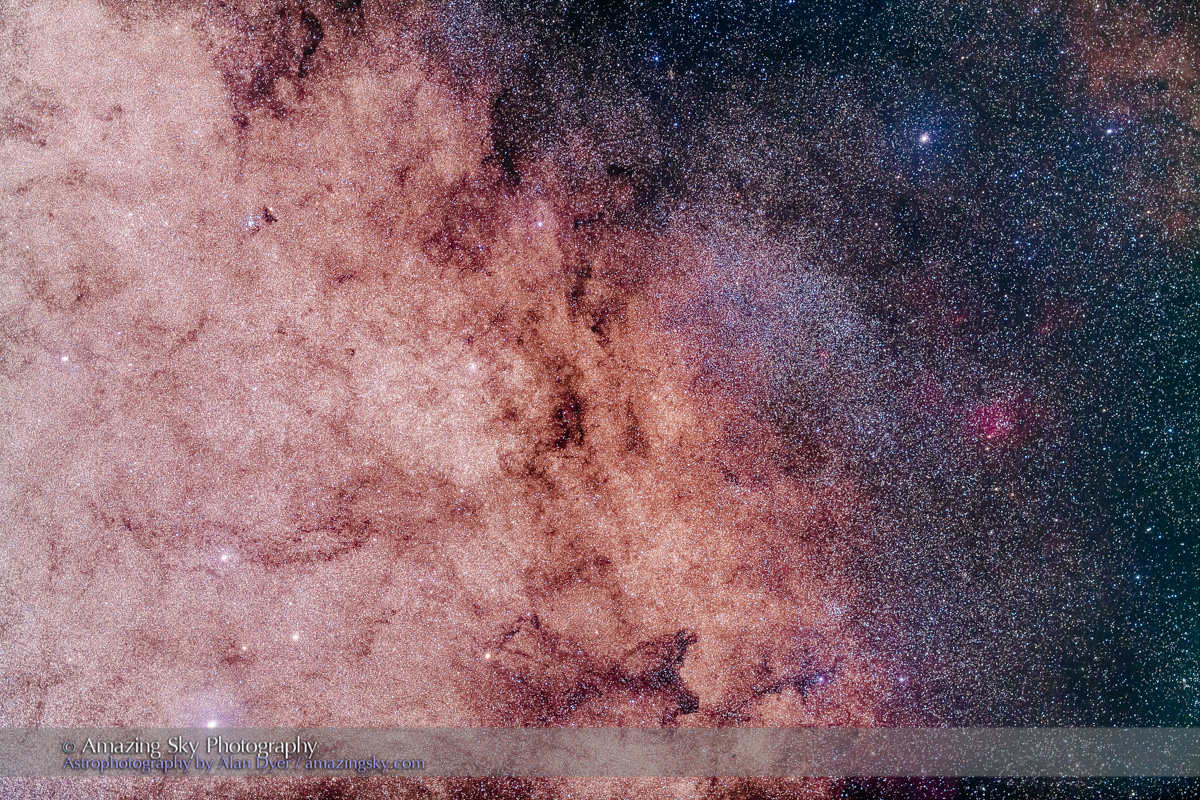
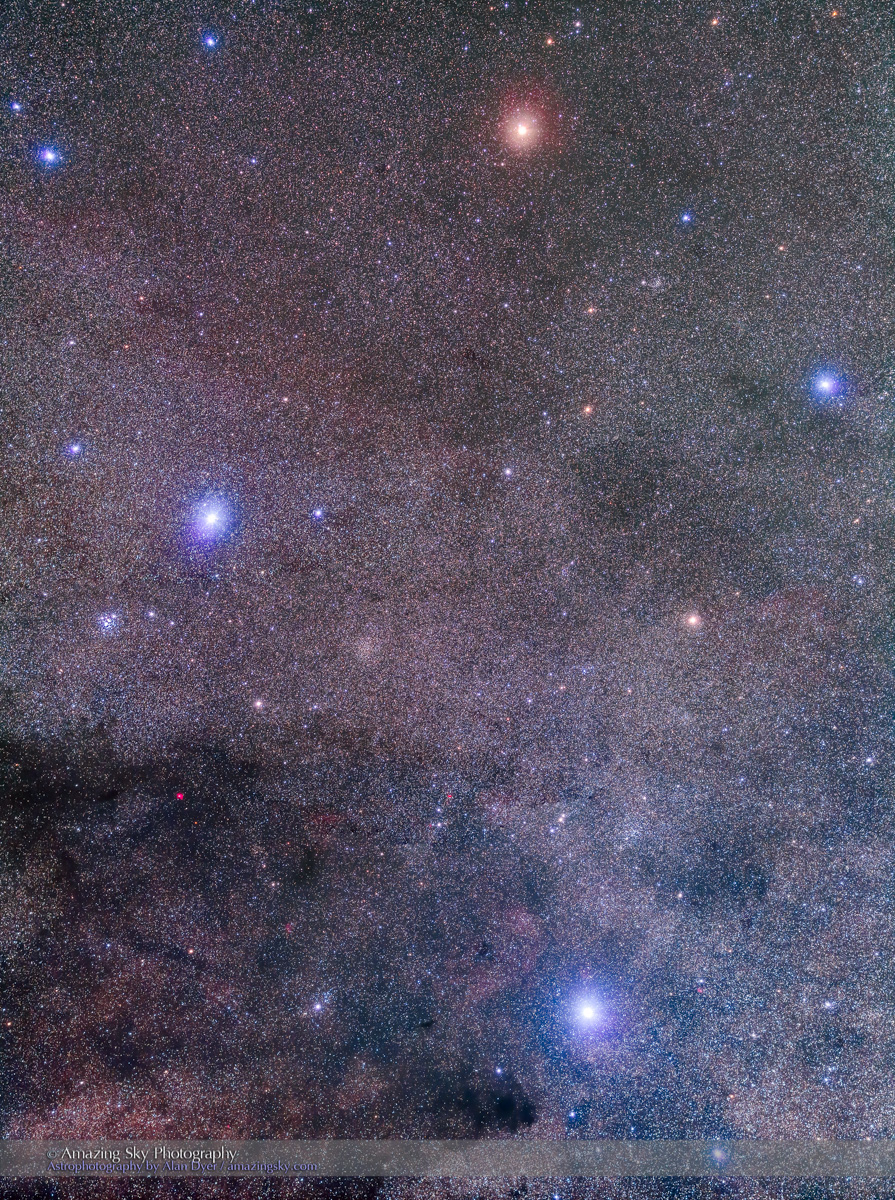
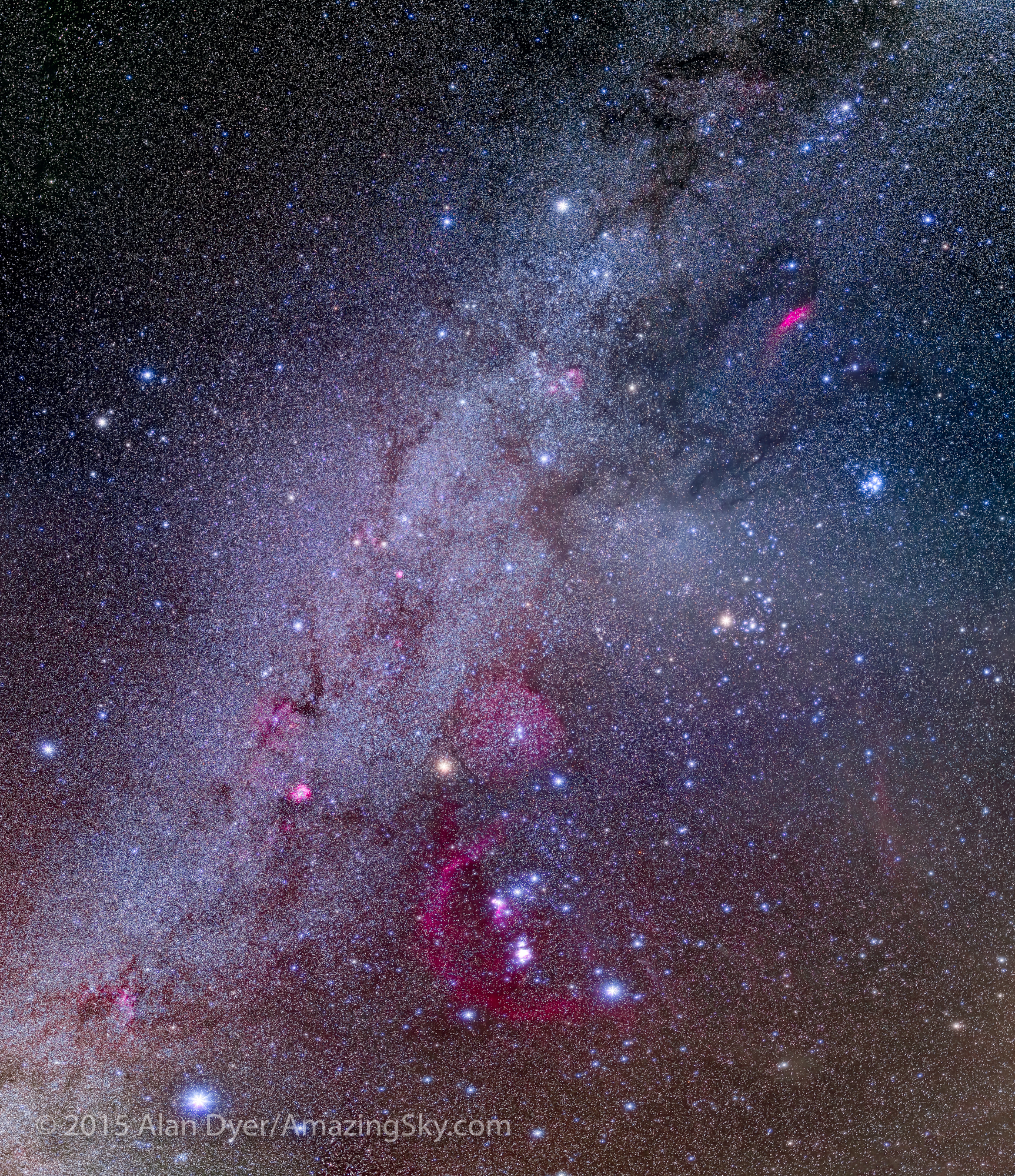
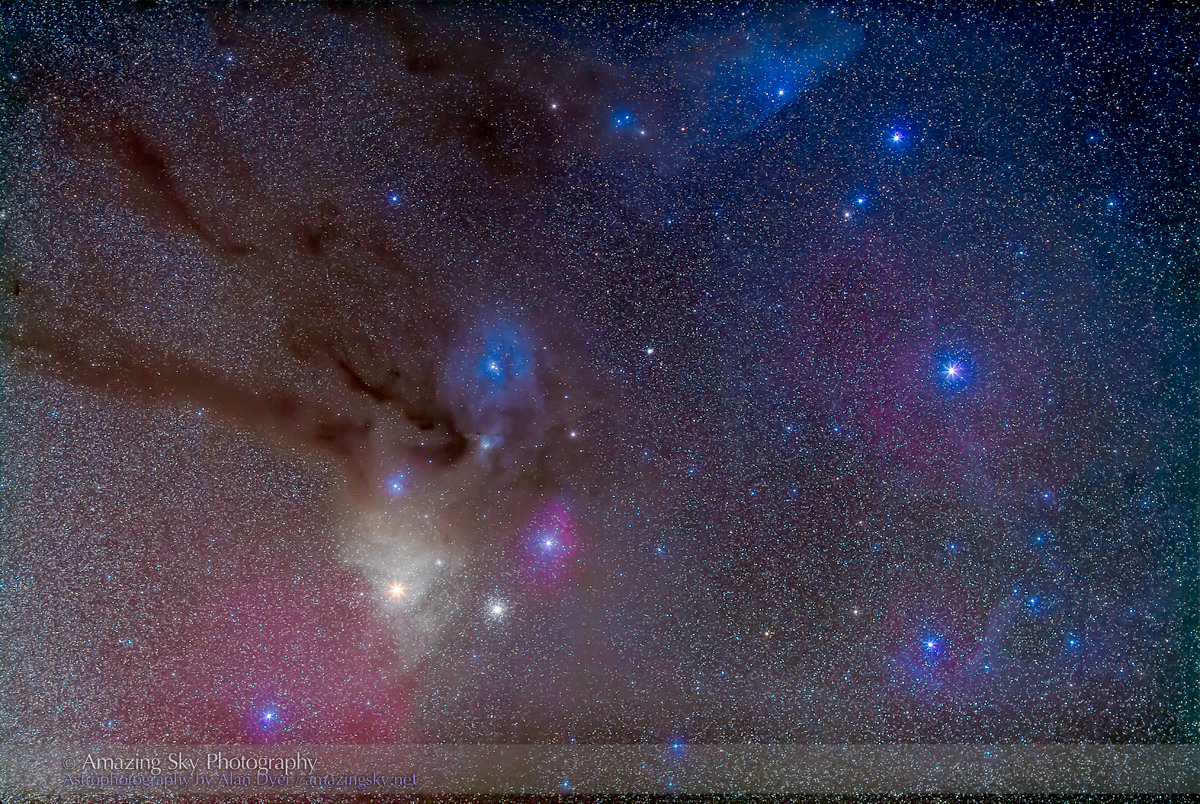
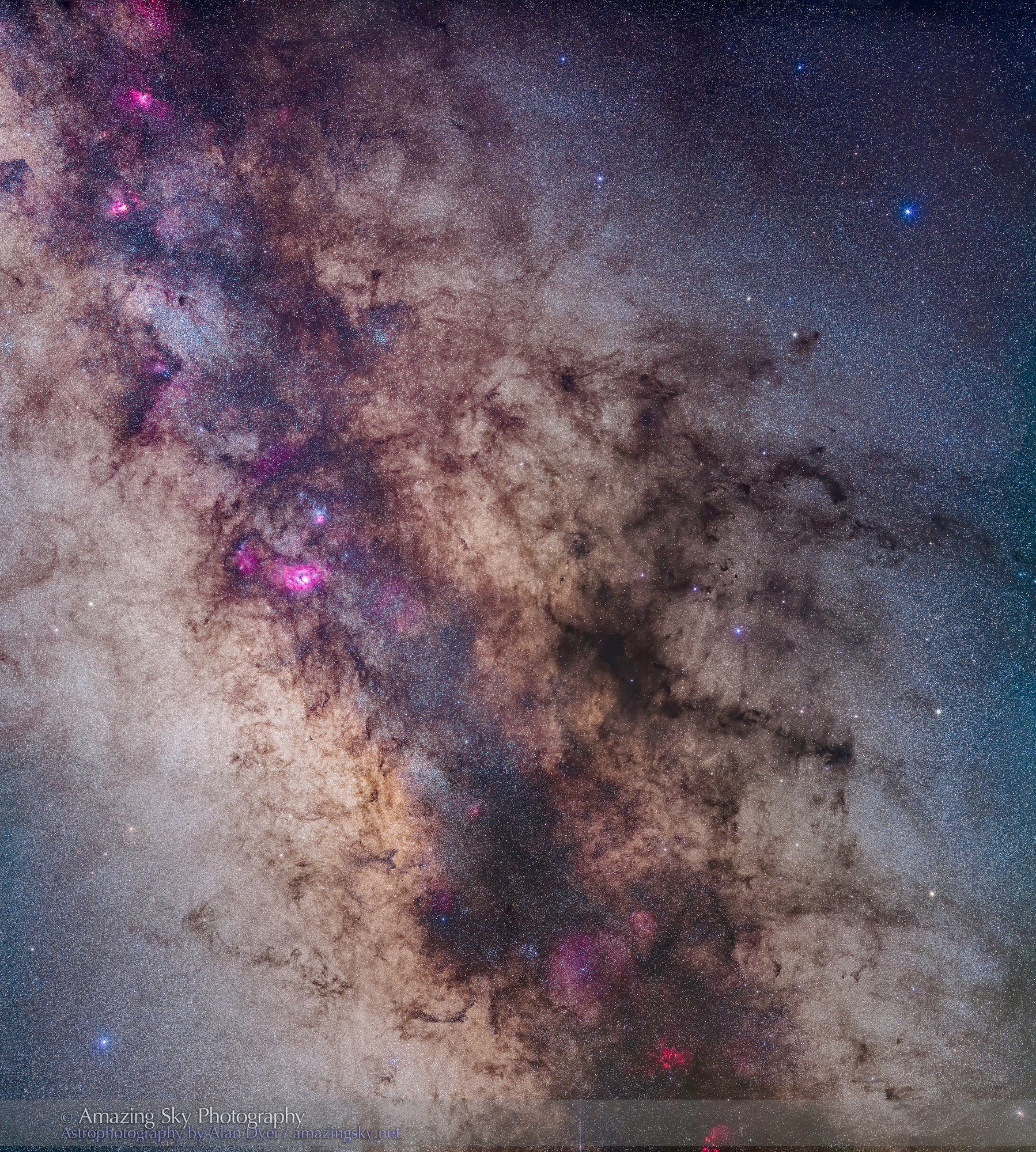
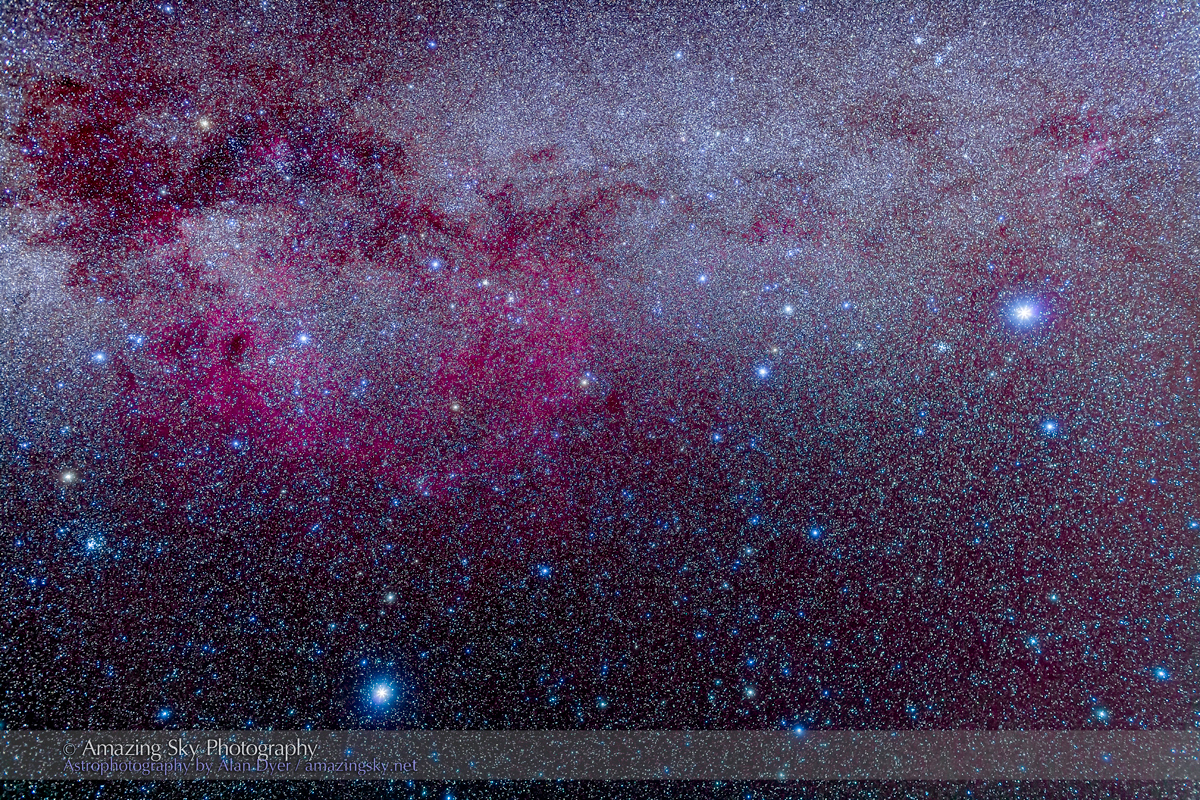
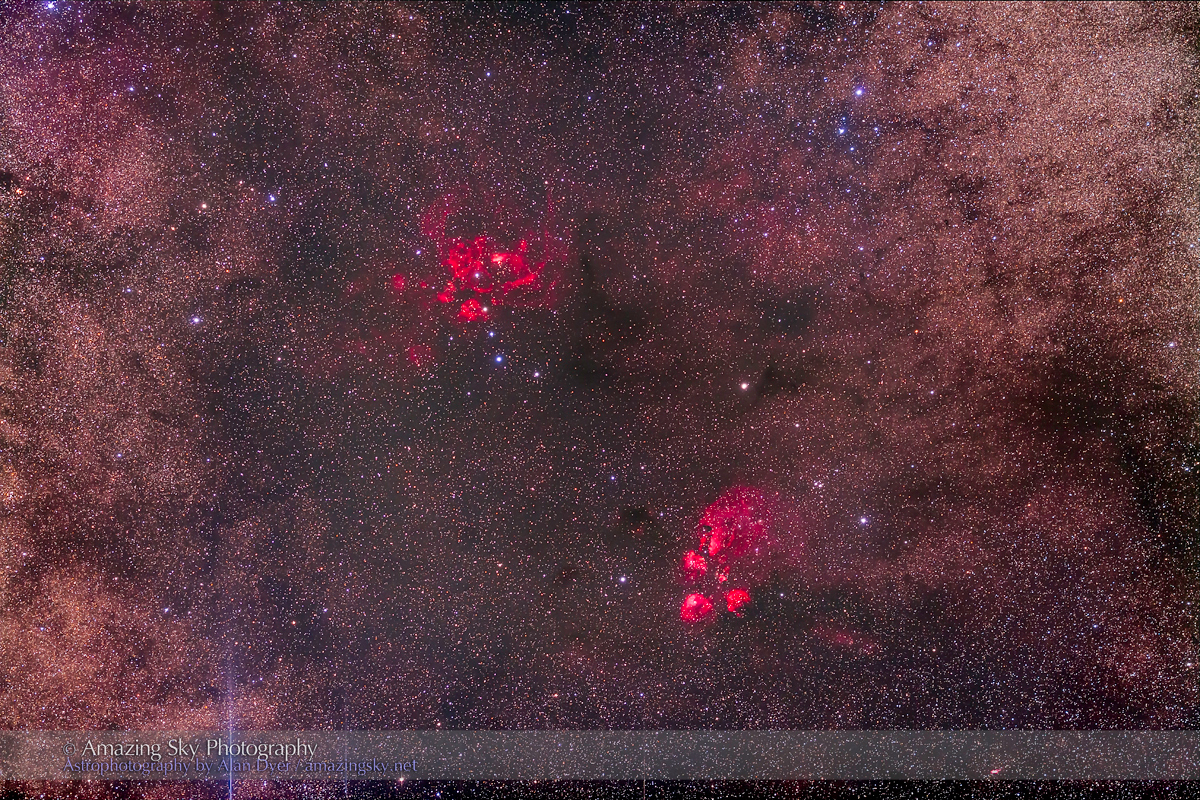
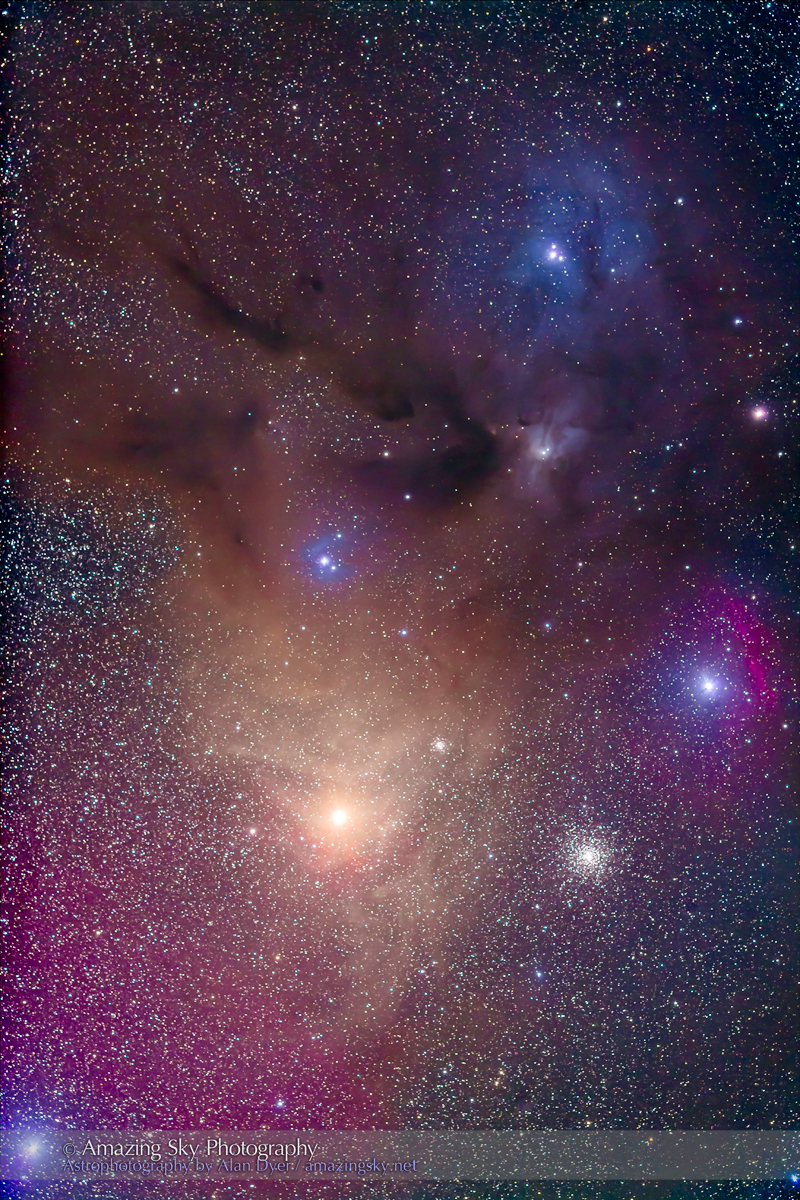
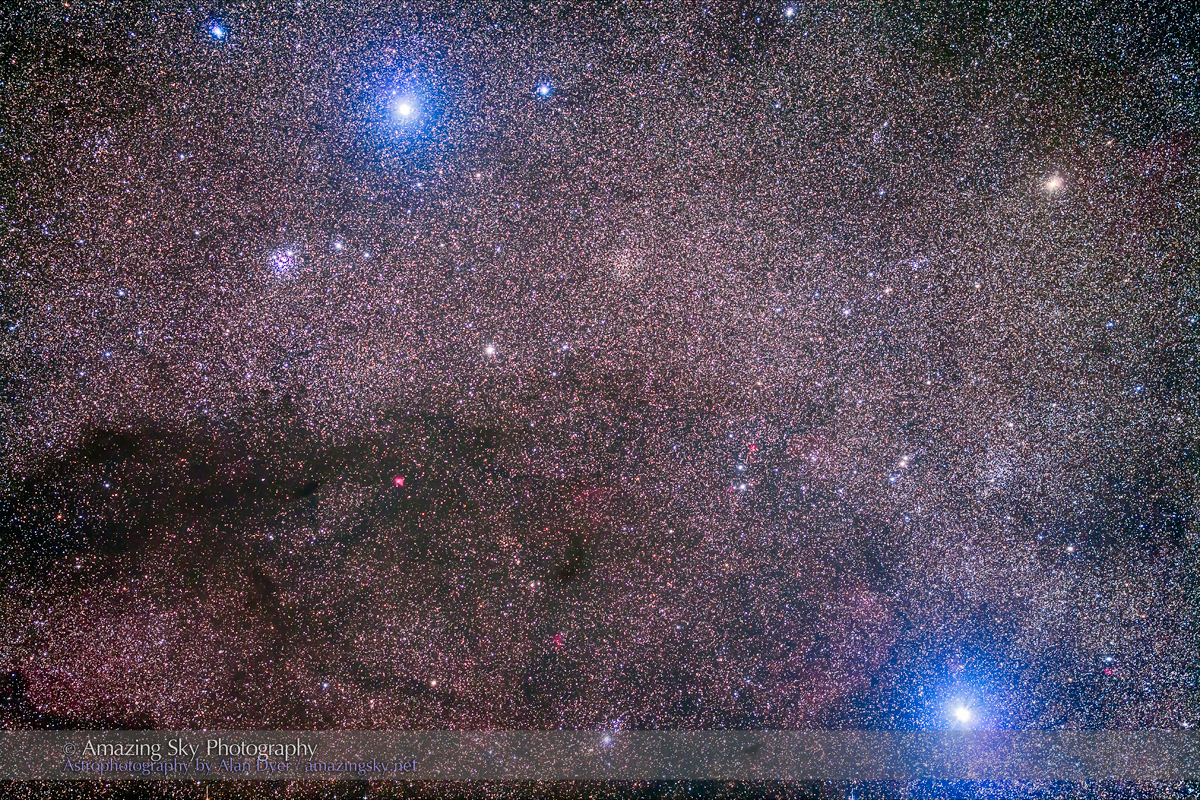
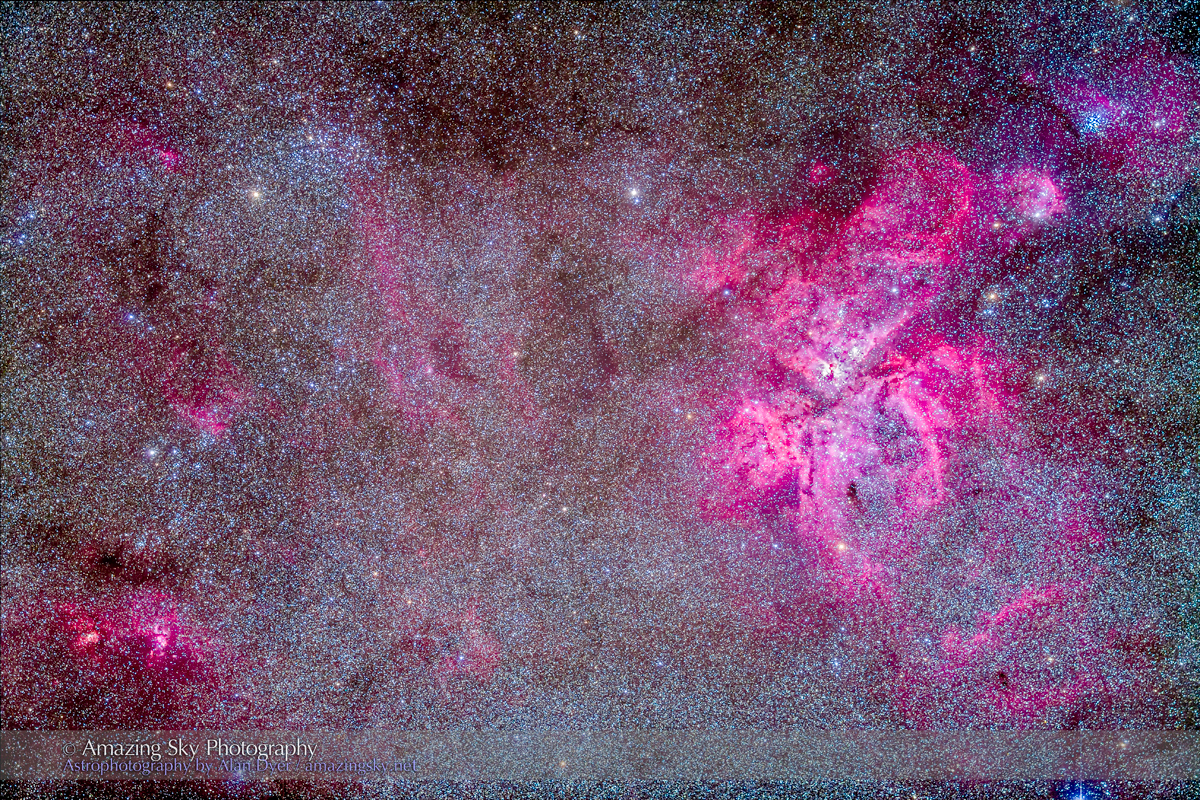
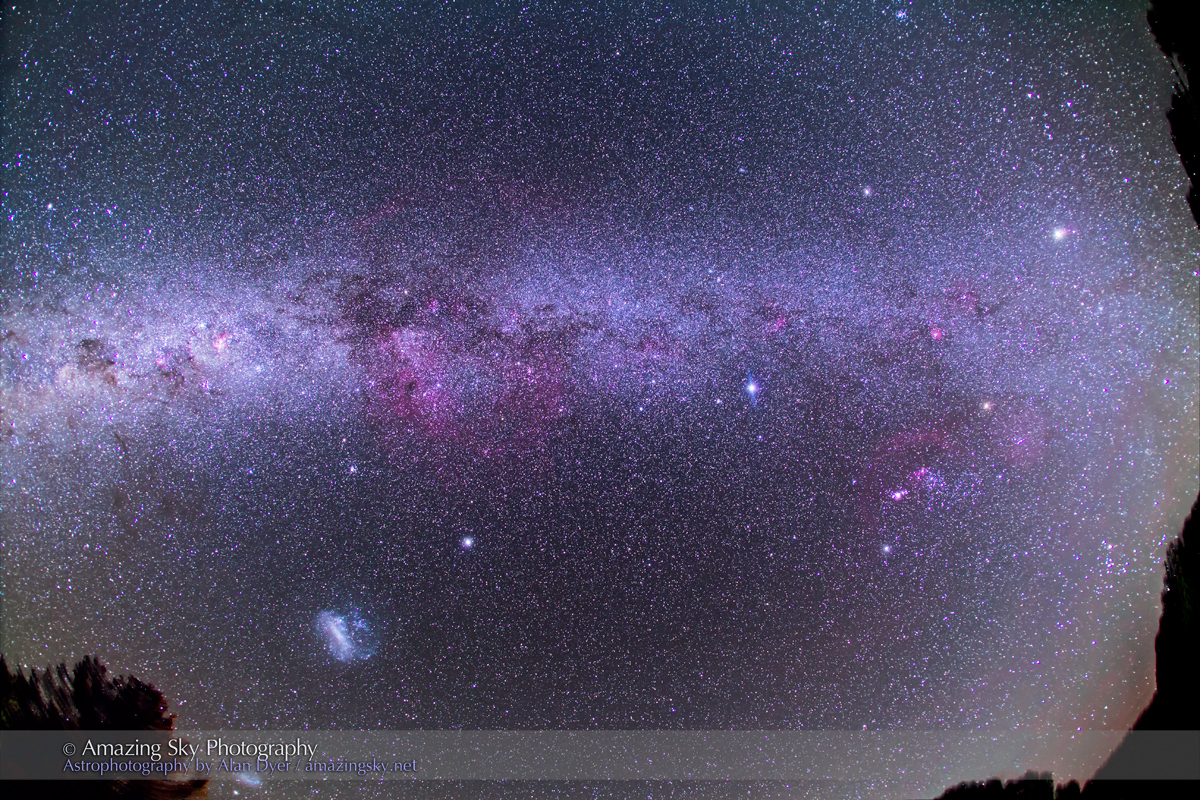
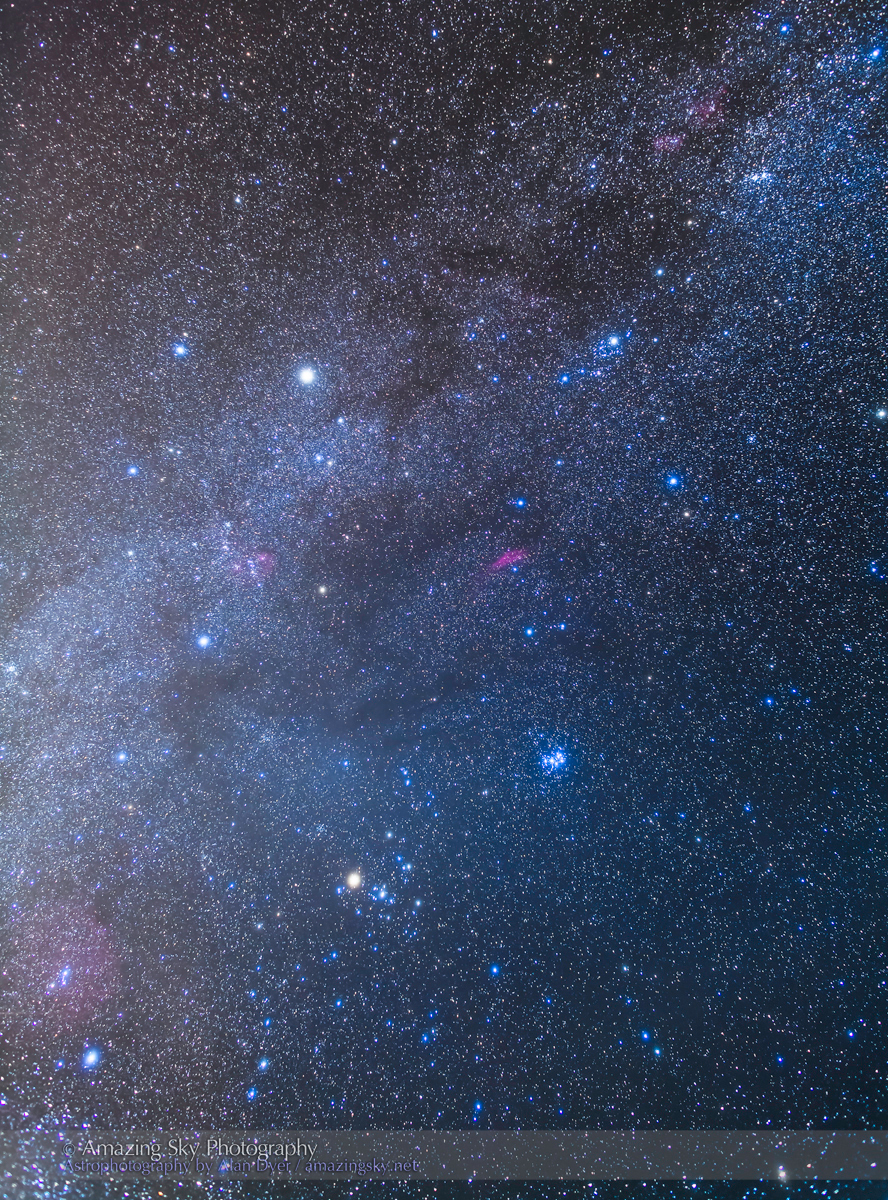
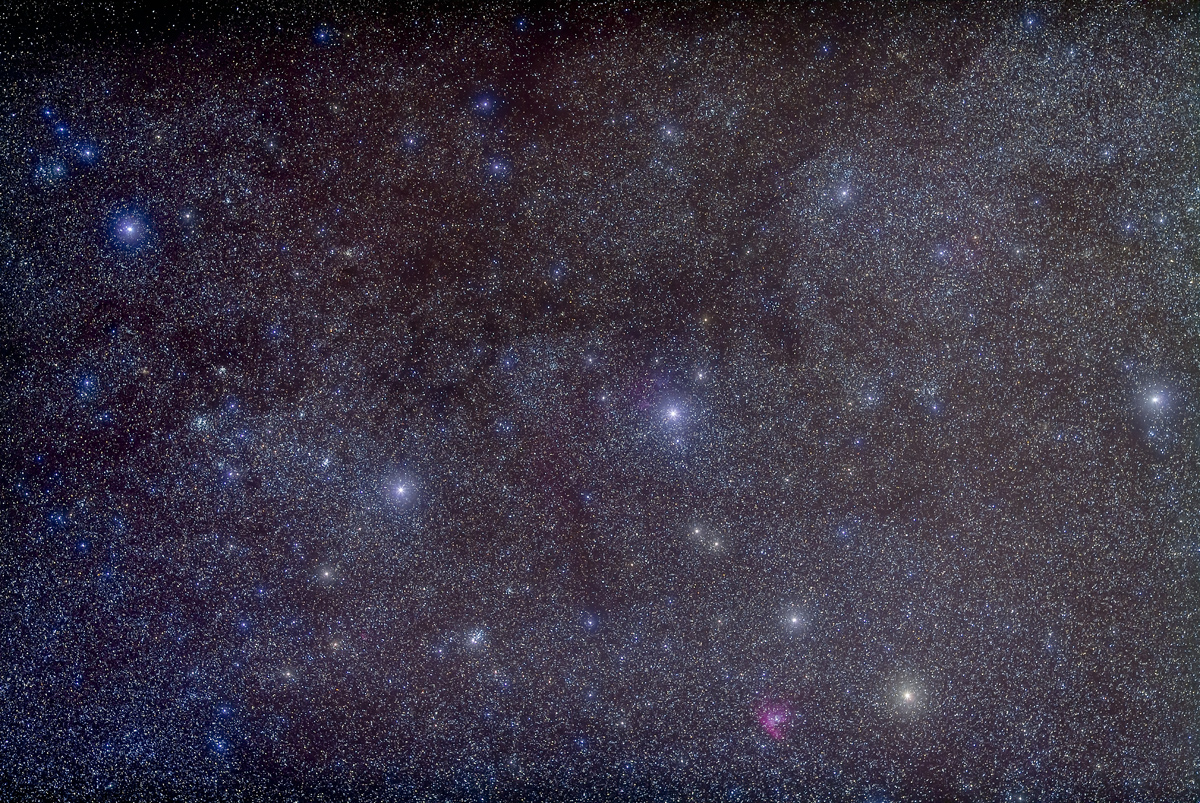
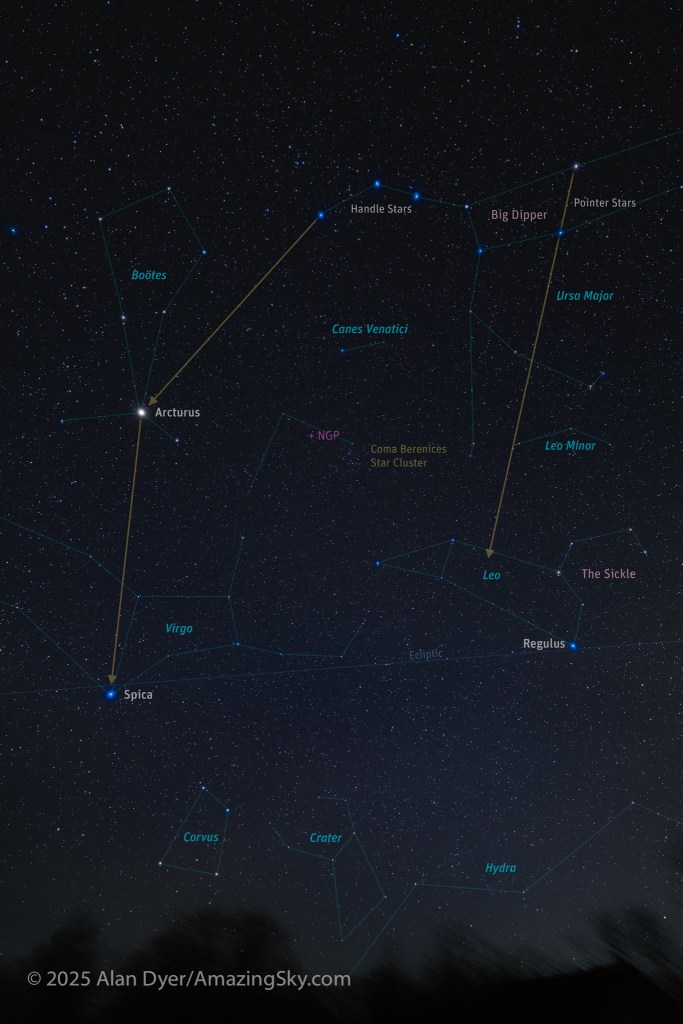
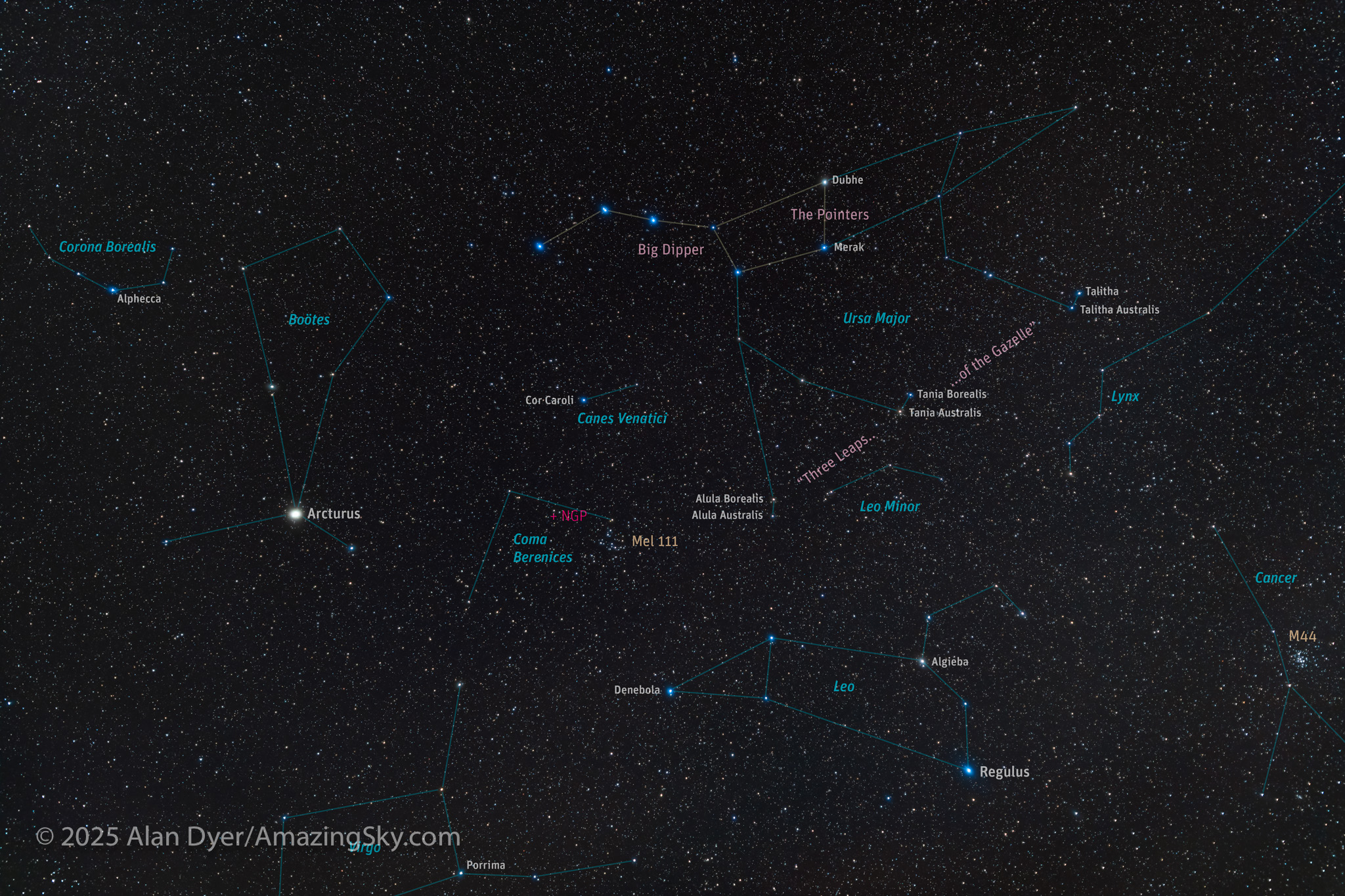
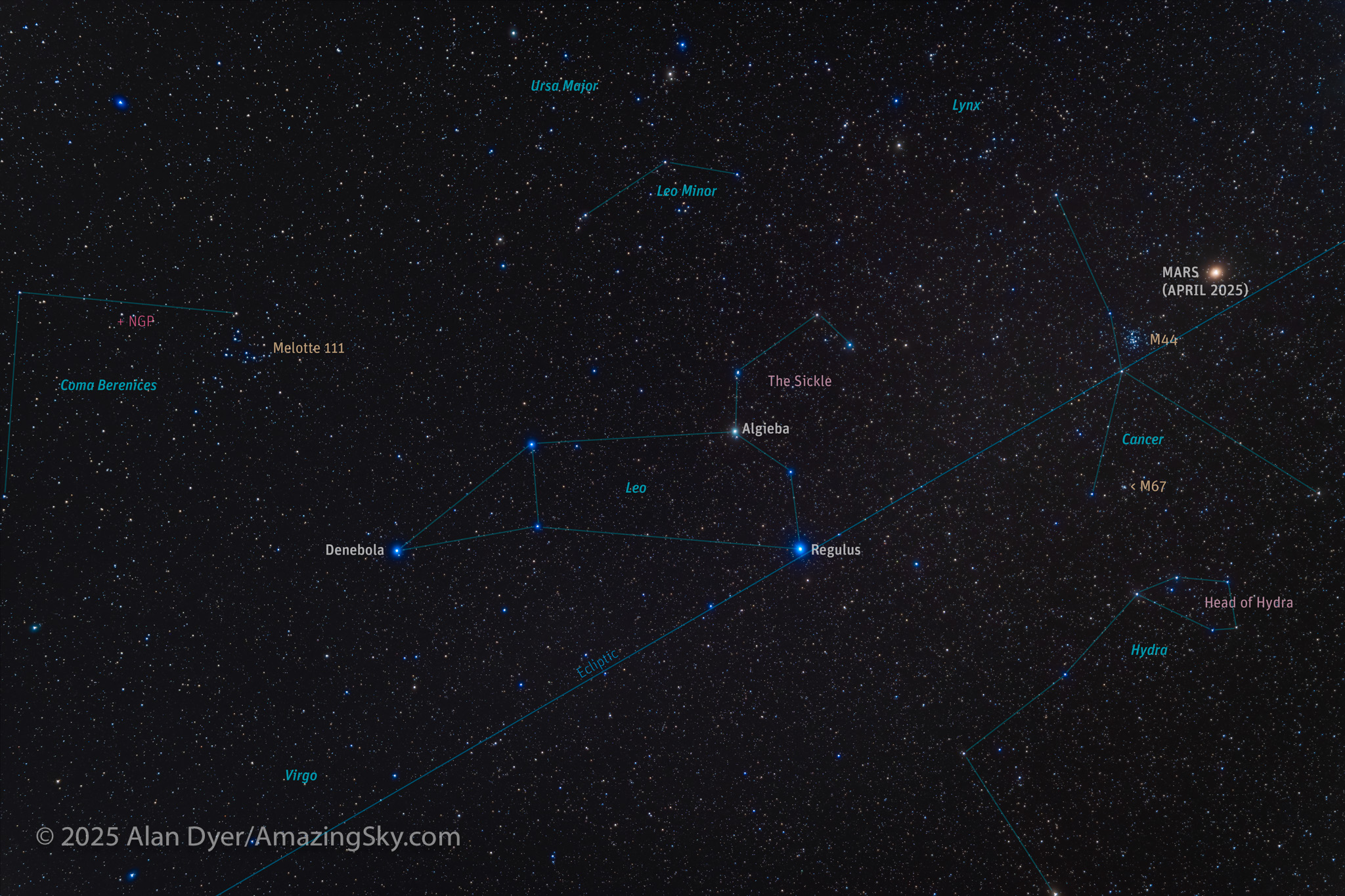
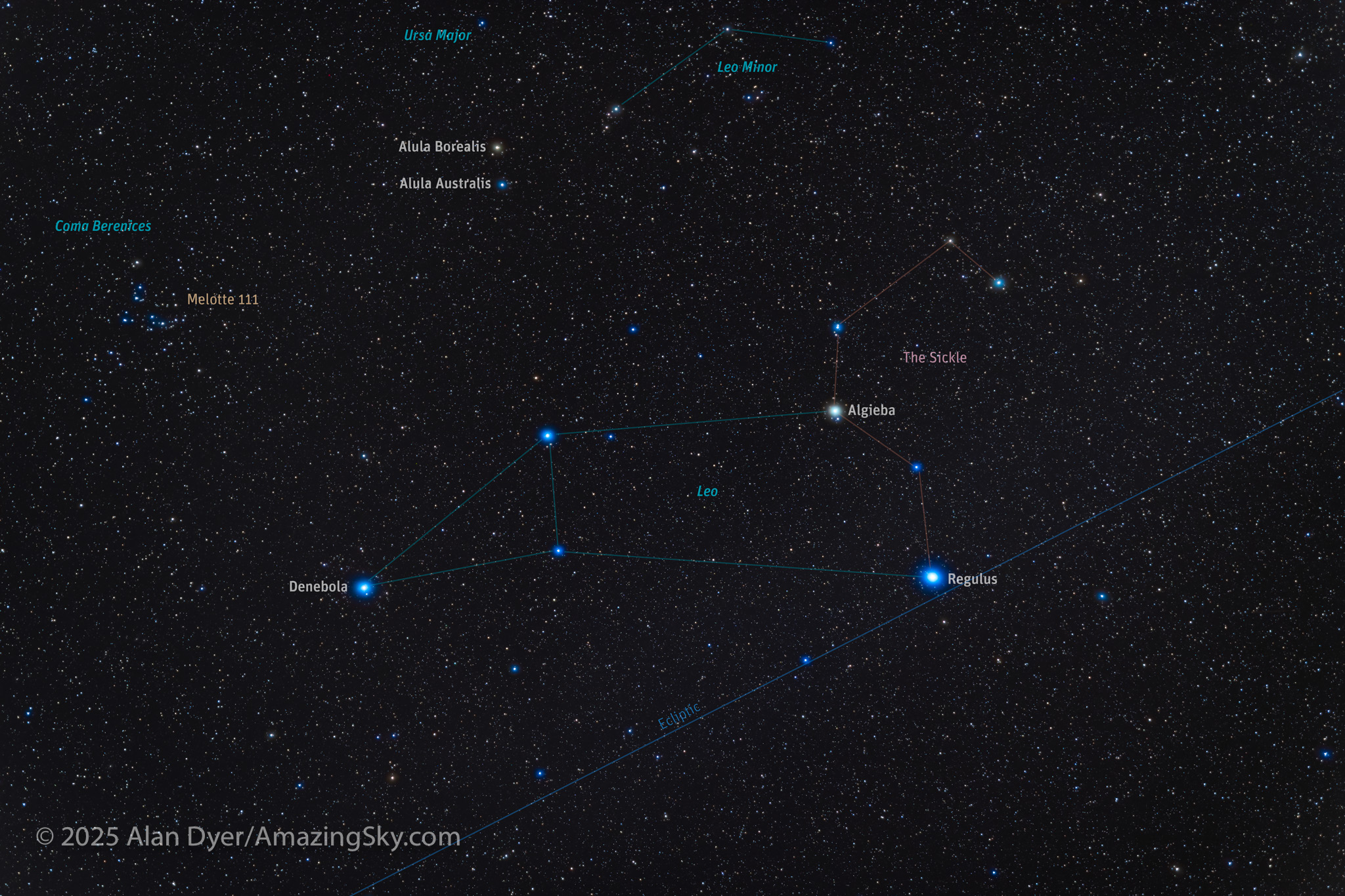
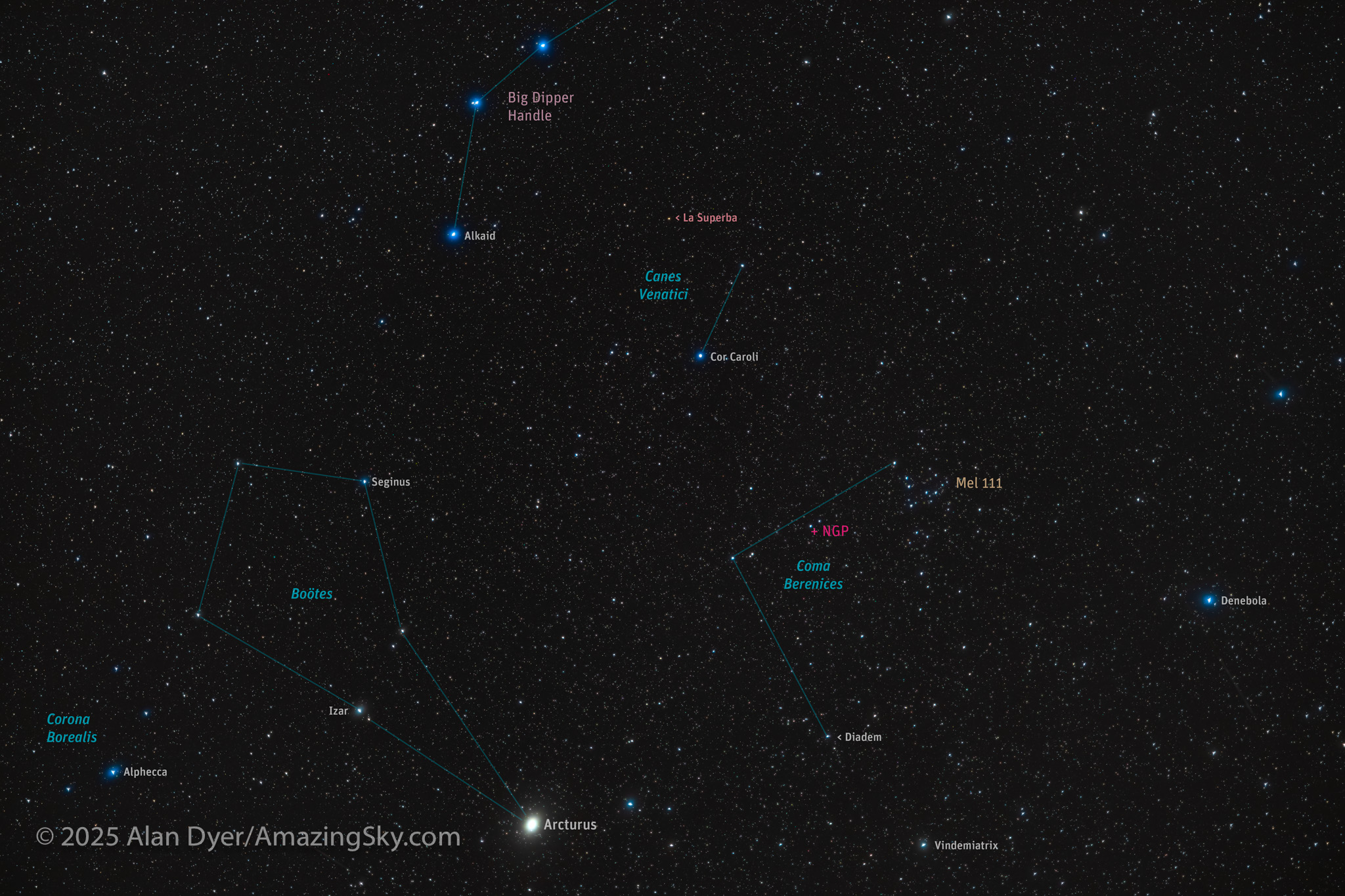
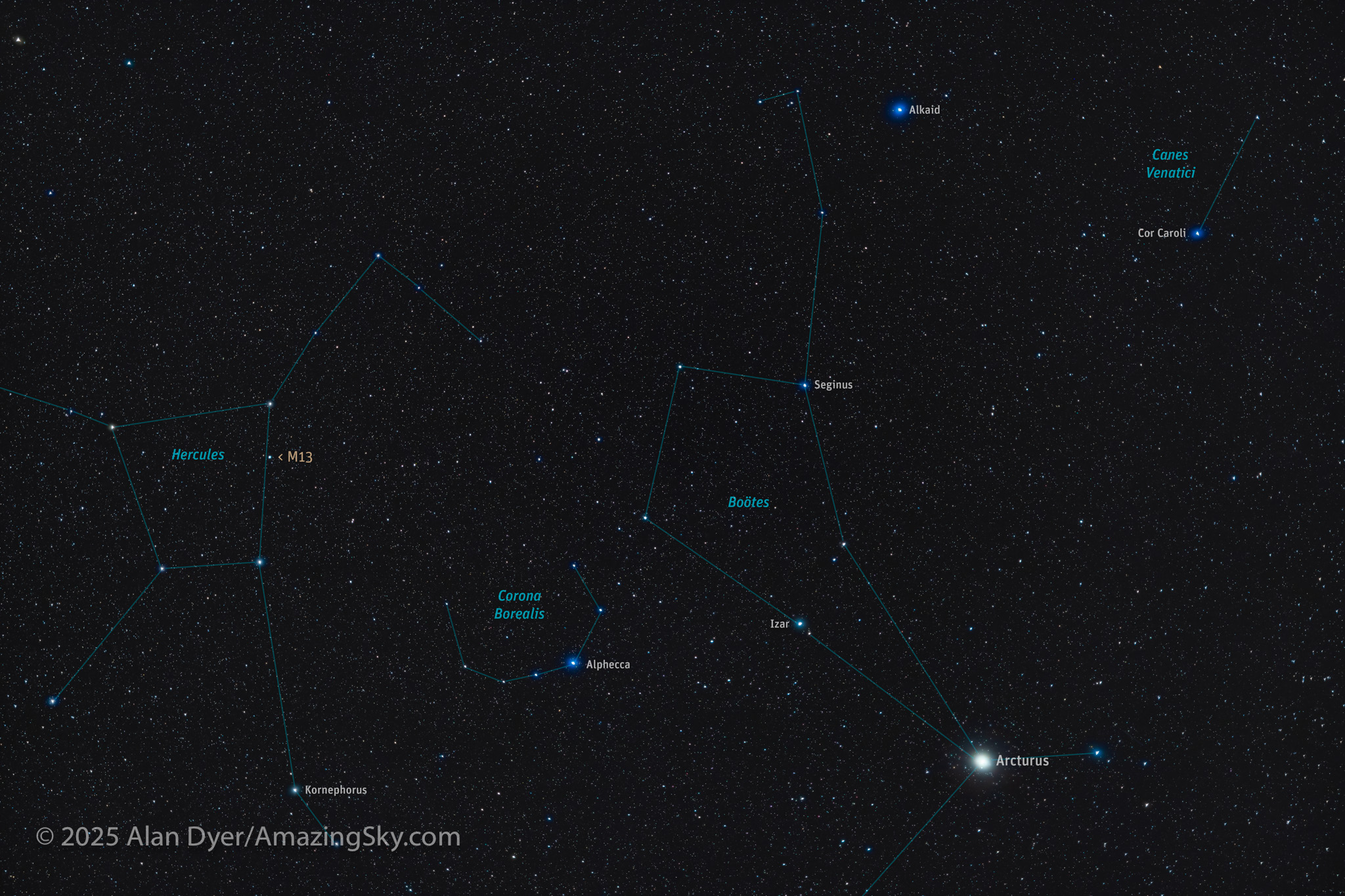
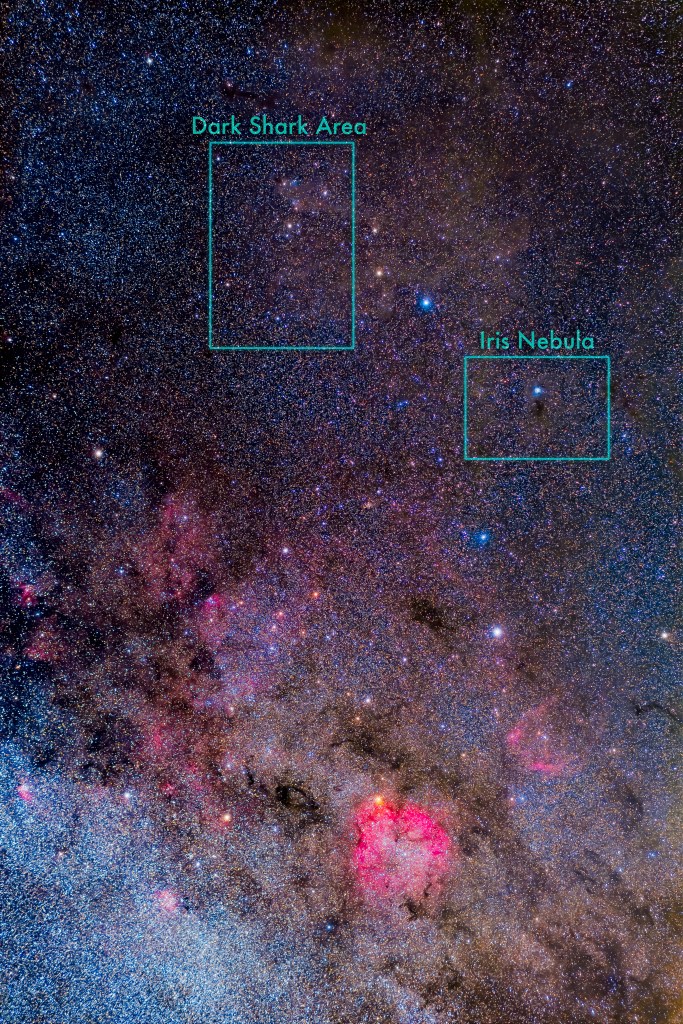
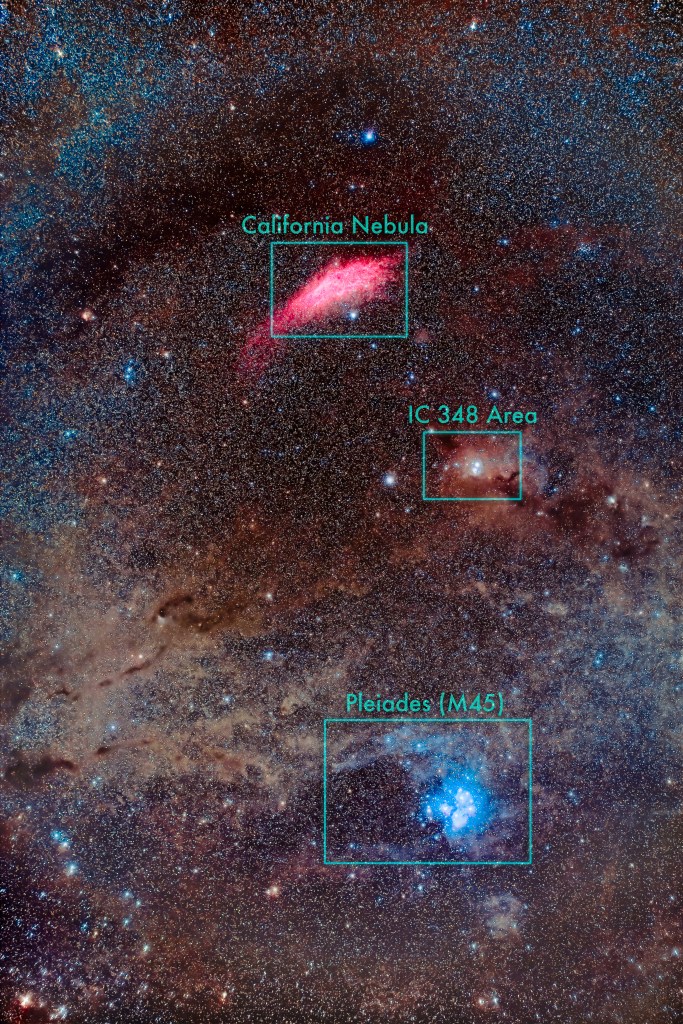
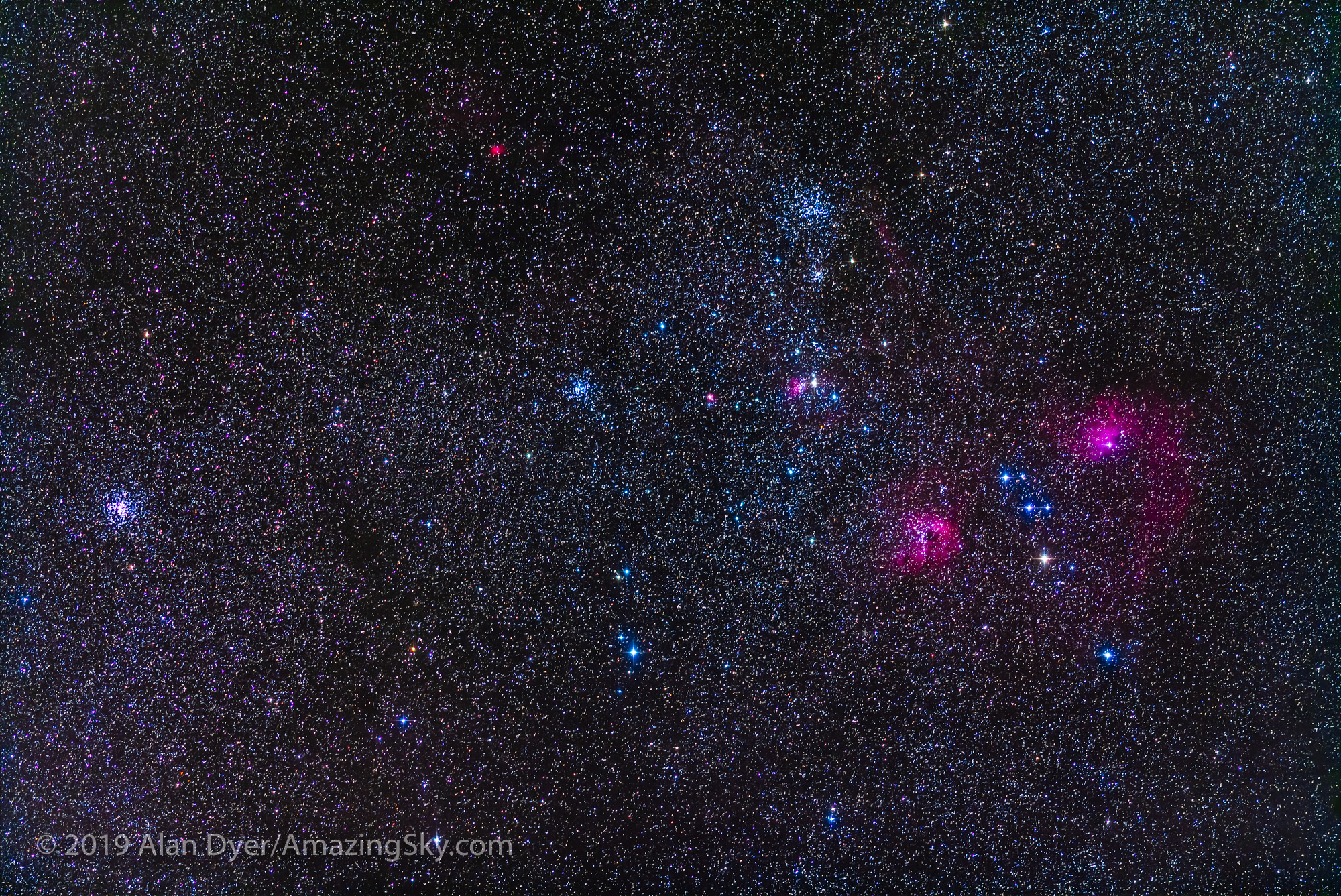
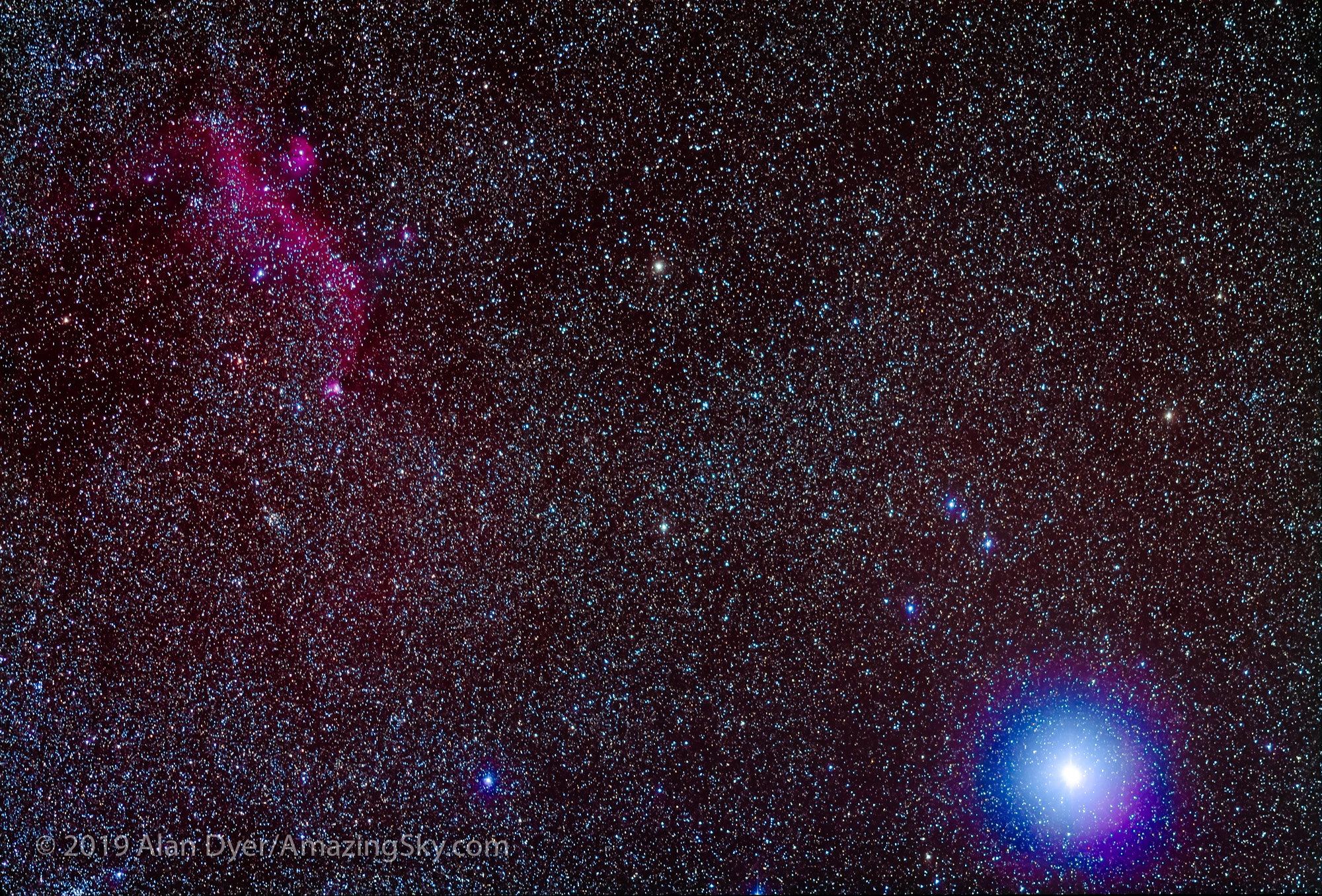
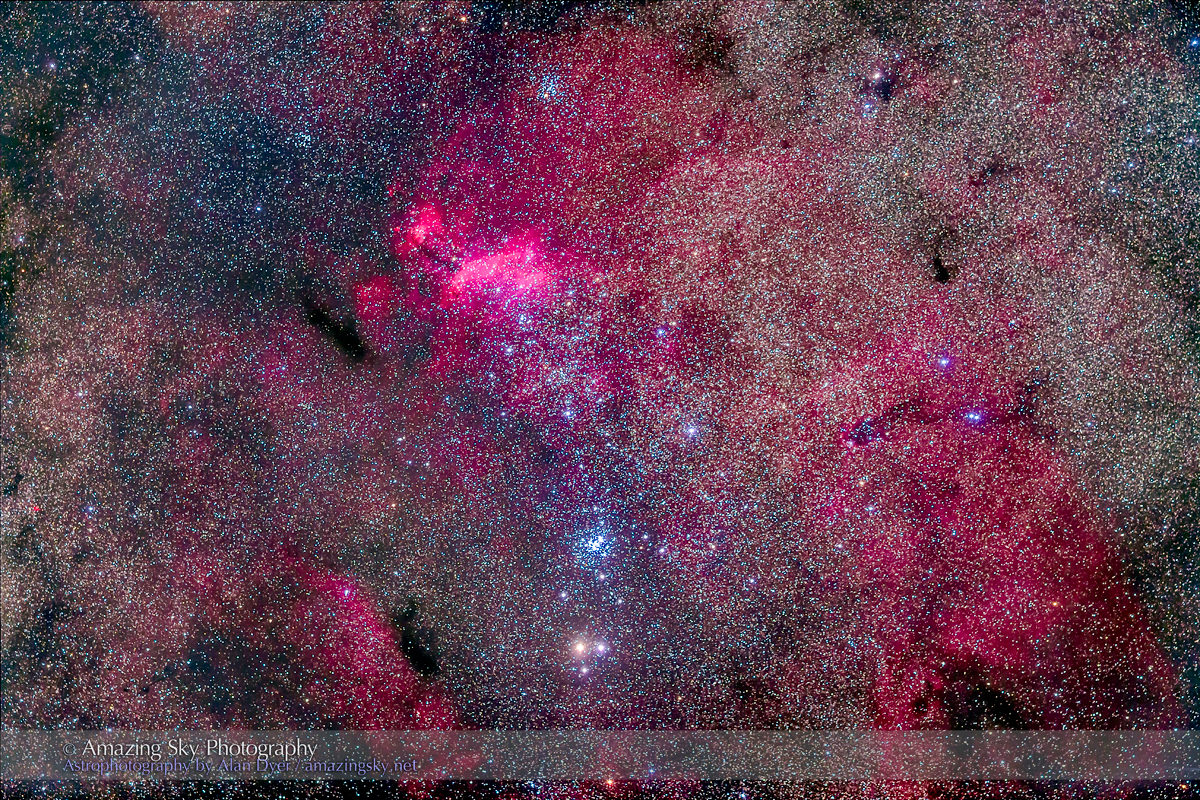
Here I present a “landscape” version of the image above, in versions with and without labels to indicate all the rich nebulas and star clusters in this area of sky in Sagittarius the Archer, home of the Milky Way core. Tap on the images to bring them up full screen.
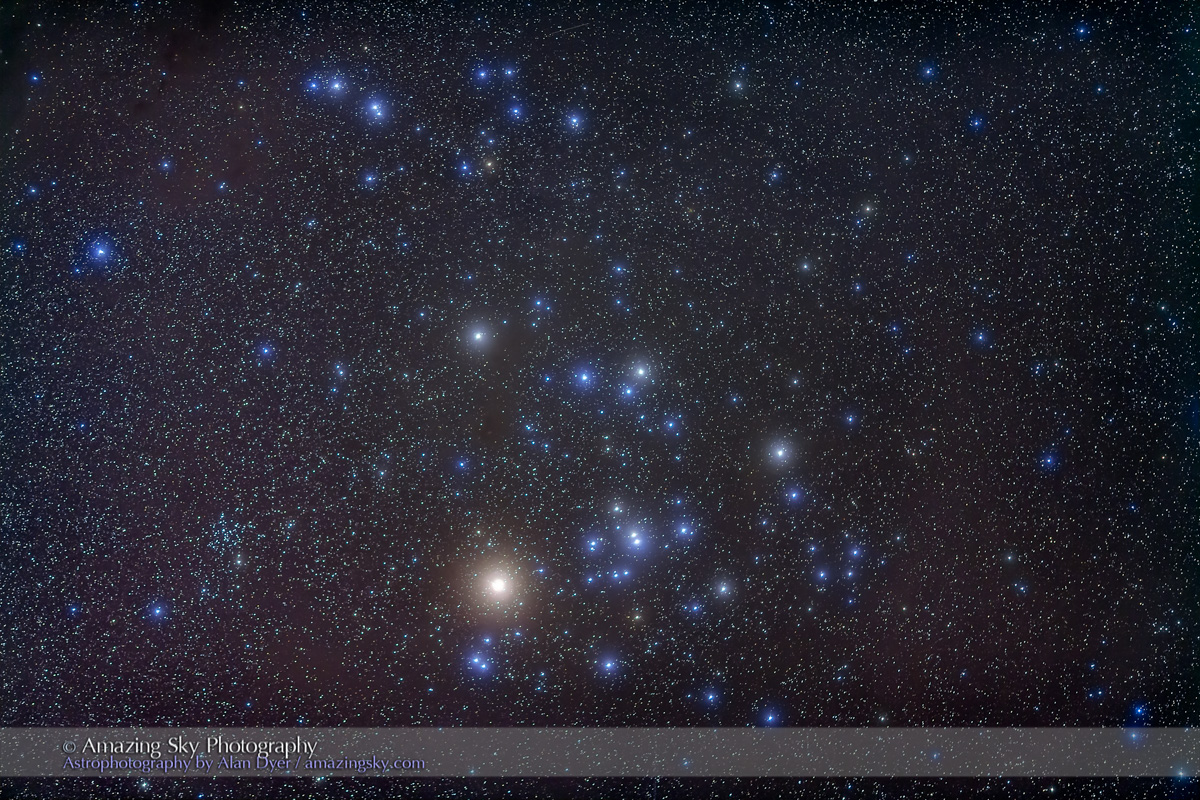
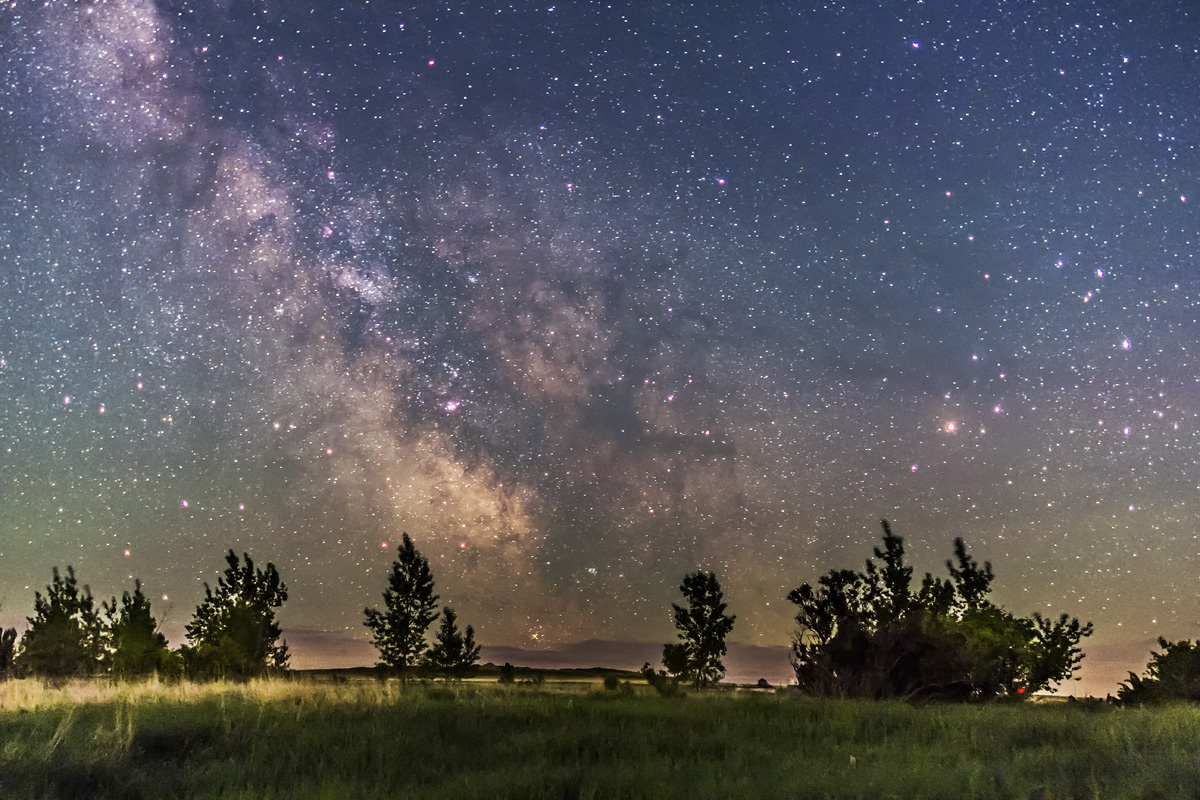
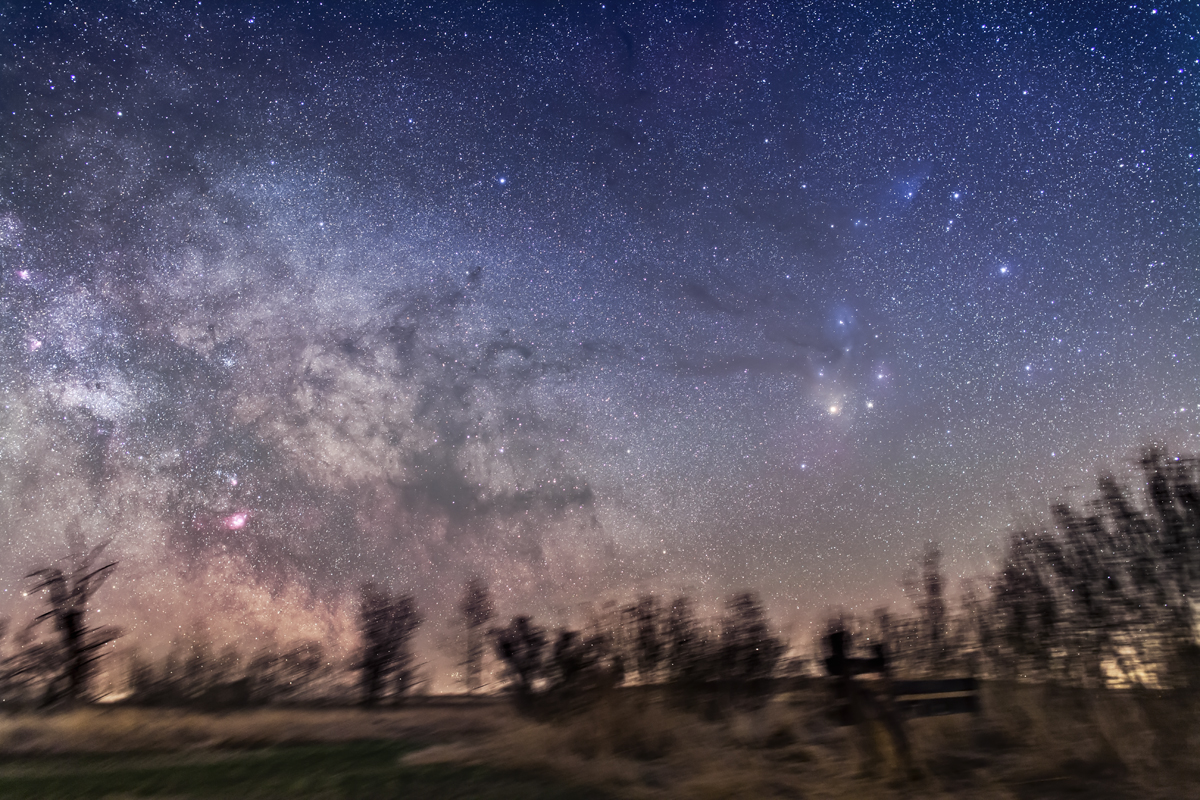
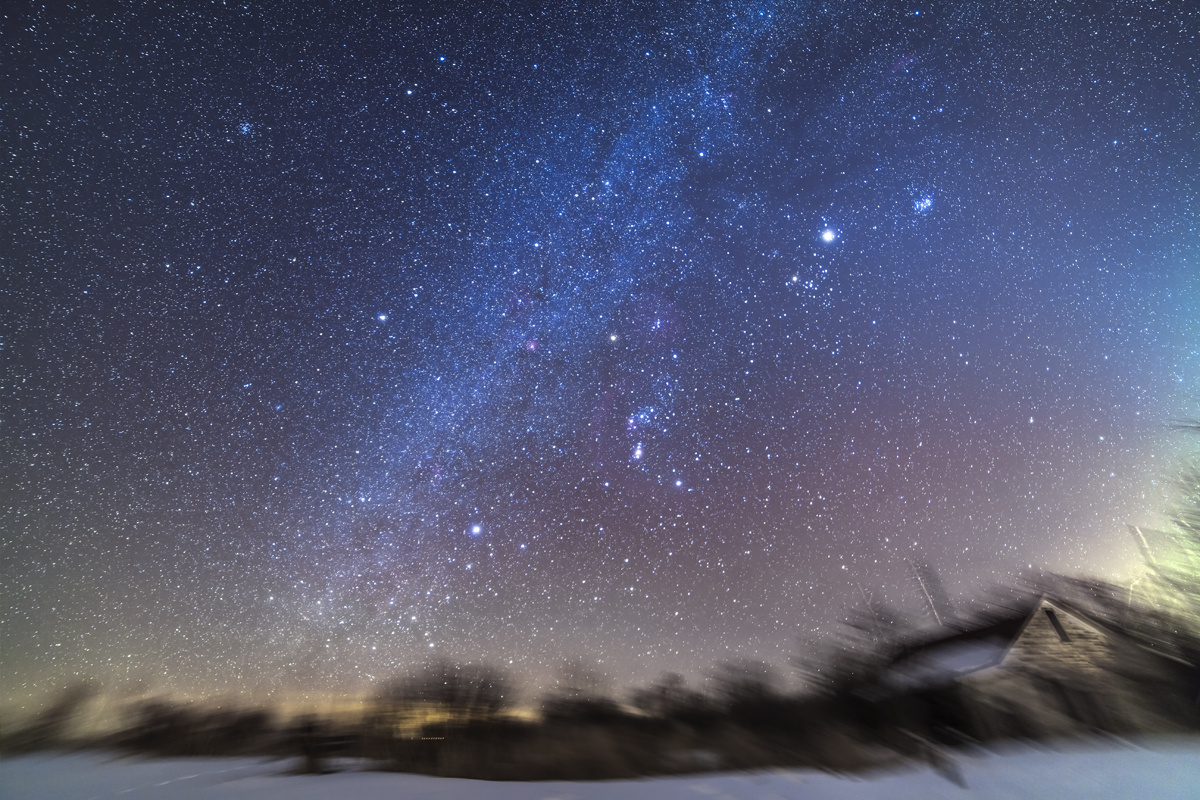
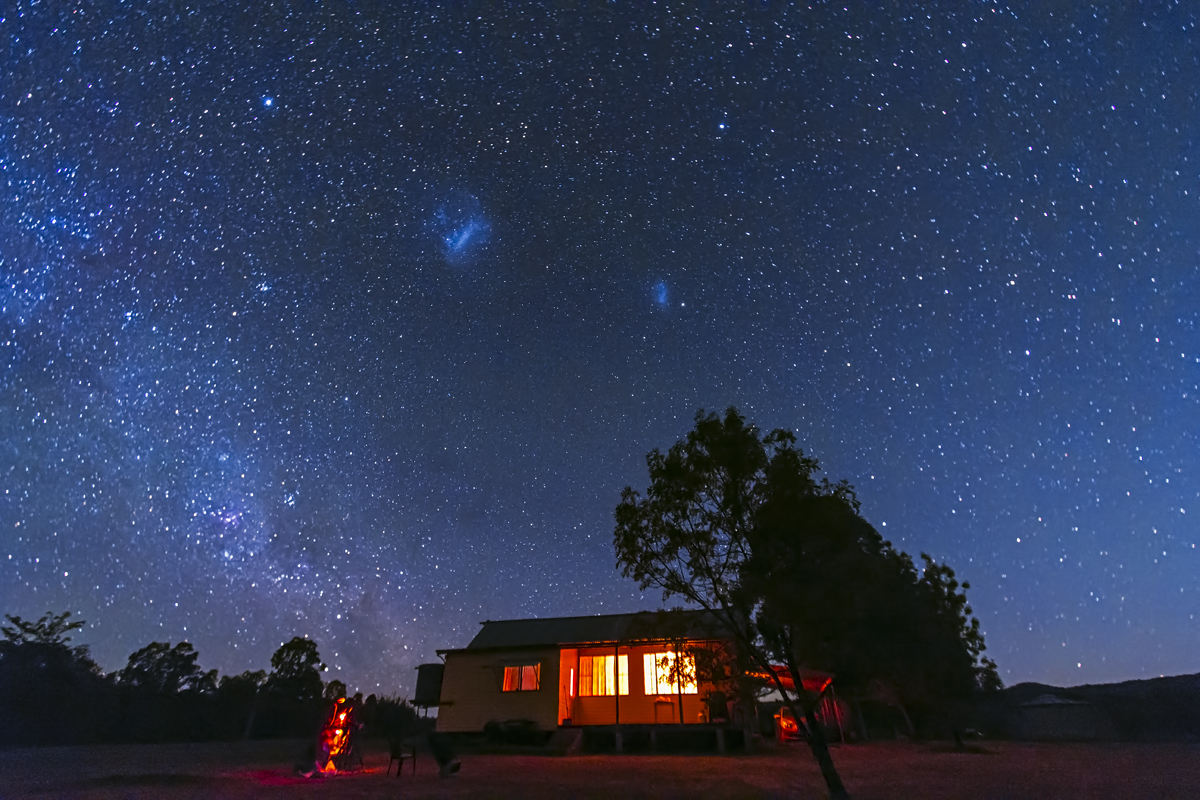
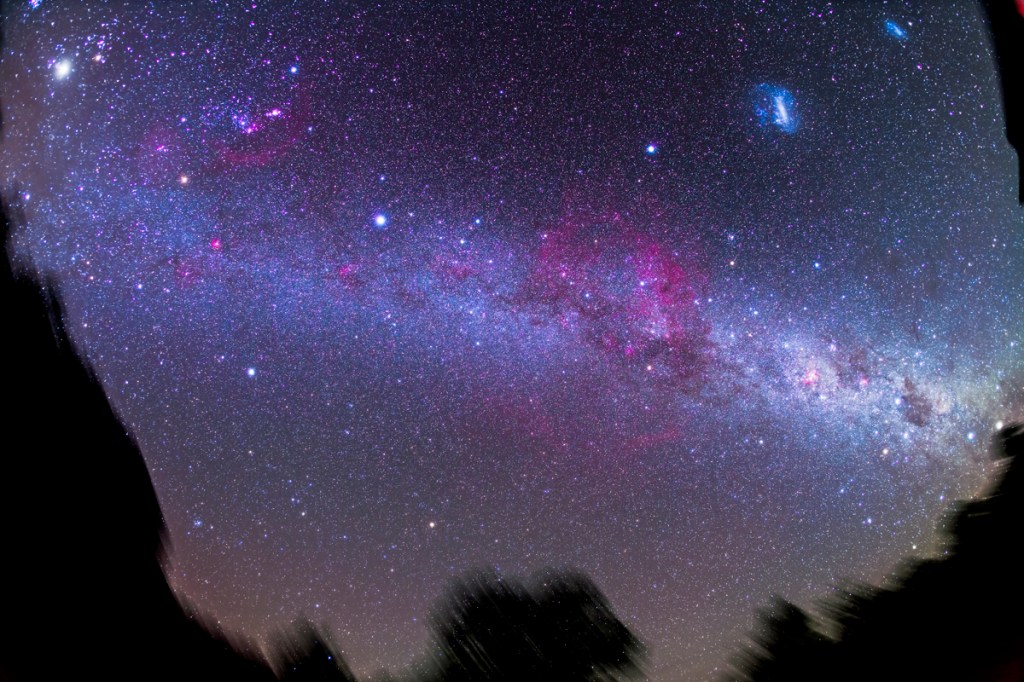
Similarly, below I present views looking east to the autumn constellations rising over the prairie. This was from the valley below Two Trees Hill, at the Riverwalk day use site. Here there were absolutely no lights visible, and hardly a sky glow on the horizon from towns and light pollution. This was paradise for a stargazing session.
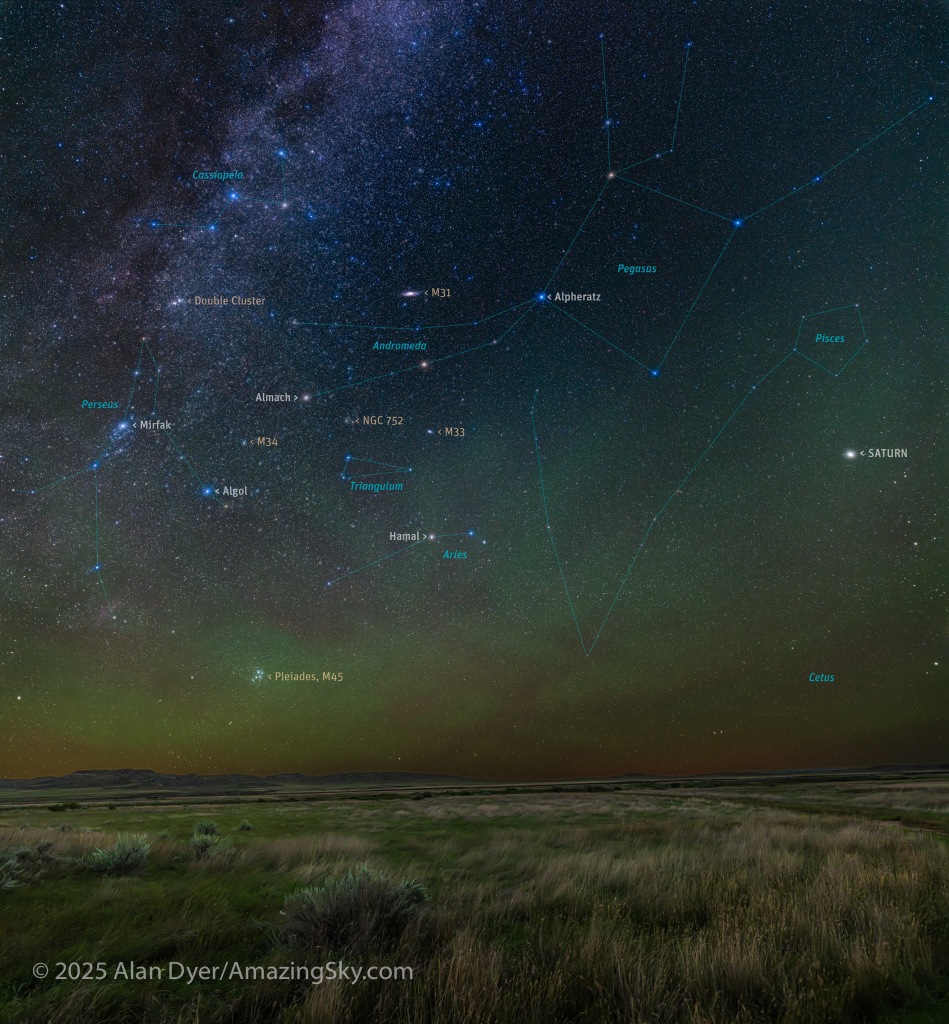
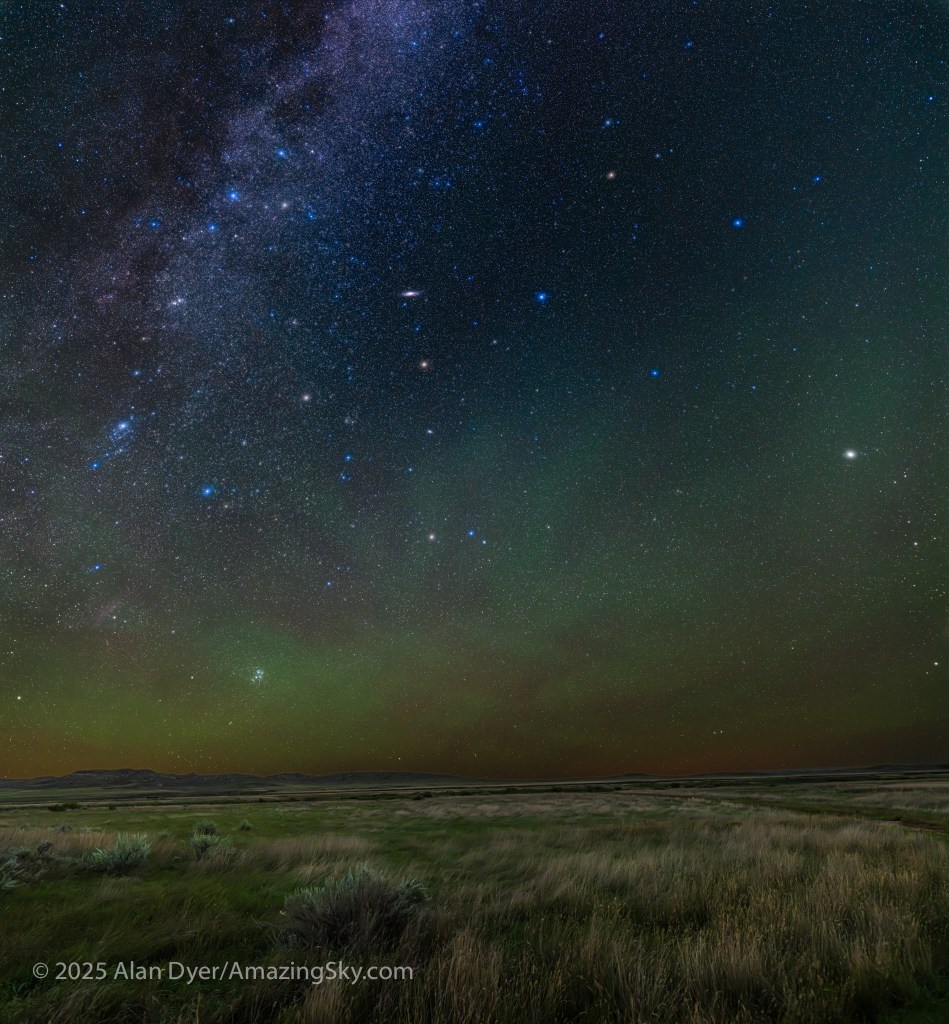


The constellations in this area of sky are the ones made famous in the classic tale of the hero Perseus riding on Pegasus the Flying Horse to rescue the lovely Princess Andromeda from Cetus the Sea Monster, while vain Queen Cassiopeia looks on.
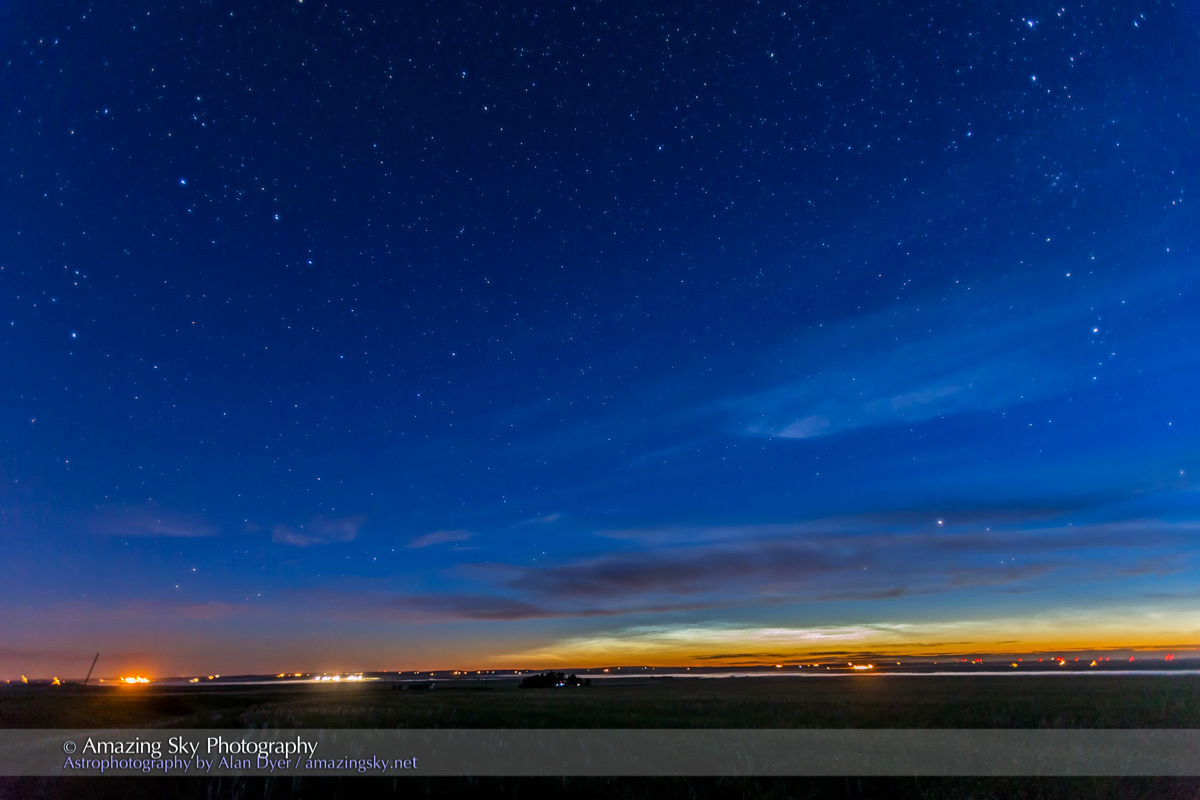
Here the sky was also tinted green, not with aurora but airglow, a natural effect caused by high-altitude oxygen fluorescing at night, giving off energy it has absorbed by day. It discolours the sky but it belongs there! It is visible only at dark sky sites.
The Great Sand Hills
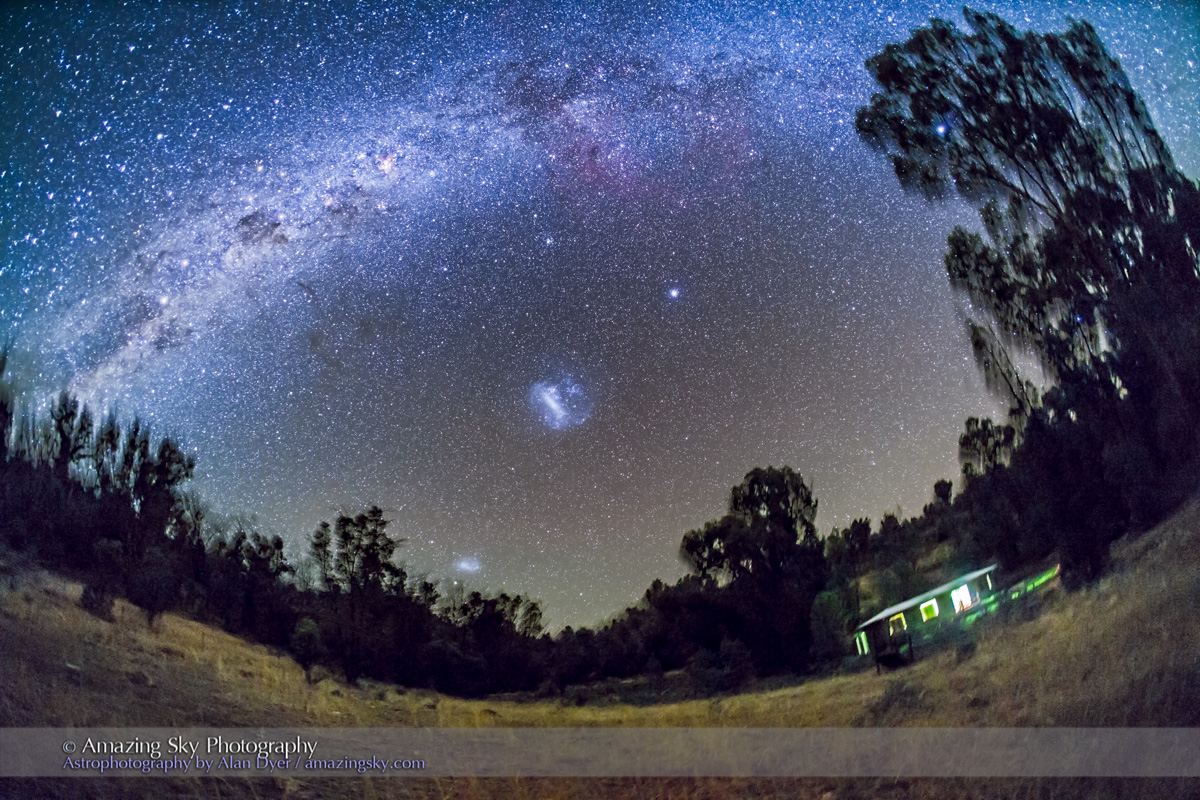
From Grasslands I ventured north to the little town of Leader, Saskatchewan, one of the jumping off points to visit the Great Sand Hills nearby. You have to have a local map to find them, but the sand dunes are extensive, and an oddity on the prairie, another Ice Age relic.
They are not a Park but are an ecological reserve, with limited access. I shot from the main spot with parking for visitors and a trail off into the dunes.
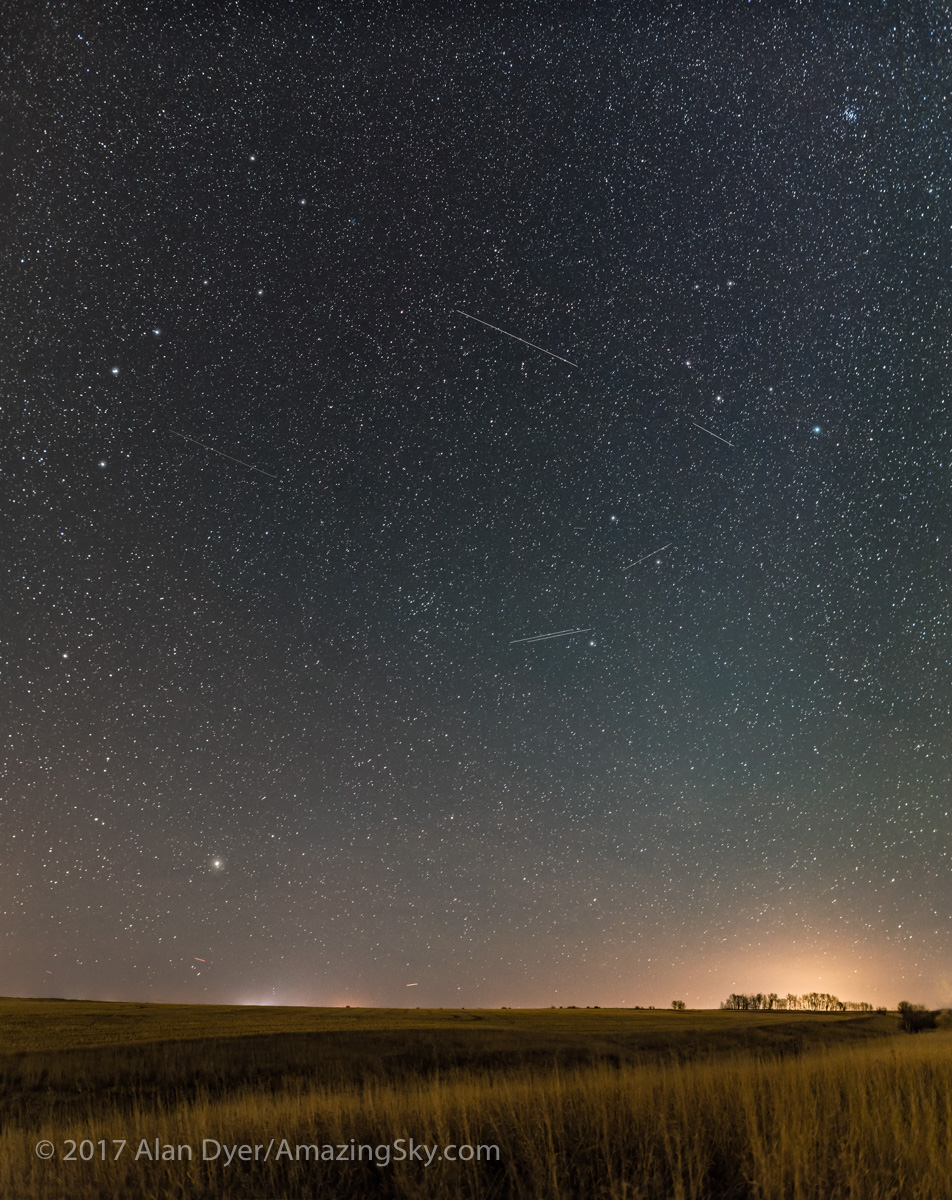
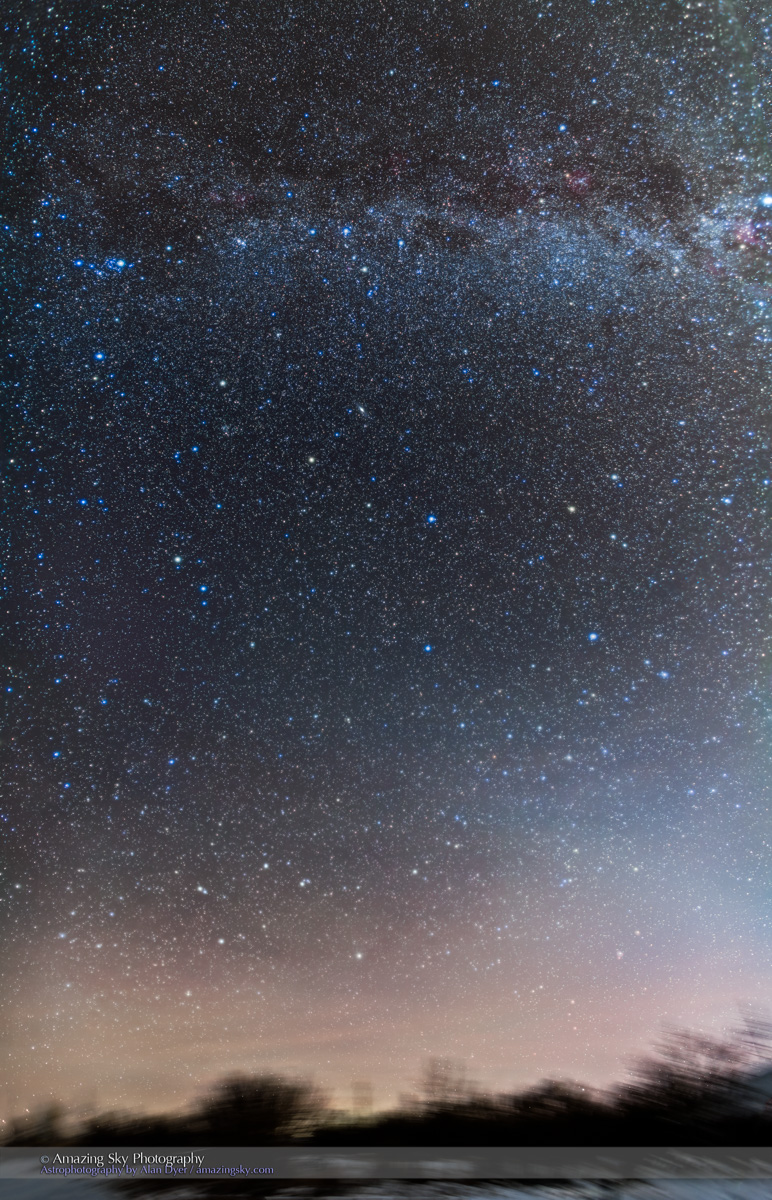
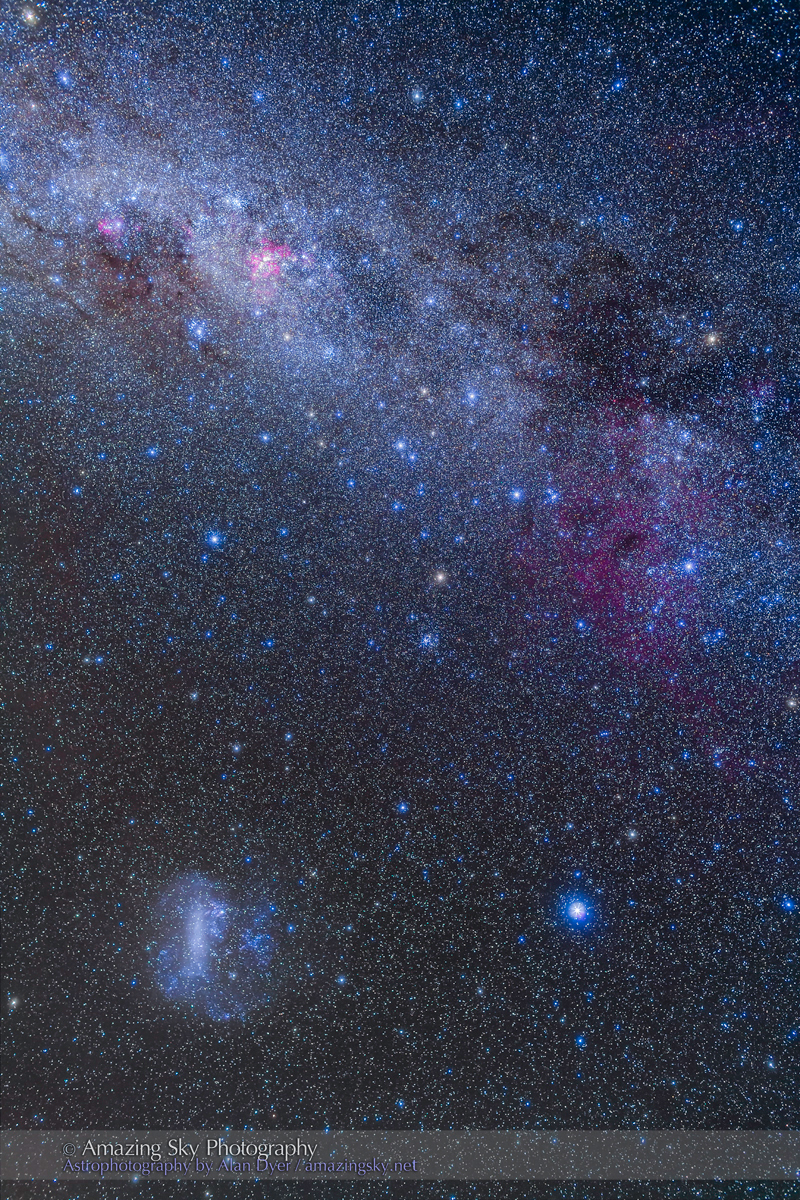
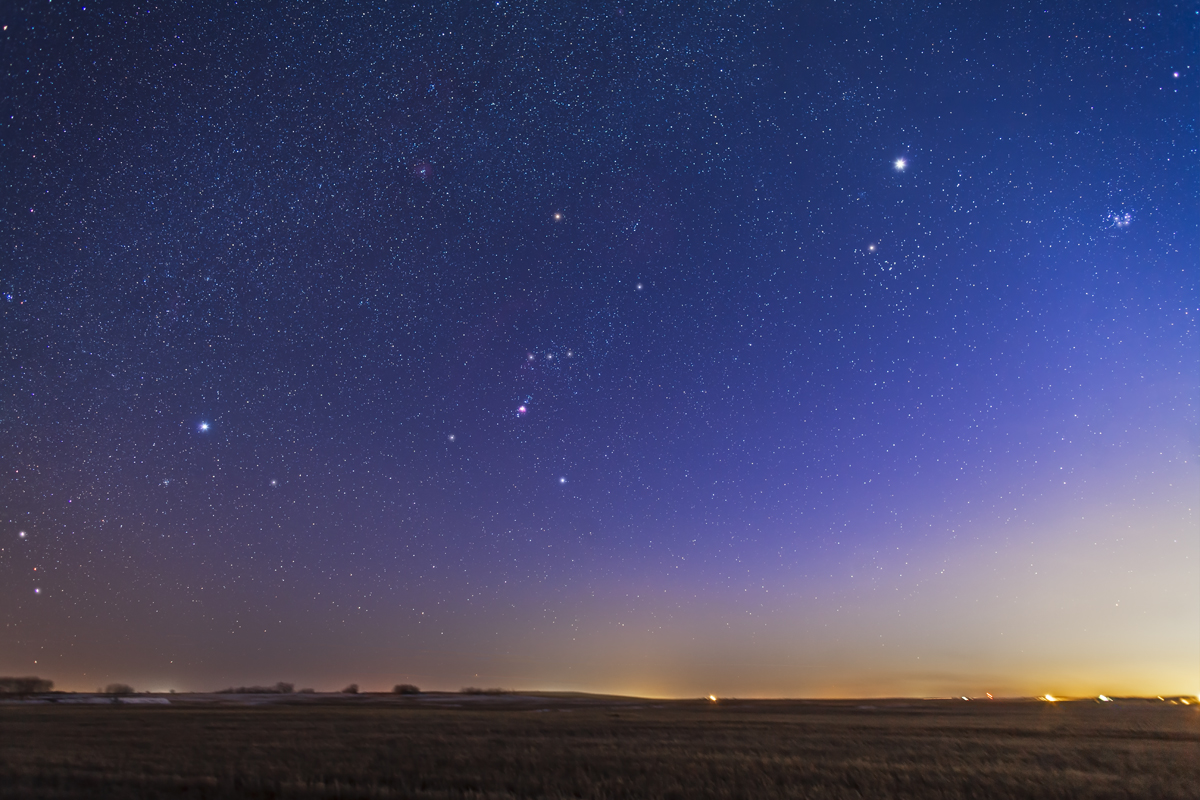
Here is another pair of images with annotations, looking north from the main dune field toward Ursa Major and the Big Dipper.
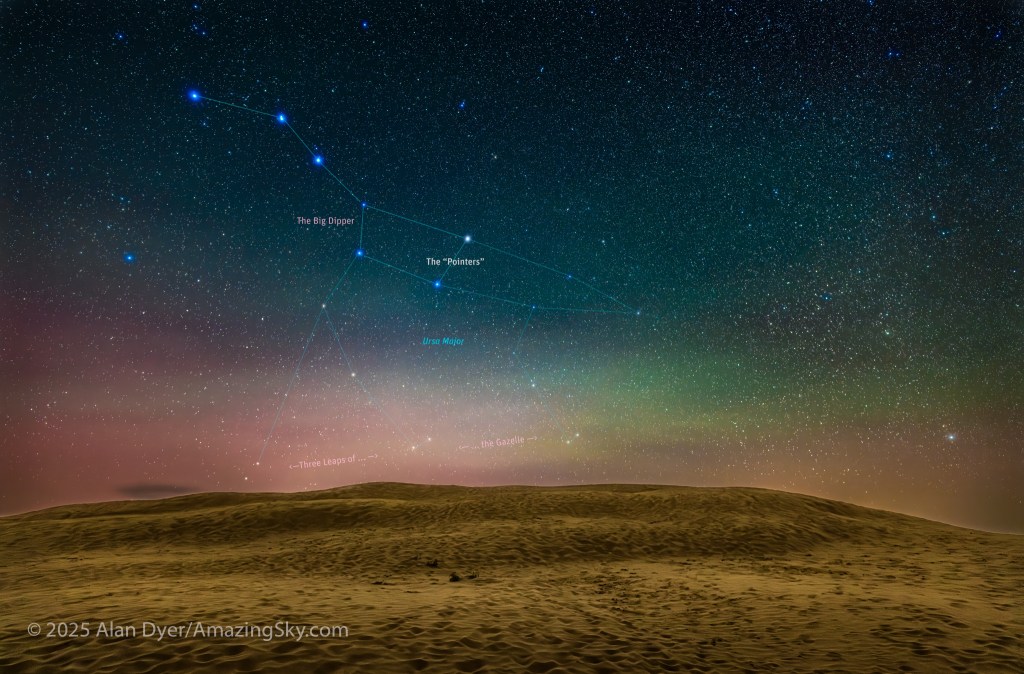
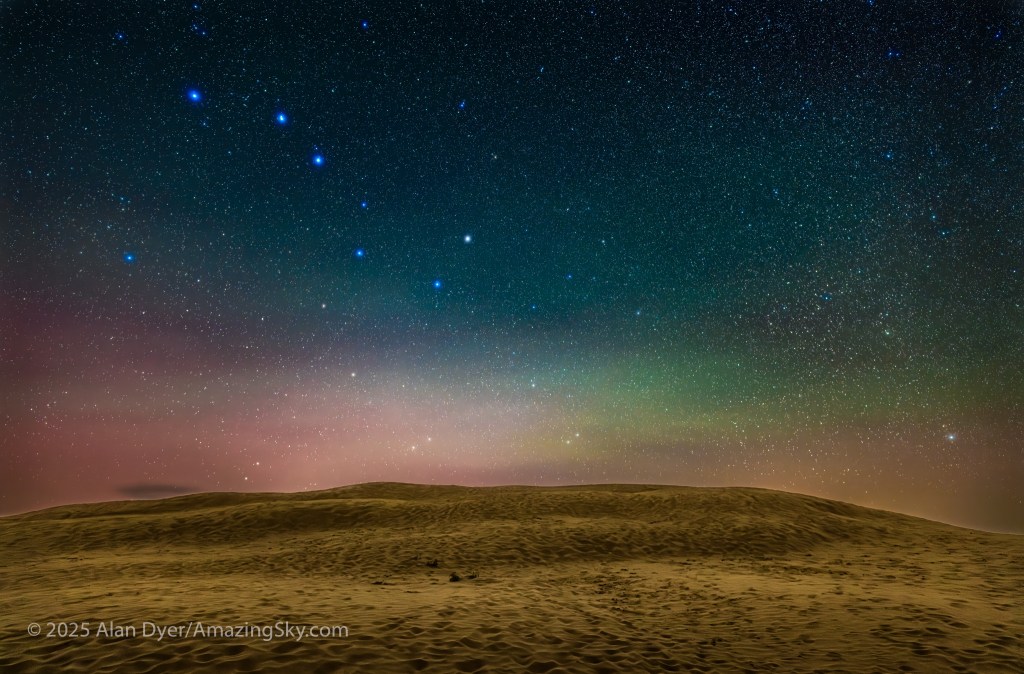


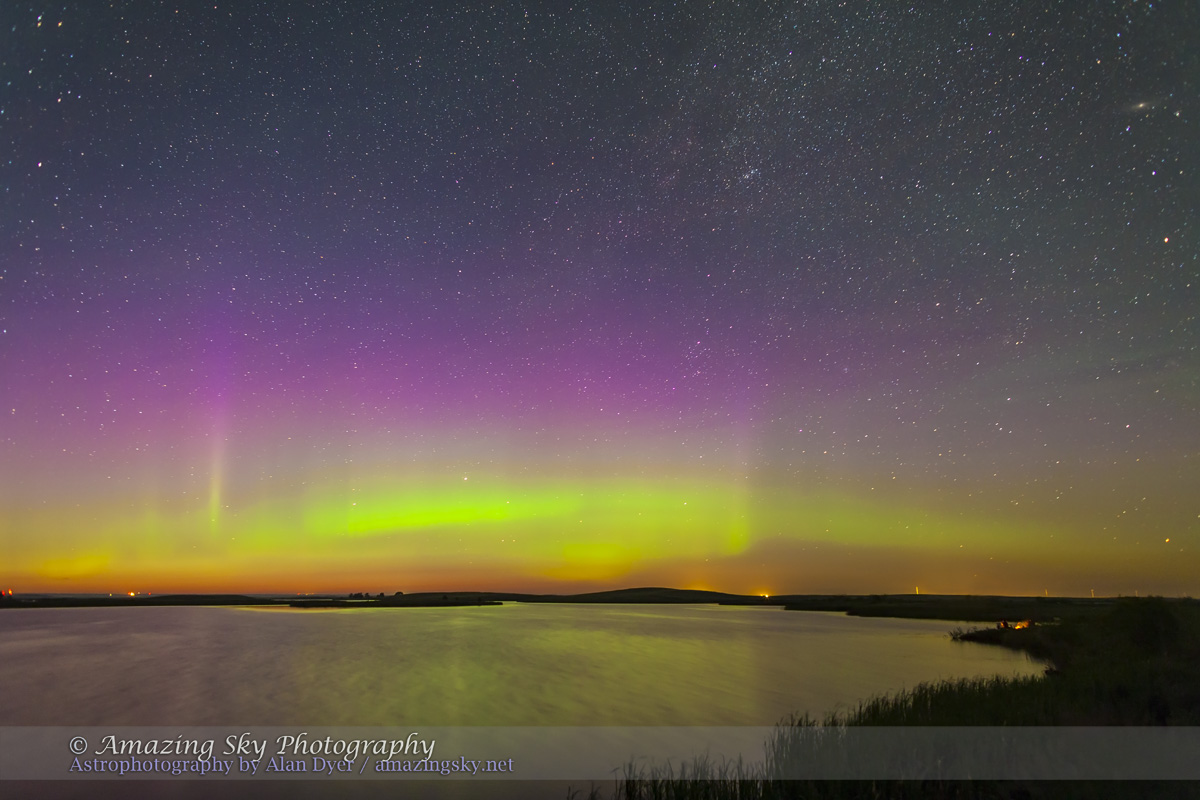
An extensive display of airglow also tints the sky, at least I think that’s the source, and not aurora.
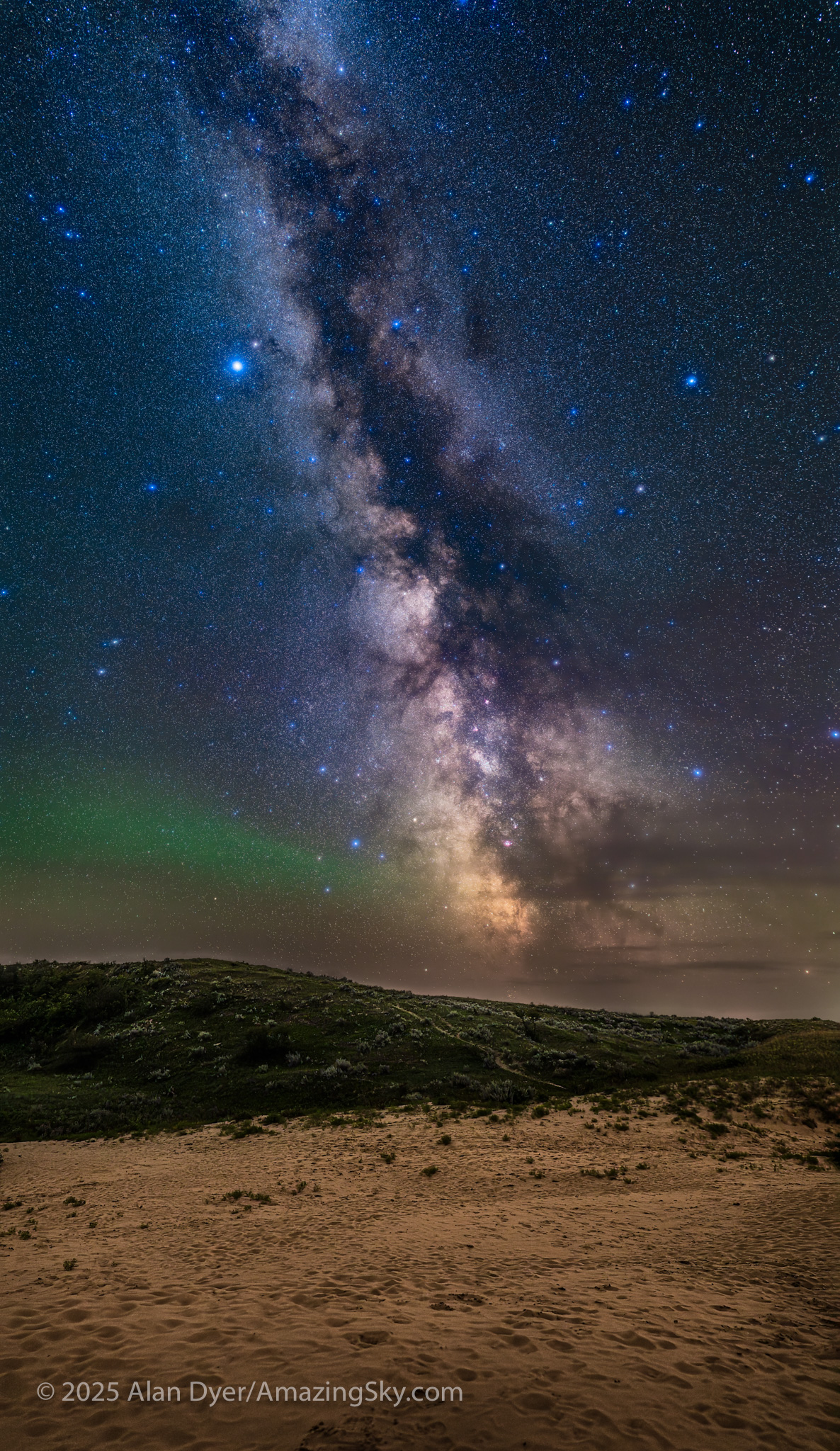

This is a blend of tracked and stacked sky exposures with a single untracked ground exposure:
– A stack of 4 x 60 seconds at f/2 tracked for the sky, plus
– 1 x 4 minutes at f/2.8 untracked for the ground, plus
– A single 60-second tracked exposure through a Tiffen Double Fog 3 diffusion filter layered in, to add the star glows.
– All with the Nikon Z8 at ISO 800 and Nikkor 20mm S lens, on the MSM Nomad tracker. And all from the same tripod position. However, the camera framing was changed for the sky and ground shots, tilting it up it to include more of the sky up the northern Milky Way.
Turning around to face south again frames the sweep of the summer Milky Way over the well-trodden dunes. Not quite the Saharan or Namibian scene you might want, but this is Saskatchewan and having even this scene on the prairies is unique. The only other dune fields are far up north and not readily accessible.
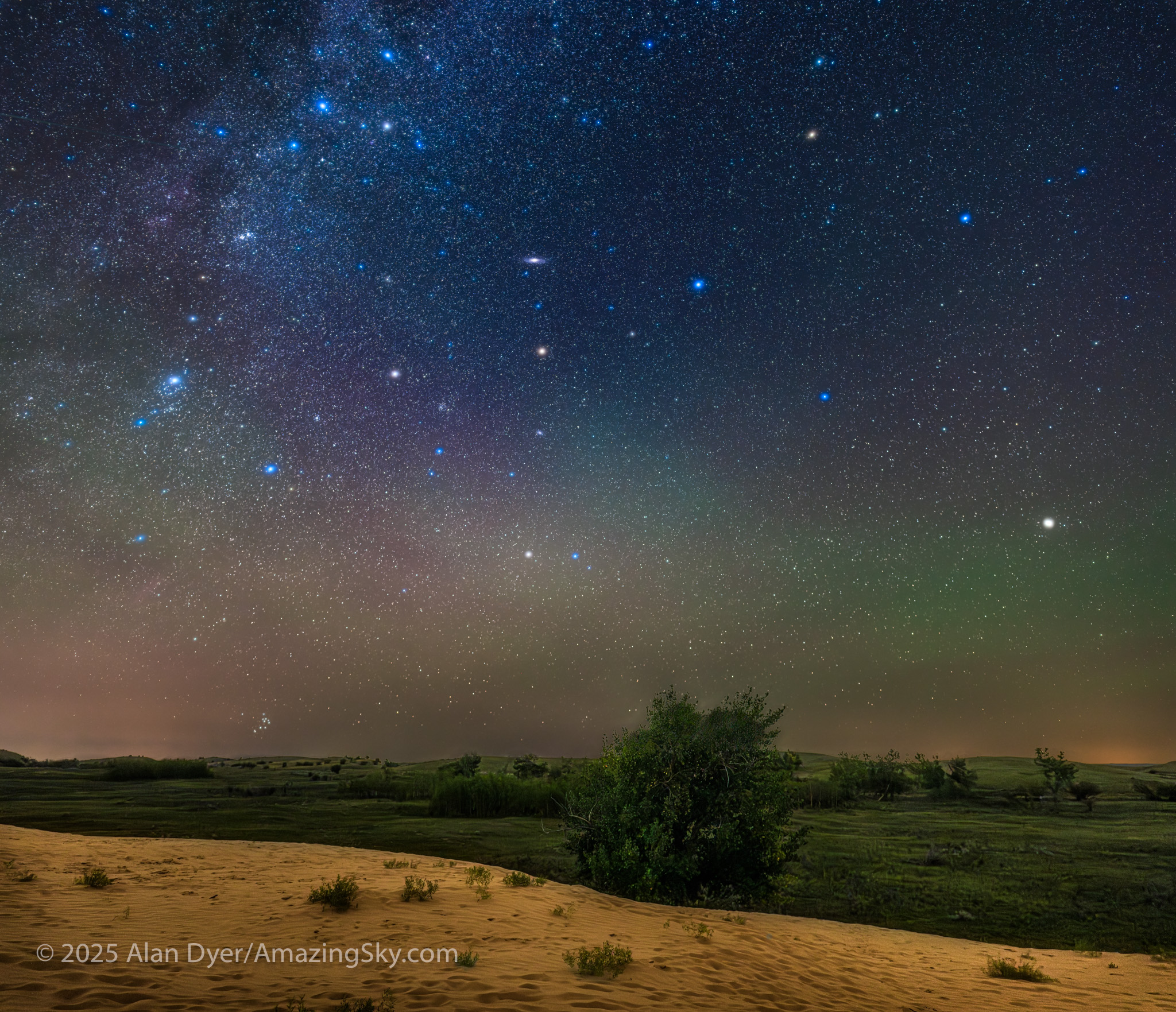

This is a blend of tracked and stacked sky exposures with a single untracked ground exposure:
– A stack of 4 x 60 seconds at f/2 tracked for the sky, plus
– 1 x 3 minutes at f/2.8 untracked for the ground to bring out the details lit only by starlight, plus
– A single 60-second tracked exposure through a Tiffen Double Fog 3 diffusion filter layered in, to add the star glows.
– All with the Nikon Z8 at ISO 800 and Nikkor 20mm S lens, on the MSM Nomad tracker. And all from the same tripod position. However, the camera framing was changed for the sky and ground shots, tilting it up it to include all the constellations in one frame but with just a sliver of ground in the frame.
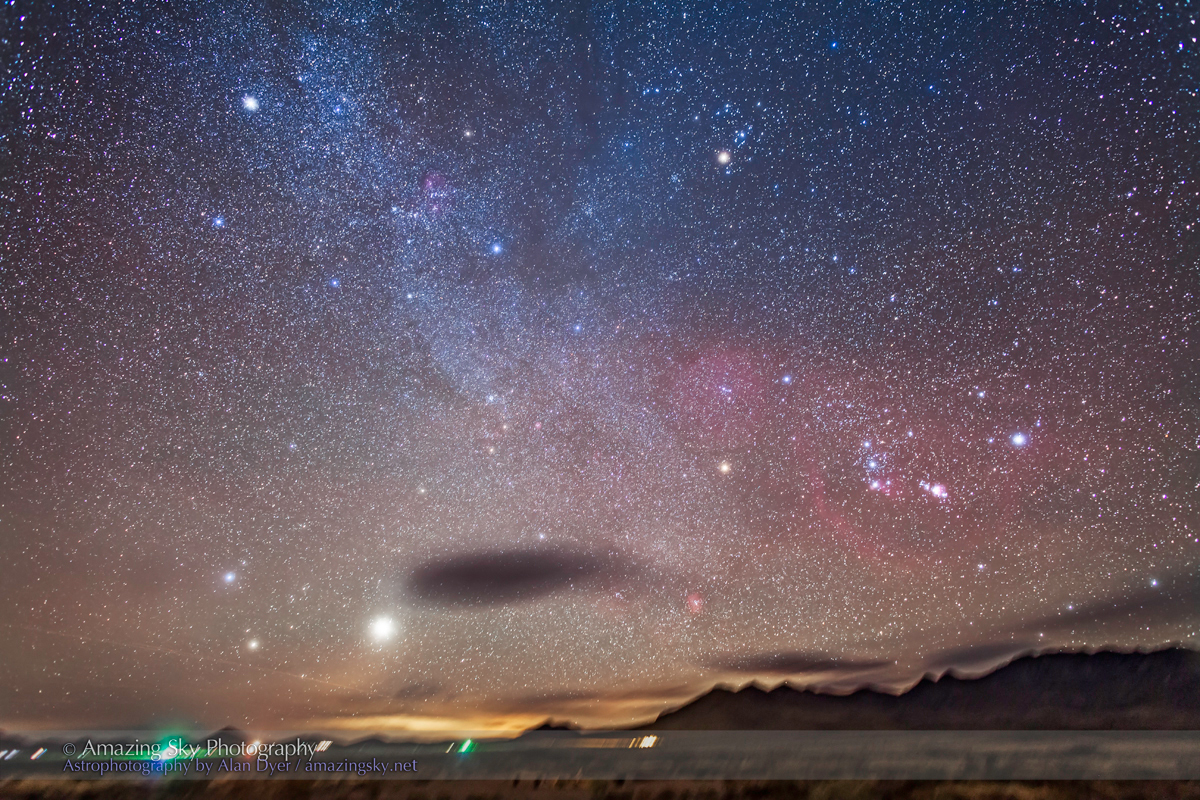
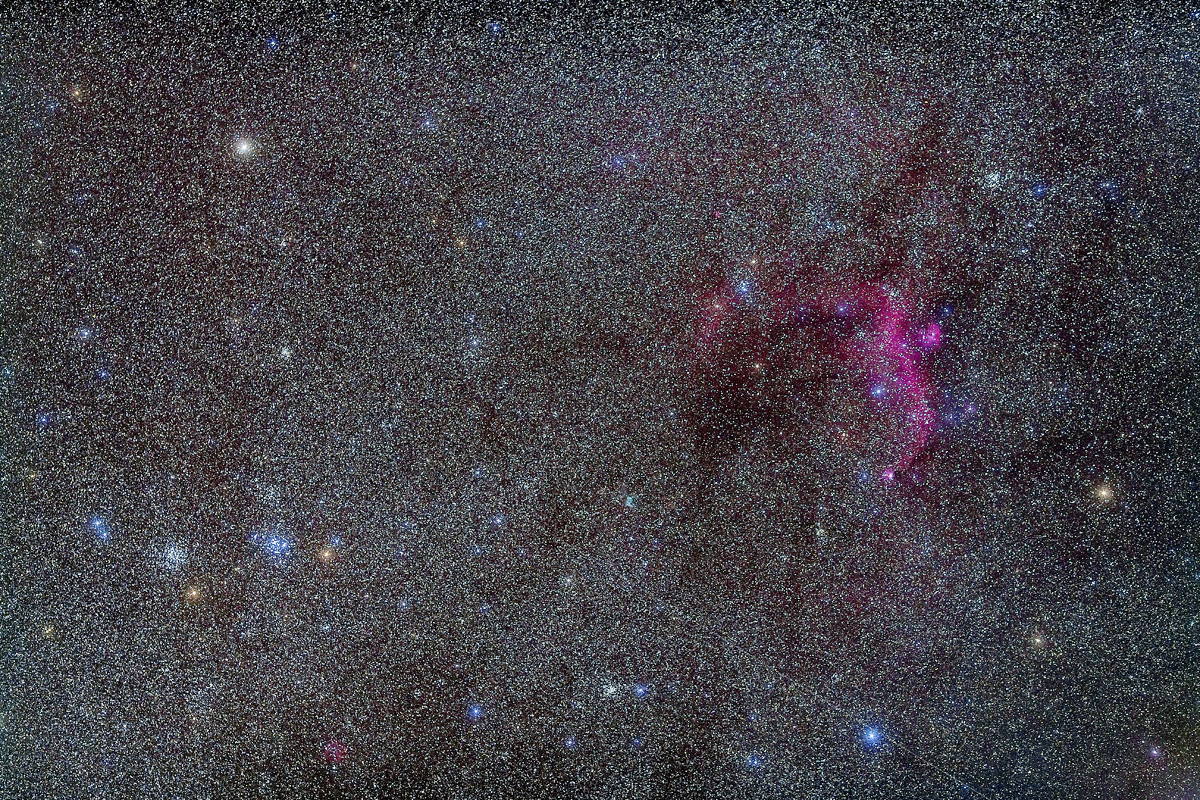
Looking east from the dune again frames the mythological autumn constellations, with the “W” of Cassiopeia at top amid the Milky Way. The bright “star” at lower right is Saturn. The Pleiades are just rising at left.
The Cypress Hills
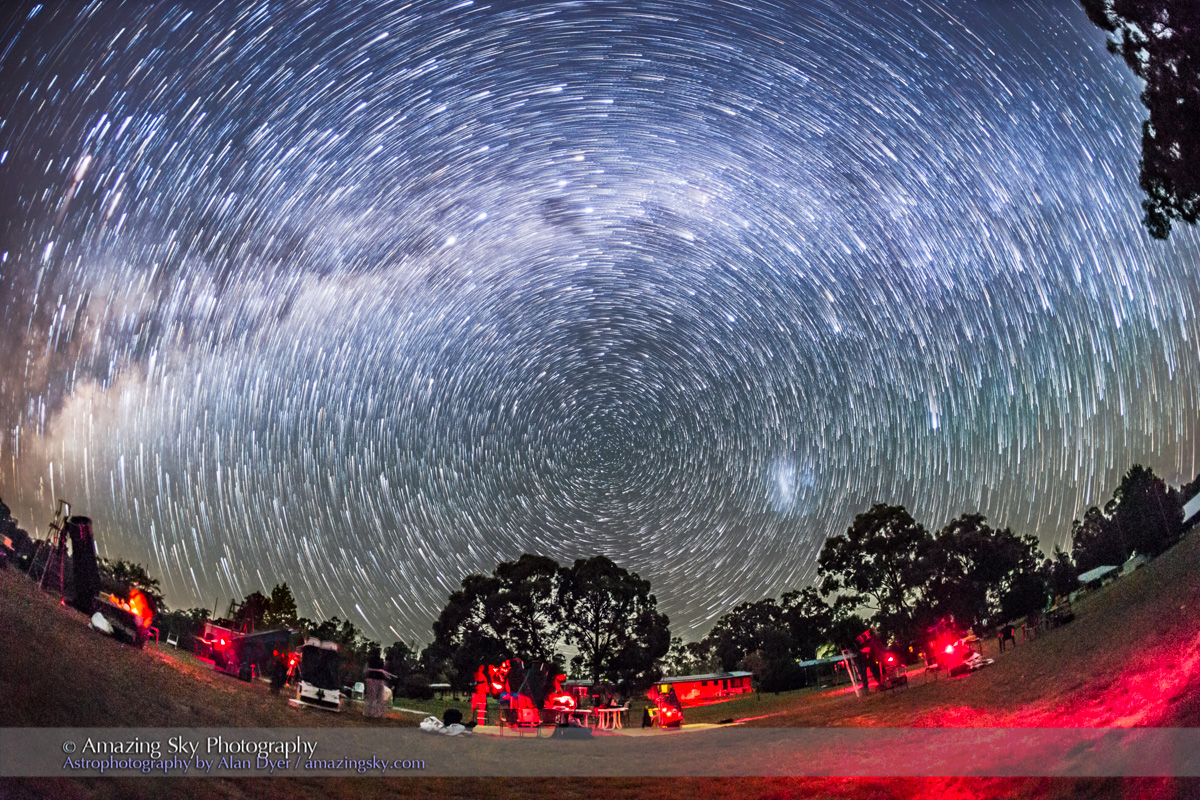
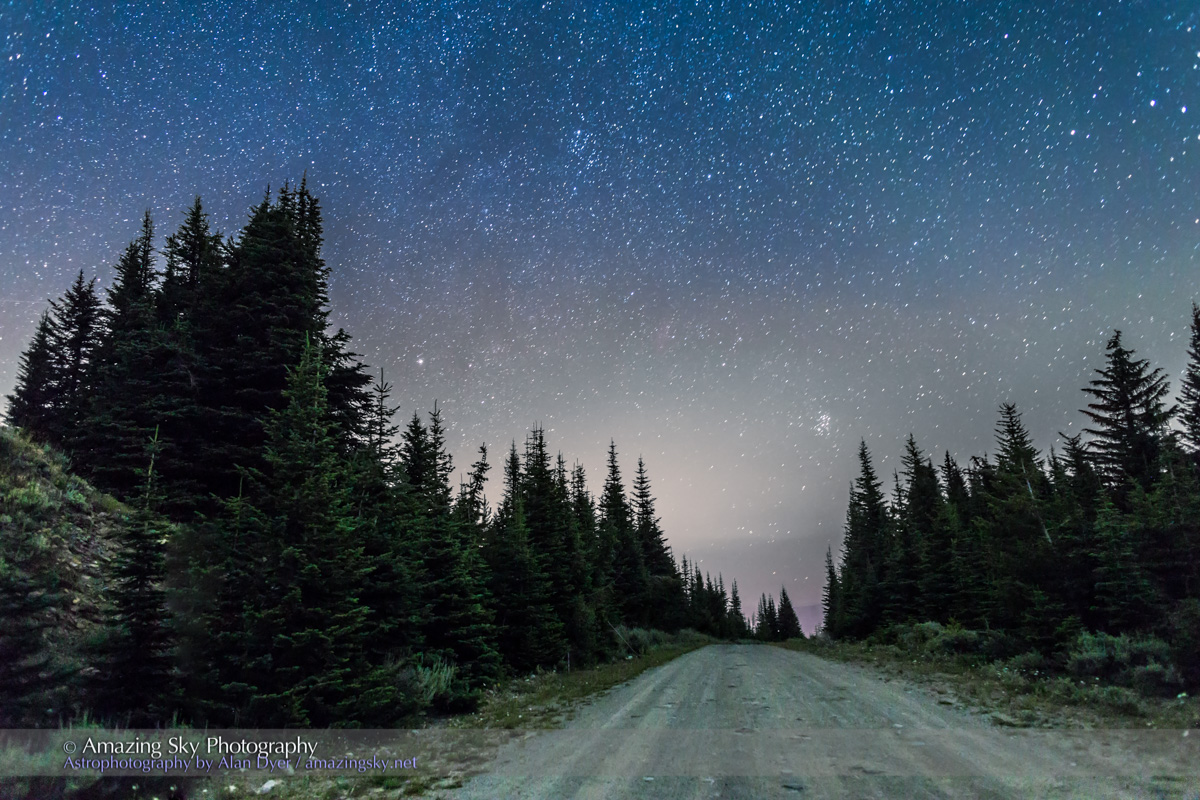
I had started my Saskatchewan journey in the Cypress Hills, another formation created by the Ice Age, or rather left untouched by the glaciers creating a high wooded oasis on the prairie. I was there for the annual Saskatchewan Summer Star Party, the subject of my previous blog here.
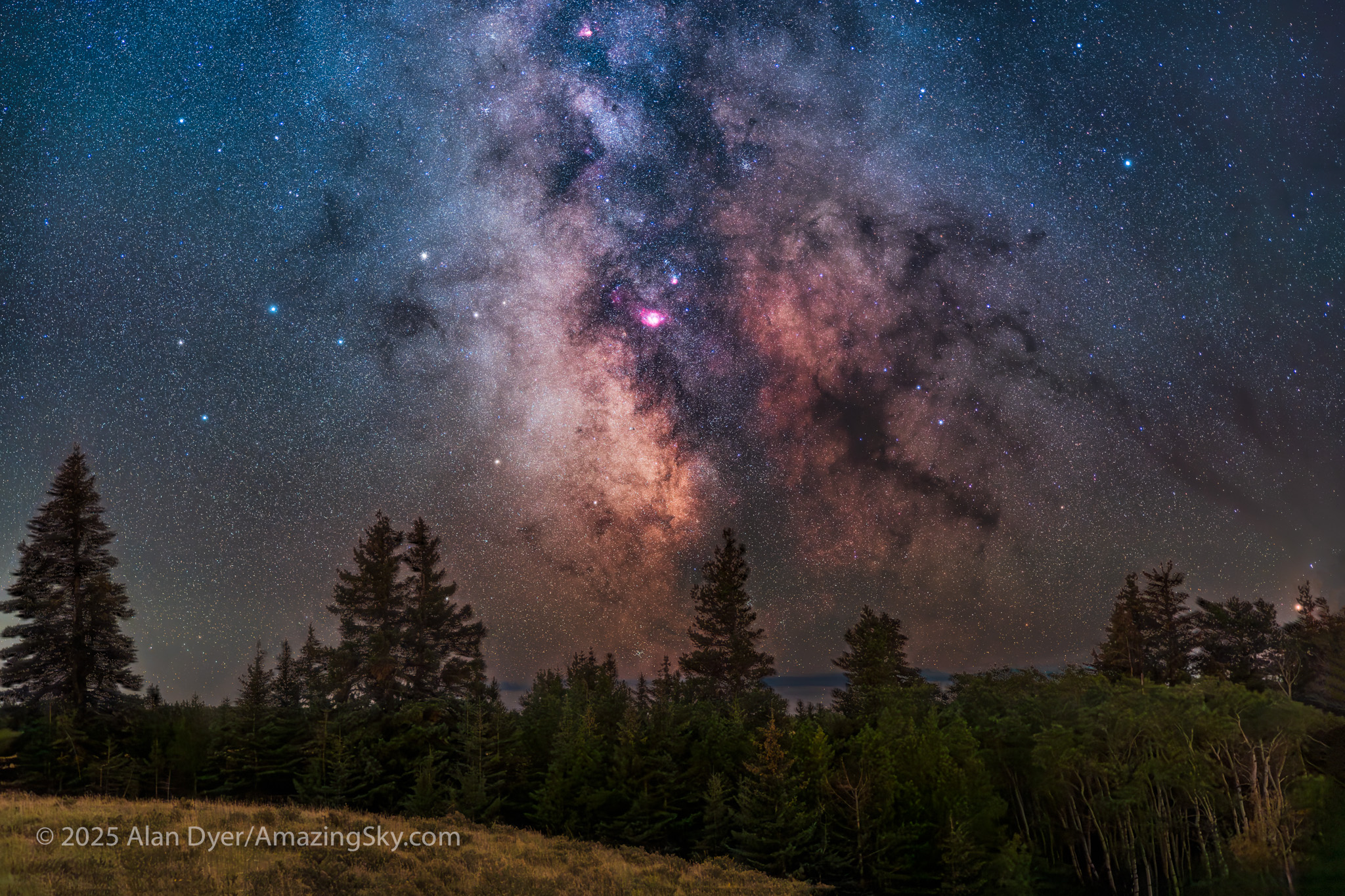

This is a blend of:
– A stack of 4 x 1 minute exposures, tracked, for the sky with …
– A stack of 2 x 1-minute exposures, untracked, for the ground,
– All with the Canon RF 28-70mm lens at f/2 and set to 48mm, on the astro-modified Canon EOS R at ISO 1600, and on the MSM Nomad tracker. No filters were employed here.
Masking and blending all the images, with the trees in the foreground was a challenge! The camera was not moved — all images were from the same tripod position.
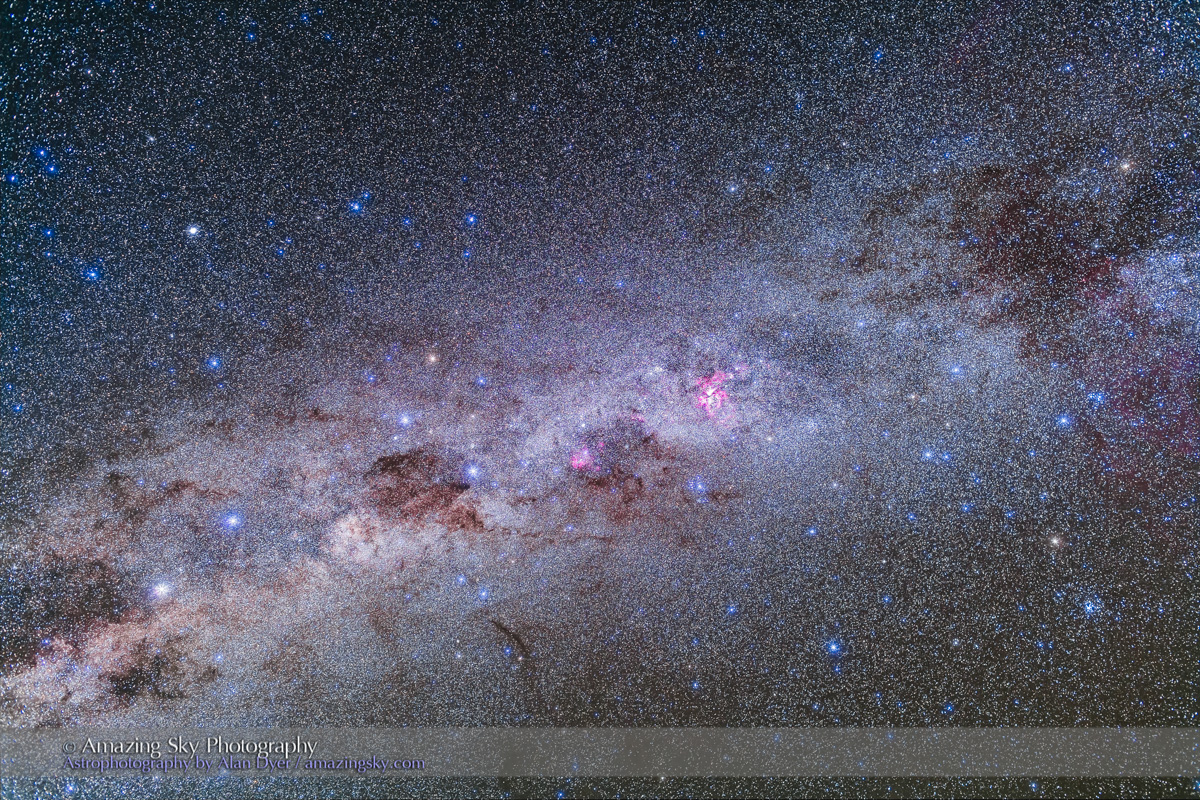
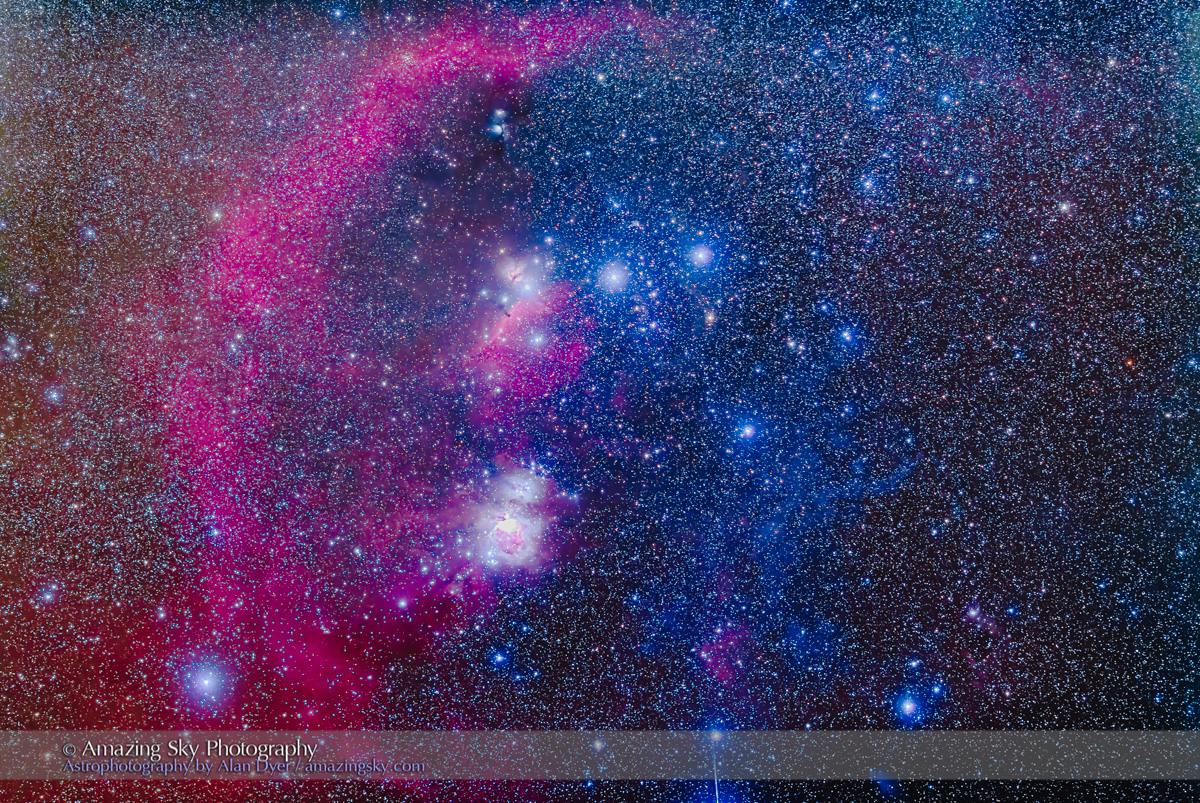
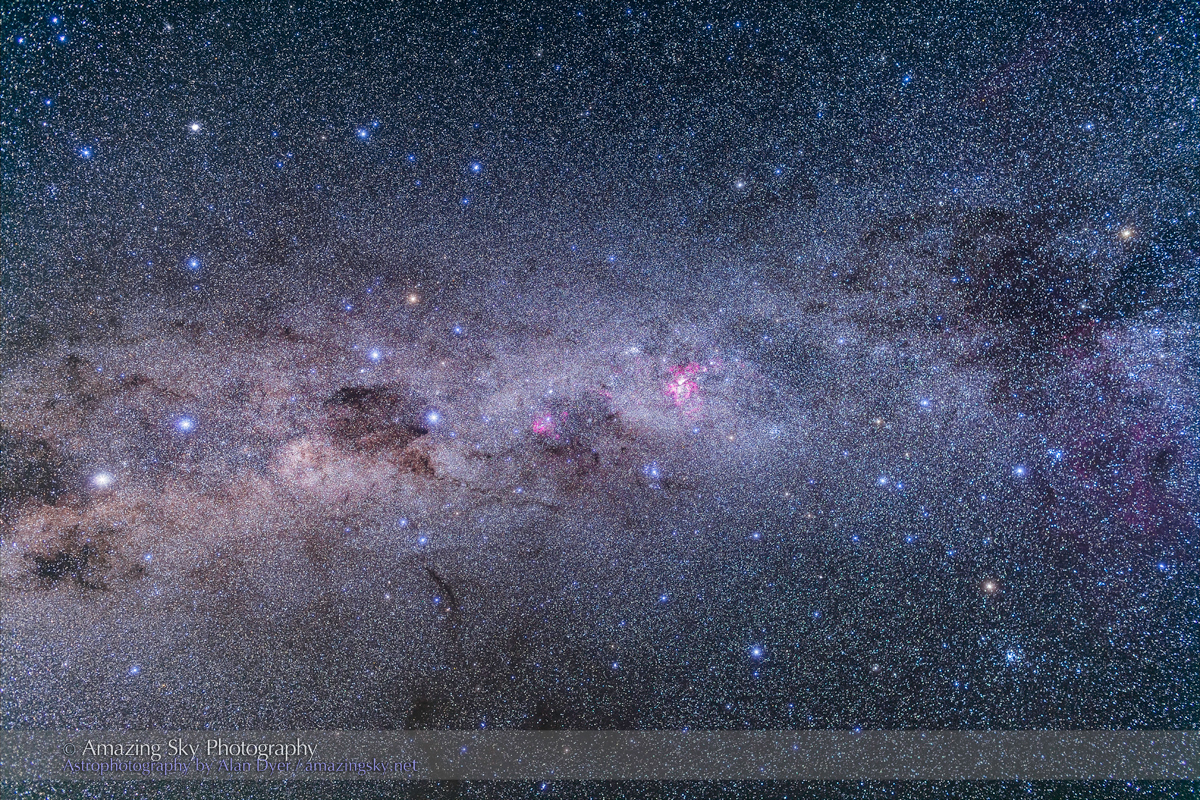
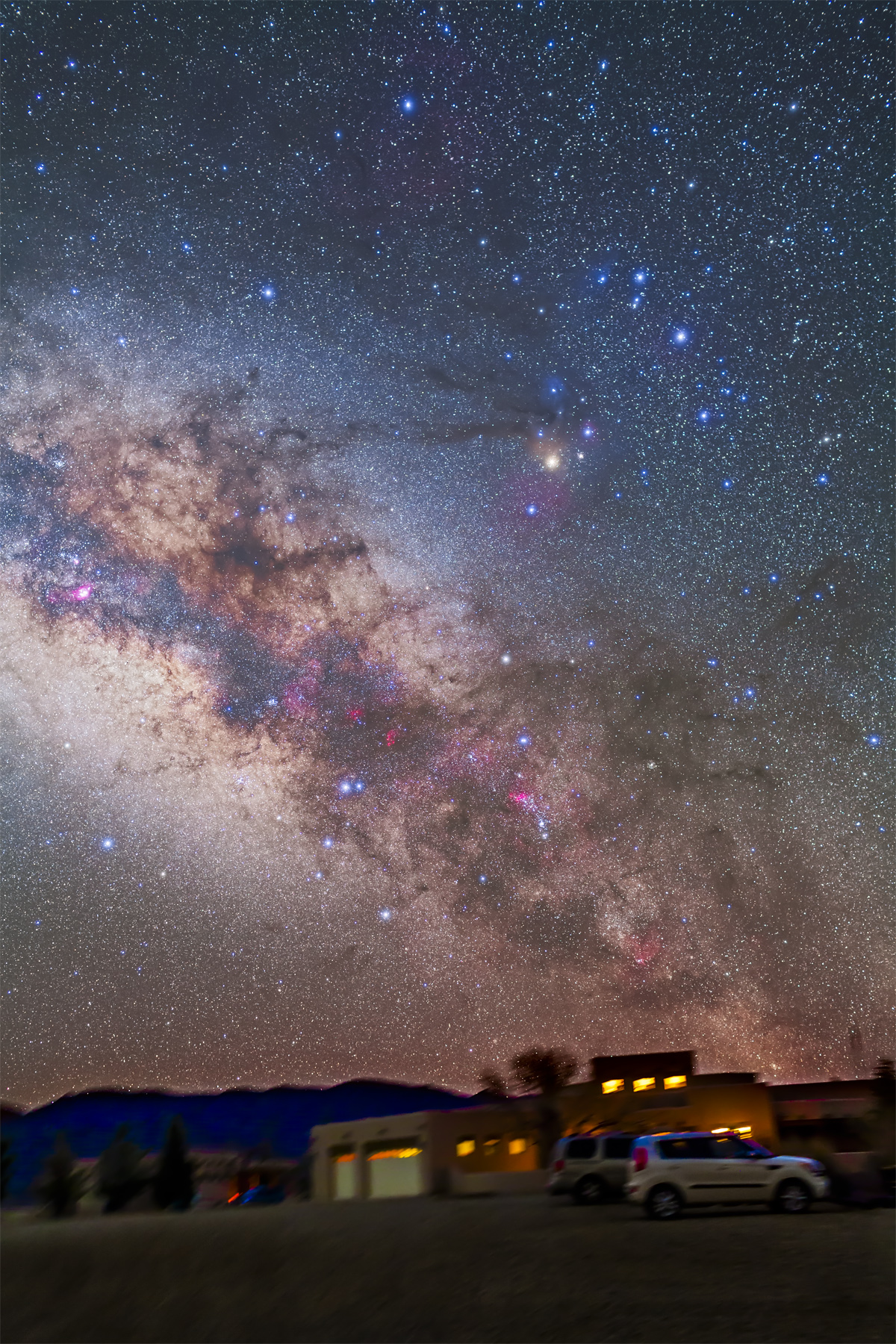
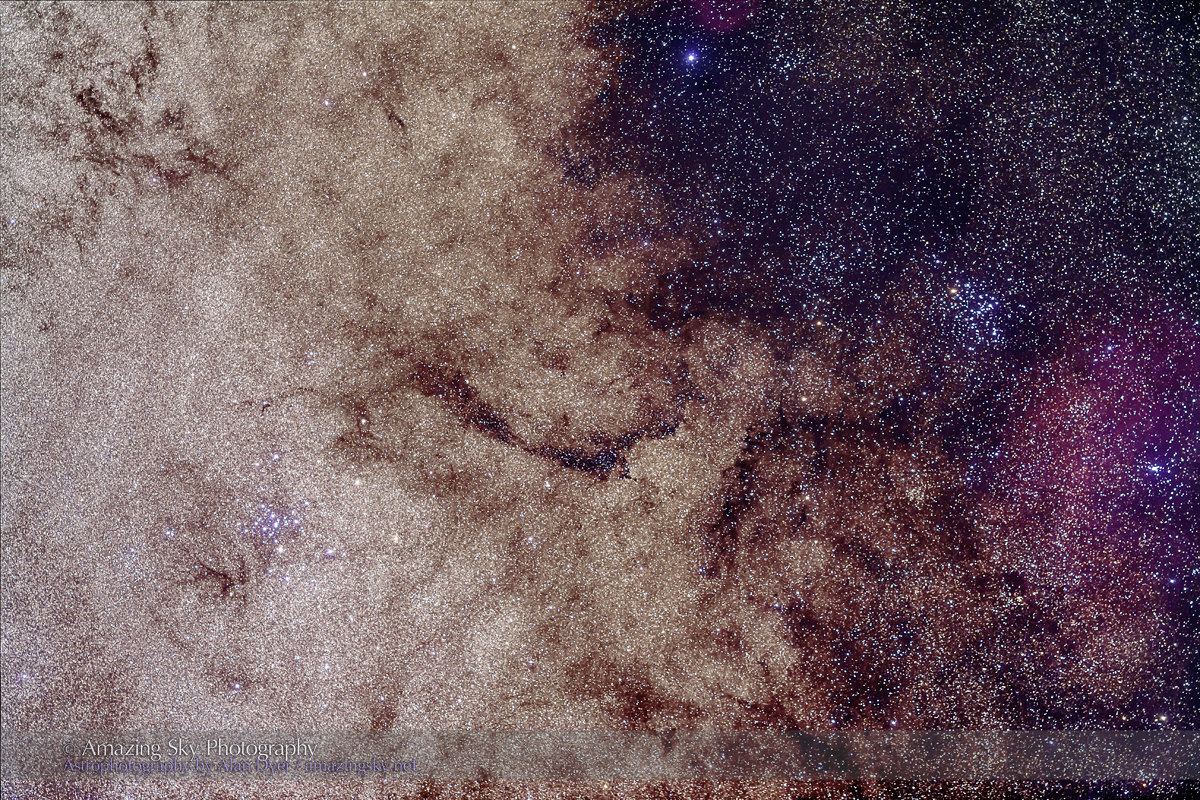
But on the first couple of nights, with the entire four nights of the Party promising to be clear, I left the Party and headed off on my own to shoot some nightscapes over the pine trees at Lookout Point, to again catch the photogenic galactic core in its last appearance for the season.
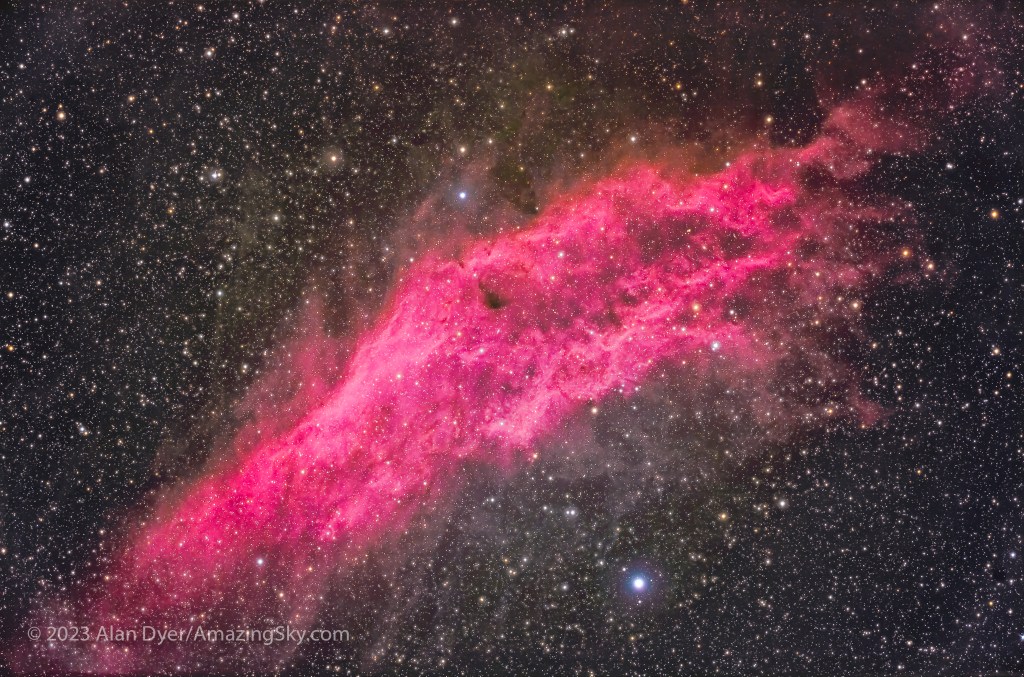
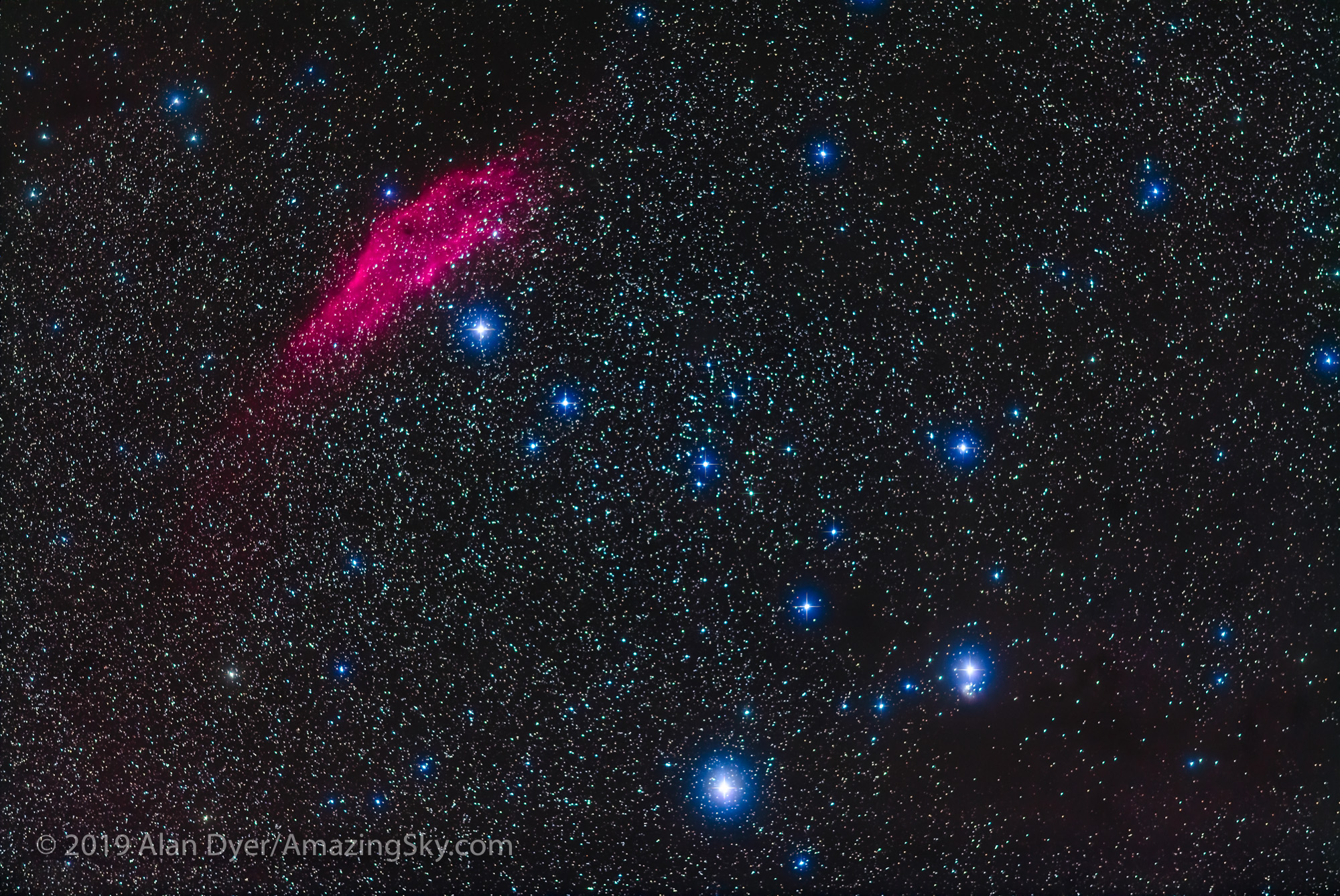
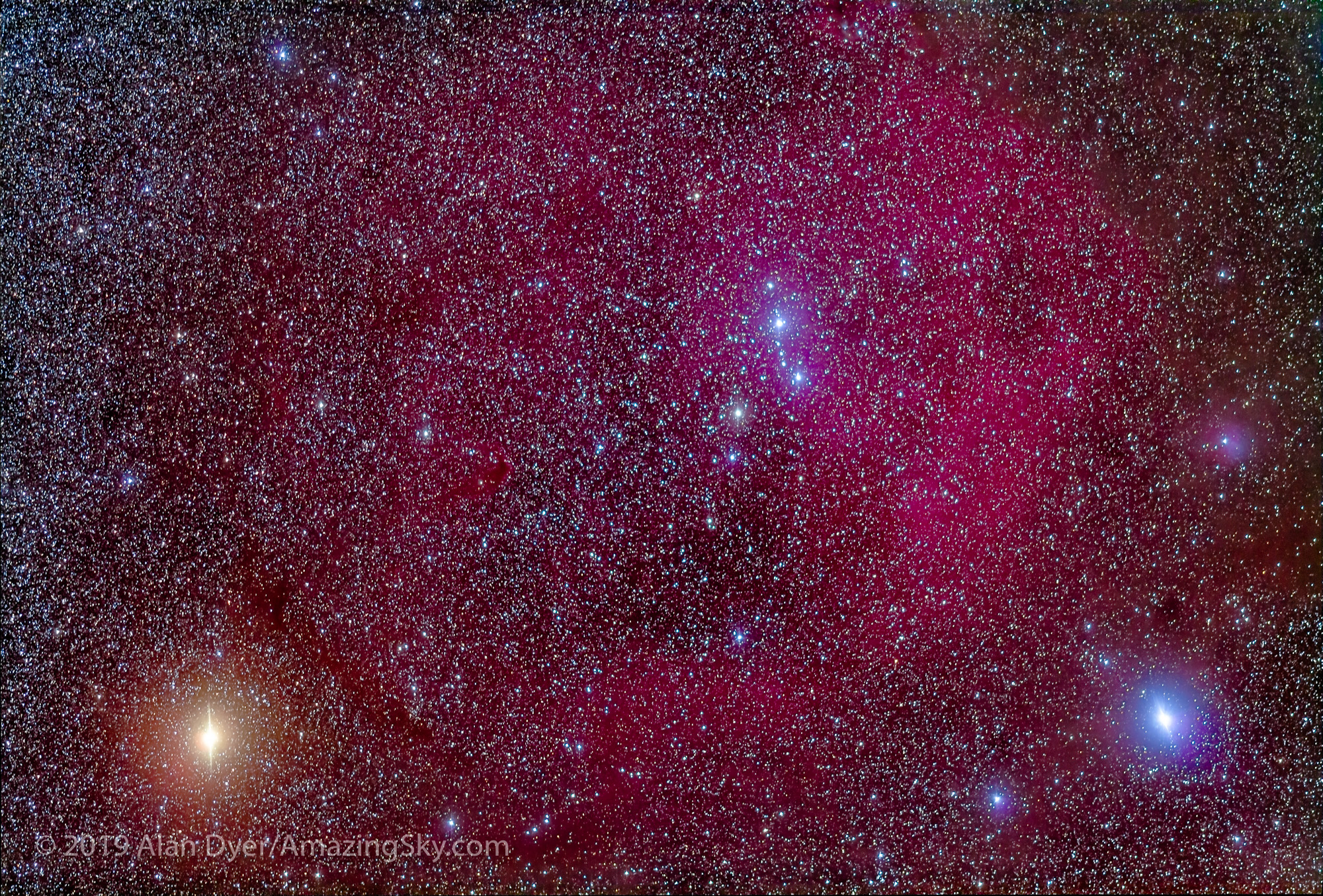
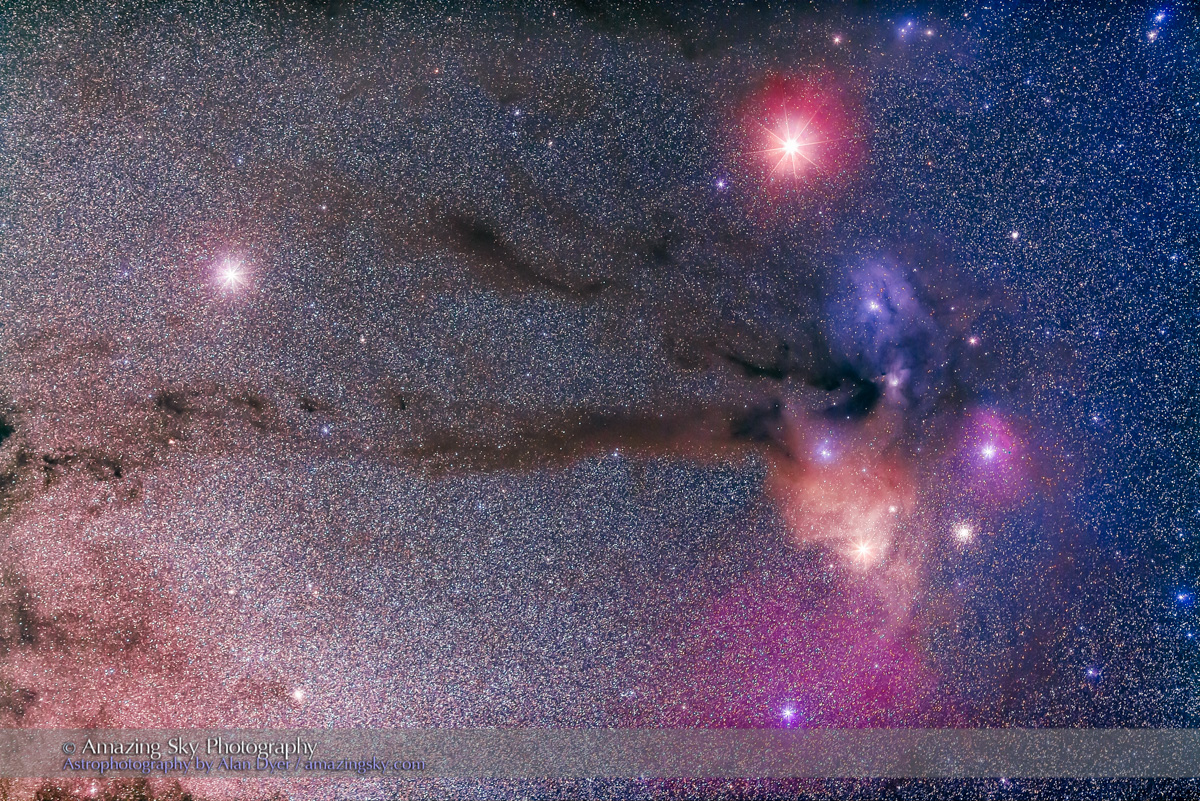
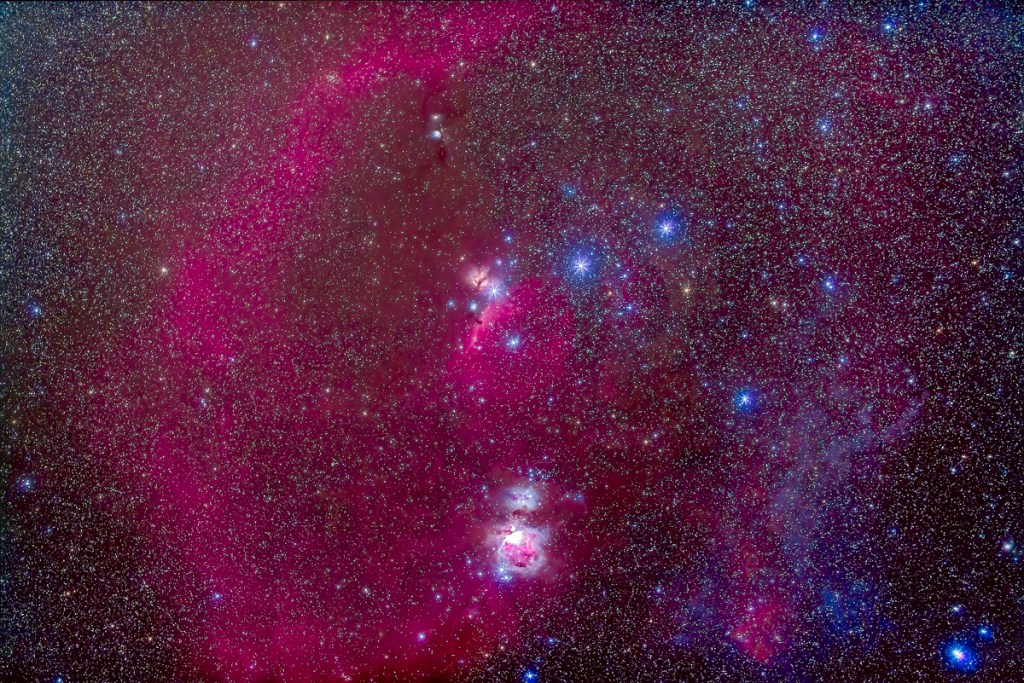
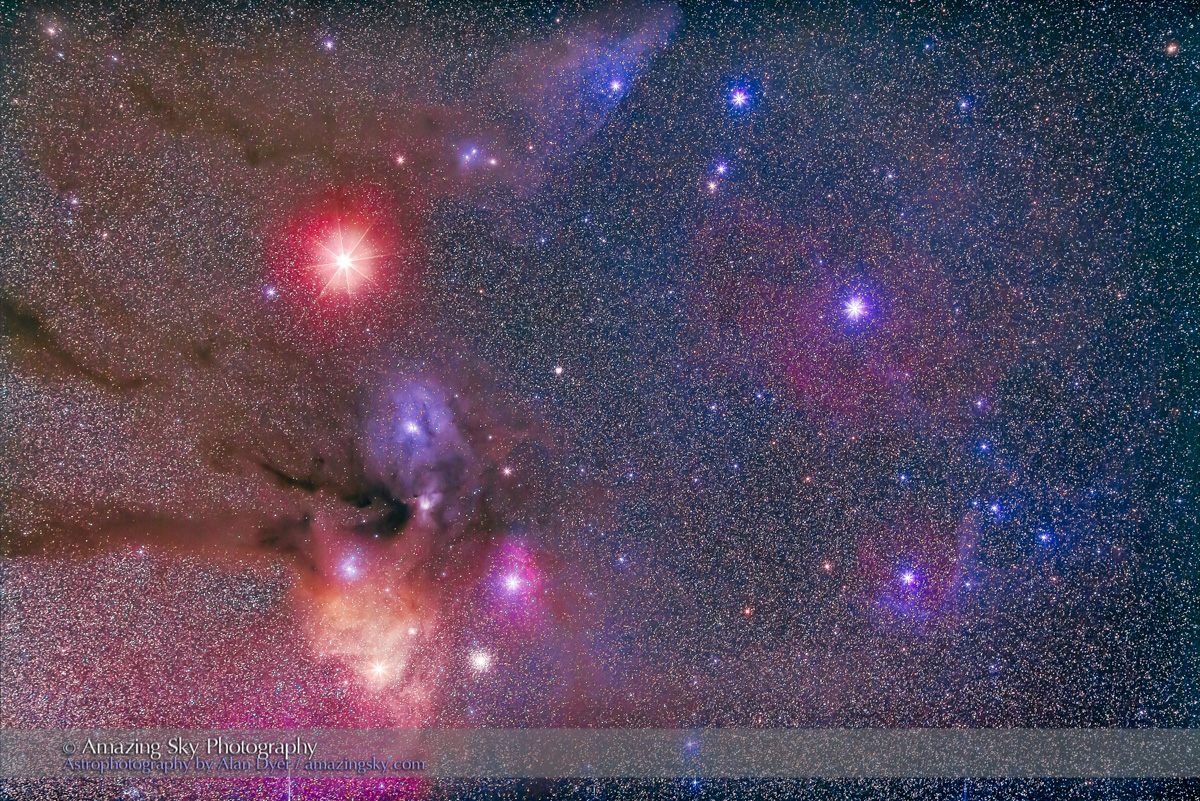
For the image below, I employed a special filter that isolates the deep red light emitted by the many hydrogen-gas nebulas toward the Milky Way core.
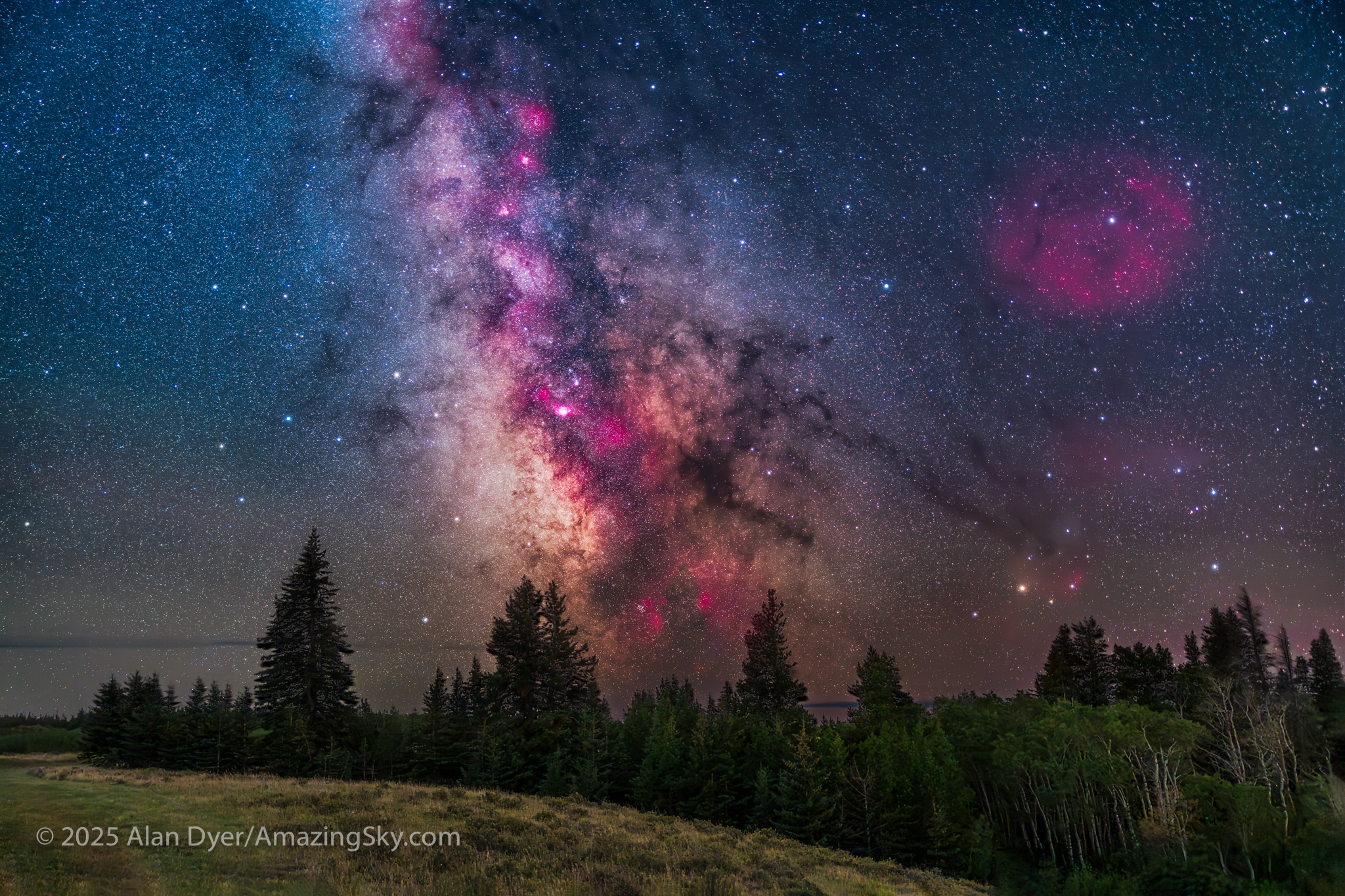

This is a blend of:
– A single 2-minute exposure, untracked, for the ground, blended with …
– A stack of 5 x 1 minute exposures, tracked, for the sky, plus …
– An additional tracked 2-minute exposure layered in, taken at the end of the set through an Astronomik “narrowband” H-Alpha clip-in filter, to add the red nebulas.
– All with the Canon RF 28-70mm lens at f/2 and set to 35mm, on the astro-modified Canon EOS R at ISO 1600 (3200 for the Ha shot), and on the MSM Nomad tracker.
Masking and blending all the images, with the trees in the foreground was a challenge! The camera was not moved — all images were from the same tripod position.
This is a technique borrowed from “deep-sky” imaging but now popular among nightscape photographers to create an even more enhanced night sky than a normal unfiltered view.
But even without the filter the long exposures used for the sky record far more detail and colours than even dark-adapted eyes could see. The filter takes that even further.
But those nebulas are there, and they do glow red. Just like the airglow that unaided eyes usually cannot see, the long exposures reveal the unseen, in this case some of the wonderful content of our Galaxy.
And that’s the attraction of astrophotography, to reveal the otherwise elusive or invisible structure of the sky, and in this case juxtaposed over familiar earthly landscapes below.
I can highly recommend Southwest Saskatchewan for anyone interested in stargazing and astrophotography. It’s always been one of my favourite destinations.
— Alan, September 17, 2025 / © 2025 AmazingSky.com